BRICS is an international grouping of the major emerging economies of the 21st century that is an acronym of its member countries Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. BRICS was founded in 2006. In this article, you will learn about BRICS, definition, introduction, objectives, history, functions, initiatives, list of member countries, summit list, significance providing key insights for GS Paper-II International relations of UPSC IAS Exam.
Table of Content
- What is BRICS?
- Background of BRICS:
- Member States:
- Functions of BRICS:
- Initiatives of BRICS:
- Significance of BRICS:
- BRICS Summits:
- Challenges for BRICS
- India in BRICS
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Reference

What is BRICS?
- BRICS is an international grouping of the major emerging economies of the 21st century that is an acronym of its member countries Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- BRICS Headquarters is situated in BRICS Tower, Shanghai, China.
- The term BRICS was first coined by Jim O’Neill an economist in 2001.
- Jim O’Neill had predicted that by 2050, these nations will surpass the six most industrialized countries in terms of economic size which can then alter global power dynamics.
- BRICS Sherpa is the main channel for communication among BRICS countries.
Background of BRICS:
- The BRIC was established as a platform during a meeting of the Foreign Ministers from the four countries Brazil, Russia, India and China during the UN General Assembly in New York in 2006.
- The inaugural BRIC Summit took place in Yekaterinburg, Russia, in 2009.
- Initially its members were limited to BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India and China).
- BRIC Foreign Ministers at their meeting in 2010 has agreed that South Africa can join BRIC.
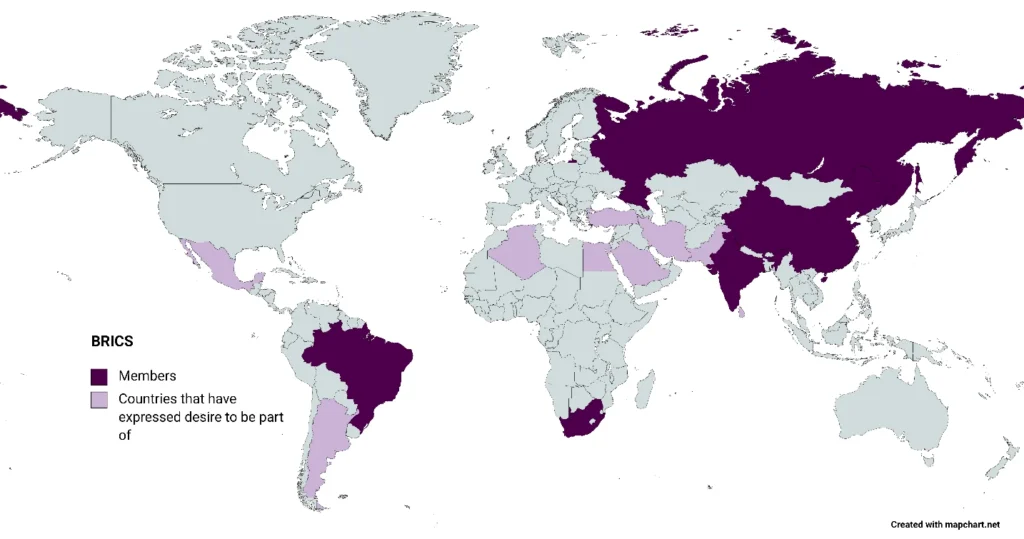
- Since South Africa’s inclusion in 2010, many countries have shown interest in joining BRICS, including Argentina, Saudi Arabia and Iran.
- Bilateral relations among the BRICS are based on non-interference, equality, and mutual benefit.
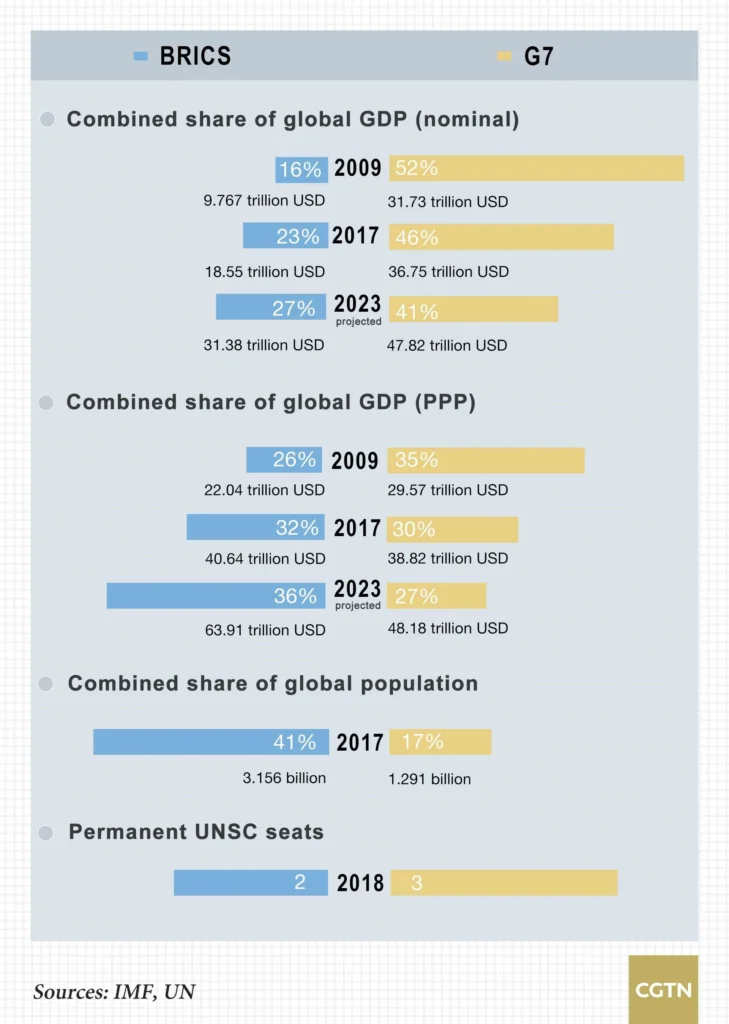
- The BRICS are considered the primary geopolitical rival to the G7 group of advanced economies.
- There is no formal application process to join BRICS, but any aspiring government must receive support from all its existing members: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- The cooperation within BRICS is based on two pillars:
- Consultations on mutual concerns through meetings attended by leaders and ministers responsible for finance, trade, health, science and technology, education, agriculture, communication, labor, and others.
- Practical collaboration across various domains through meetings of working groups and officials.
Member States:
Functions of BRICS:
- They aim to explore regional markets, with each country serving as a gateway to macro regions such as South Africa for the African region and Brazil for the Latin American region.
- BRICS addresses issues such as political and economic, Sustainable Development Goals, international terrorism, climate change, food and energy security, global governance reform, trade, tax, health, traditional medicines, labour, disaster management, etc.
- BRICS alliance engages people-to-people exchanges among its member countries through culture, sports, youth, cinema, academics, tourism, skill development, science, technology, and innovation.
Initiatives of BRICS:
New Development Bank:
- BRICS has established the New Development Bank (NDB) on July 2015 with the aim to mobilize resources for infrastructure and sustainable development projects in BRICS and other emerging economies and developing nations.
- The concept for creating the New Development Bank was initially proposed during the Fourth BRICS Summit in 2012.
- In 2014, during the Sixth BRICS Summit the member countries had officially ratified the Articles for the New Development Bank and authorised a capital of USD 100 billion.
- It facilitates member countries in raising funds for their infrastructure and sustainable development initiatives.
- The first meeting of the Bank’s Board of Governors took place in 2015, marking its official establishment as a legal entity.
- The Bank’s headquarters are located in Shanghai, China.
- The regional hub for the NDB- the ‘New Development Bank Africa Regional Center,’ was established in Pretoria, South Africa.
- The former Brazilian President Dilma Vana Rousseff has been elected as its new President.
Contingent Reserve Arrangement:
- The Contingent Reserve Arrangement serves as a financial safety net for BRICS countries during times of financial crises or short-term balance of payments crises by allowing currency swapping.
- It provides support through liquidity and precautionary instruments in response to financial crises.
- It was established in 2015 during 7th BRICS summit.
The BRICS basket reserve currency:
- It is a new reserve currency to better serve the economic interests of its member nations.
- It will be based on a basket of the currencies of the five-nation bloc: Brazilian Real, Russian Ruble, Indian Rupee, Chinese RMB Yuan and South Africa’s Rand.
- It will help to reduce reliance on the US Dollar and the Euro and thus protect their economies against the volatility of exchange rate.
- the BRICS is set to build a joint financial infrastructure that will enable a reserve currency to be created.
The BRICS Joint Statistical Publication:
- It is an annual publication that publishes about economic and social indicators, population, labour force, National Accounts, price Indices among others.
- It presents a brief overview of the Statistical System of each country.
The BRICS payment system:
- “BRICS Pay” is a payment system of BRICS countries that was launched in 2018 by the BRICS Business Council.
- BRICS Pay aims to enable digital payments between the different countries in BRICS PLUS format, allowing businesses and consumers to securely and seamlessly make and receive payments in their local currency.
- BRICS Pay is built on blockchain technology for making settlements using digital financial asset.
Significance of BRICS:
- All five member nations are members of the G20 and with a combined:
- Nominal GDP of around 26.6% of the world’s gross product
- A total Gross Domestic Product (PPP) of approximately 32.5% of global GDP (PPP)
- An estimated combined foreign reserve of US$4.46 trillion.
- These countries were among the world’s largest in terms of population and, area.
BRICS Summits:
First summit
- The first BRICS summit was held in Yekaterinburg, Russia in 2009 to address economic and financial issues rooted in the 2008 financial crisis.
- It focused on reforming international financial institutions, promoting sustainable development, and implementing measures to combat climate change.
Second summit
- The second summit was held in Brasilia, Brazil in 2010.
- The joint declaration from this summit emphasized increasing the voting quotas of BRICS countries within the IMF and enhancing involvement in selecting leaders for the IMF and the World Bank.
Third summit
- The third summit was held in Sanya, China in 2011.
- It led to the addition of South Africa as a new member, expanding BRICS’ geographical reach into the African continent.
Fourth summit
- The fourth summit was held in New Delhi, India in 2012 has established financial cooperation with third countries through the establishment of the BRICS Bank.
- An agreement was also signed to facilitate credit approvals in local currencies, thereby strengthening the economies of BRICS countries.
Fifth summit
- The fifth summit was held in Durban, South Africa in 2013.
- The summit laid the foundation for the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) with an initial amount of USD 100 billion.
- The feasibility report for establishing the BRICS Development Bank was adopted.
- Two significant centres- the BRICS Business Council and the BRICS Think Tanks Council, were established to enhance coordination and cooperation among member countries.
Sixth summit
- During the sixth summit in Fortaleza, Brazil in 2014, agreements were signed to fund infrastructure and sustainable development projects in emerging markets.
- The Contingent Reserve Arrangement has allocated USD 100 billion to address short-term Balance of Payments crises.
- The New Development Bank (NDB) was launched at this summit with a startup capital of USD 50 billion.
- This was eventually increased to USD 100 billion over time.
Seventh summit
- The seventh BRICS Summit was held in Ufa, Russia in 2015.
- The Contingent Reserve Arrangement became fully operational and strengthened, investment among the five BRICS countries.
Eighth Summit
- At the eighth Summit in Goa, India in 2016, member countries condemned terrorism in all its forms and manifestations.
- Agreements were signed to establish the BRICS Agricultural Research Platform, and regulate the Customs Cooperation Committee.
- The summit discussed the establishment of an independent BRICS Rating Agency based on market-oriented principles to strengthen the global governance architecture.
- The summit fostered new ties between BRICS and BIMSTEC nations.
Eleventh summit
- The eleventh summit was held in Brasilia, Brazil in 2019.
- The members made mutual agreements to help stop drug trafficking and organized crime; both internationally and internally.
Twelfth summit
- The first virtual BRICS summit was held in this summit in 2020.
Thirteenth summit
- The twelfth summit was held in New Delhi, India in 2021.
- The summit established BRICS Games 2021 which was then held in India.
Fourteenth summit
- The fourteenth summit was held in Beijing, China in 2022.
- The summit led the creation of a new, basket type reserve currency.
- The currency that combines BRICS currencies and is backed by precious metals.
Fifteenth summit
- This summit is scheduled to be held in South Africa in 2023.
Challenges for BRICS
- The BRICS economies face common domestic and socio-economic challenges that need to be independently addressed to achieve their collective goals.
- The challenges include inequality (economic, social, and political), corruption, improvements in healthcare and education, and human rights.
- There is another group called IBSA, formed in 2003 that has overlapping mandates with the BRICS, this poses challenges for BRICS.
- IBSA consists of India, Brazil, and South Africa.
- The ultimate aim of BRICS is to assume a leadership role in reforming global financial and political institutions, while ensuring the existing institutions remains relevant and effective.
- Enhancing mutual understanding among the member states regarding this is a significant challenge.
India in BRICS
- India maintains close economic and cultural ties with its BRICS partners.
- India’s strengths lie in its labour, services, generic pharmaceuticals, and information technology.
- There are significant opportunities for synergy with other BRICS partners, which can be leveraged to strengthen intra-BRICS connections in these areas.
- The New Development Bank was proposed by India.
- India has hosted the first Negotiation Meeting in 2012 to advance this initiative.
- India has introduced the Urbanization Forum as part of BRICS cooperation mechanisms to emphasize intra-BRICS cooperation and facilitate learning from each other’s experiences in addressing the challenges of rapid urbanization faced by all BRICS members.
- India has established the practice of holding BRICS Academic Forum meetings as preparatory sessions that contributes towards the agenda of the Summit.
- The first such meeting took place in New Delhi in 2009.
- During the 6th BRICS Summit India proposed initiatives to enhance intra-BRICS cooperation through online education, an affordable healthcare platform, a virtual BRICS university, BRICS language schools, a Young Scientists Forum among others.
Conclusion
BRICS is an influential and dynamic association of emerging economies that holds great potential for global economic cooperation and development. With their combined strength, BRICS nations can shape international trade, finance, and governance in a more inclusive and balanced manner. The importance of BRICS for India can be understood through the various initiatives such as New Development Bank that has potential to help India during its balance of payment crises. BRICS serves as a platform for addressing common challenges, such as poverty, inequality, and climate change, while also championing the principles of multilateralism and a multipolar world order.
Ref: Source-1
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are the objectives of BRICS?
The establishment of BRICS was meant to explore regional markets, with each country serving as a gateway to macro regions such as South Africa for the African region and Brazil for the Latin American region.
What does BRICS stands for?
BRICS stands forBrazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
When was BRICS established?
BRICS was formed in 2006.
When did South Africa join BRICS?
South Africa joined BRICS in 2010.
How many countries in BRICS?
There are 5 members of BRICS- Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
Which country hosted the first virtual annual BRICS summit?
The first BRICS summit was held in Yekaterinburg, Russia in 2009.