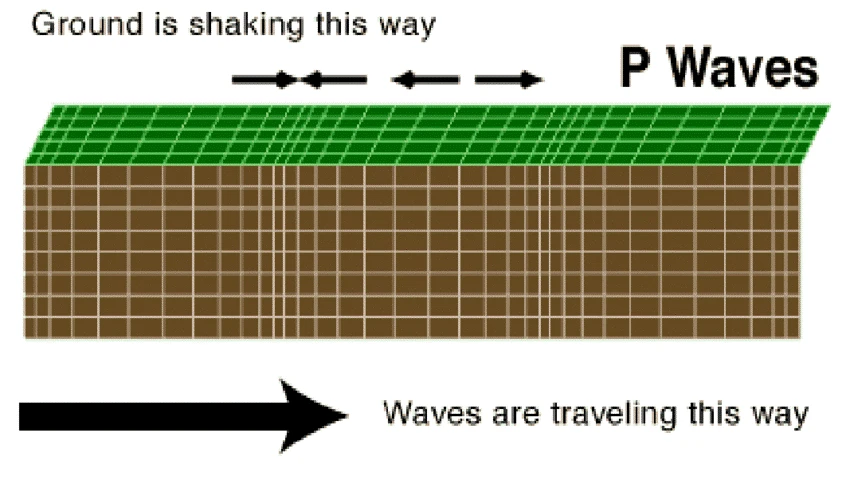
P-Waves (Primary Waves) are the fastest seismic waves that travel through the Earth’s interior. They cause the ground to shake back and forth in the same direction they move. Animals display sensitivity to P waves. Scientists have used animal behaviour to predict earthquakes. P-Waves (Primary Waves) will be helpful for UPSC IAS Exam preparation. GS Paper-1 Geography.
Table of Content
- What are P-Waves (Primary Waves)?
- Why do P-waves travel faster than S-waves?
- Emergence of Shadow Zone of P-Waves (Primary Waves)
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are P-Waves (Primary Waves)?
- Primary waves are also referred to as P waves or Push waves.
- Meaning: It is a longitudinal earthquake wave that travels through the interior of the earth and is usually the first conspicuous wave to be recorded by a seismograph.
- P waves have the highest speed among the body waves, travelling at approximately 6 kilometres per second.
- They can propagate through solid rocks as well as fluids like underground water.
- These waves cause the ground to shake back and forth in the same direction they are moving.
- Although humans cannot perceive Pwaves, animals display sensitivity to them.
- Dogs start barking, pigs and cattle become restless, and even birds stop chirping upon sensing P waves.
- Scientists have effectively predicted earthquakes by studying animal behaviour.
Why do P-waves travel faster than S-waves?
- P-waves are about 1.7 times faster than the S-waves.
- P-waves are compression waves that apply a force in the direction of propagation.
- Hence transmit their energy quite easily through the medium and thus travel quickly.
- On the other hand, S-waves are transverse waves or shear waves (the motion of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave).
- Hence less easily transmitted through the medium.
Emergence of Shadow Zone of P-Waves (Primary Waves)
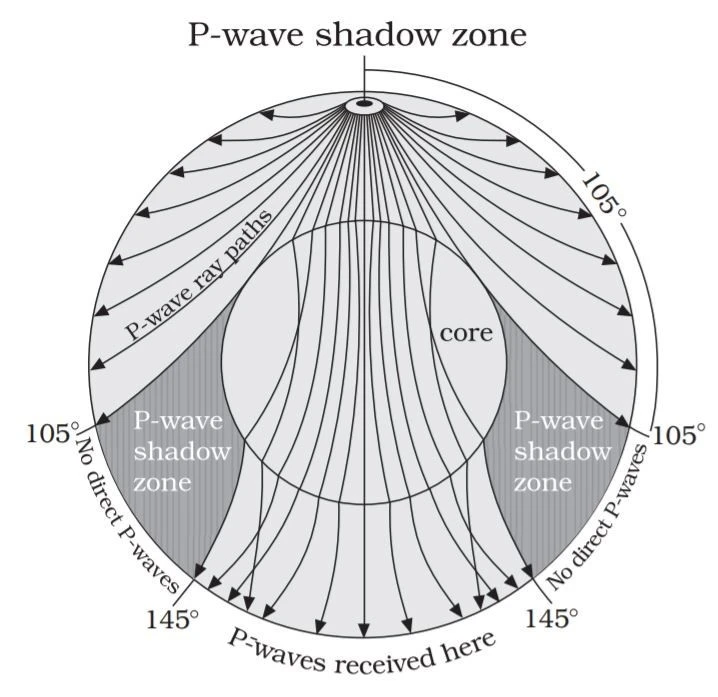
- The shadow zone for P-waves appears as a band between 103° and 142° from the epicentre.
- P-waves are refracted when passing through the transition between the semisolid mantle and the liquid outer core.
- Seismographs located beyond 142° from the epicentre detect P-waves but not S-waves, providing insights into the solid inner core.
- The zone between 103° and 142° from the epicentre is recognized as the shadow zone for both types of waves.
- Seismographs within 103° from the epicentre record the arrival of both P and S-waves.
- Span of the shadow zone for P-waves = 78° (2 times the difference between 142° and 103°).
Conclusion
P-Waves travel faster than S-Waves due to their nature as compression waves that transmit energy more easily through the medium. The refraction of P waves at the boundary between the mantle and outer core creates a shadow zone, while S waves cannot propagate through liquids, contributing to the differences in wave behaviour. Understanding seismic body waves and their observations is crucial for studying Earth’s deep interior.
Ref:
FAQs(frequently asked question)
What are the two types of body waves?
There are two types of body waves: P-waves and S-Waves.
What layers do P waves travel through?
P-waves travel through all of the layers of the earth.