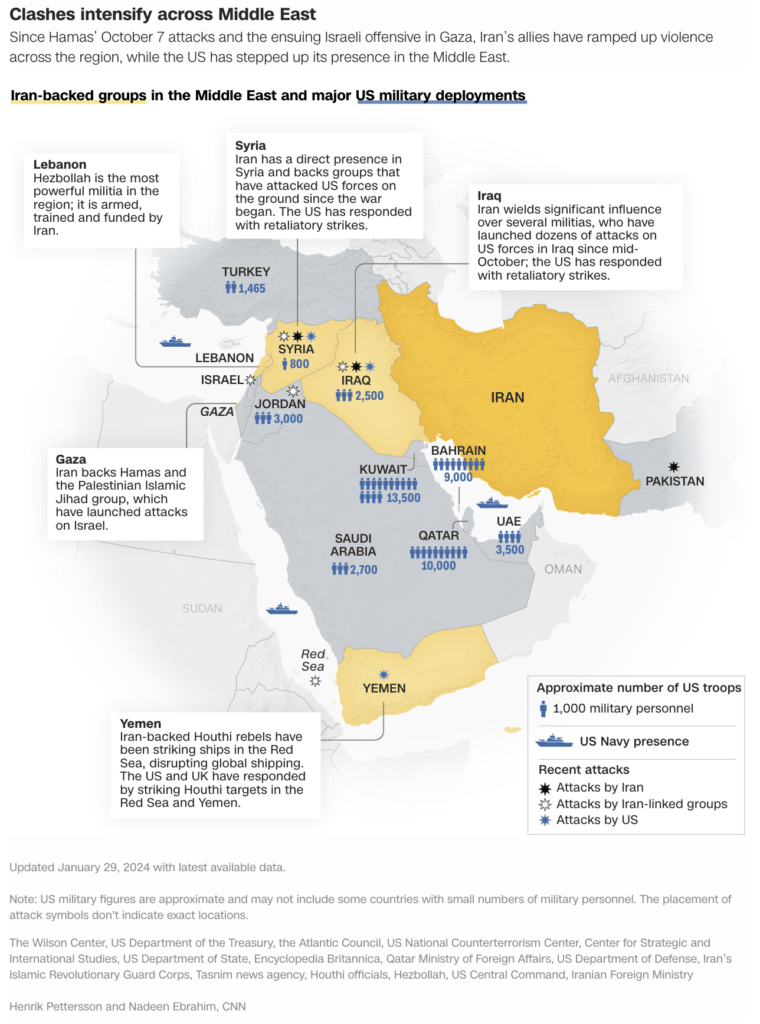
Iran recently attacked Israel in retaliation for Israeli airstrikes that targeted an Iranian consulate in Syria, harming the Bilateral Iran-Israel Relations.
- This strike killed senior Iranian military commanders.
Background:
- Ambivalent (1947-1953): Relations were uncertain initially as Iran navigated its foreign policy amidst regional tensions.
- Friendly (1953-1979): A period of close ties and cooperation in various sectors, including economic and military domains.
- Worsening (1979-1990): The Islamic Revolution led to a sharp downturn in relations, as Iran’s new regime adopted a hostile stance towards Israel.
- Open Hostility (1991-present): Marked by indirect confrontations, such as cyberattacks and proxy warfare. Both nations have engaged in strategic attacks, including the Stuxnet cyberattack attributed to Israel and US targeting Iran’s nuclear facility.
- Iran supports groups like Hezbollah and Hamas, which oppose Israel, raising concerns about potential regional escalations.
Impacts of Conflict:
Global Trade and Energy Security
- Maritime Disruptions: Major shipping routes in the Strait of Hormuz and the Red Sea are at risk, affecting global trade flows and the operation of the Suez Canal.
- Oil Price Instability: Significant fluctuations in oil prices due to Iran’s crucial role in OPEC and as a major crude oil producer.
Geopolitical Risks and Nuclear Threats
- Nuclear Escalation Potential: Israel’s nuclear capabilities heighten the risk of escalation.
- Regional Instability: Persistent unrest in the Middle East poses broader risks to the Global South and international governance structures.
Implications for India
- Diaspora Safety Concerns: Increased security risks for the substantial Indian community living in the Middle East.
- Oil Supply Disruptions: Threats to India’s crude oil supply could lead to increased piracy and hostage-taking incidents.
- Market Impact: Indian stock market sentiments are adversely affected by disruptions in oil supplies.
Regional and Global Geopolitical Dynamics
- Crude Oil Supply Threats: Iran-Israel tensions could severely disrupt global crude oil supplies.
- Inflation Concerns: Potential spike in global inflation due to rising commodity prices.
- Shifts in Financial Markets: Increased investment in safer assets, with a move away from riskier investments, including Indian stocks.
India’s Strategic Position and Concerns:
- Trade and travel disruptions are likely, including temporary airspace closures by several Middle Eastern countries.
- India faces challenges in maintaining strategic relationships with both Iran and Israel, which include defence cooperation, technology exchange, and energy imports.
- Ensuring stability in the Middle East is critical for India to safeguard its energy security and the welfare of its diaspora.
Solutions for De-escalating Tensions:
- Promote a sustainable ceasefire and a two-state solution to address the Iran-Israel conflict.
- Foster direct dialogue and diplomacy between conflicting parties with help from international mediators.
- Propose regional cooperation and a comprehensive security architecture in the Middle East to ensure long-term peace and stability.
- Encourage normalization of diplomatic relations between Iran and Israel to reduce regional tensions.
Ref:Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |