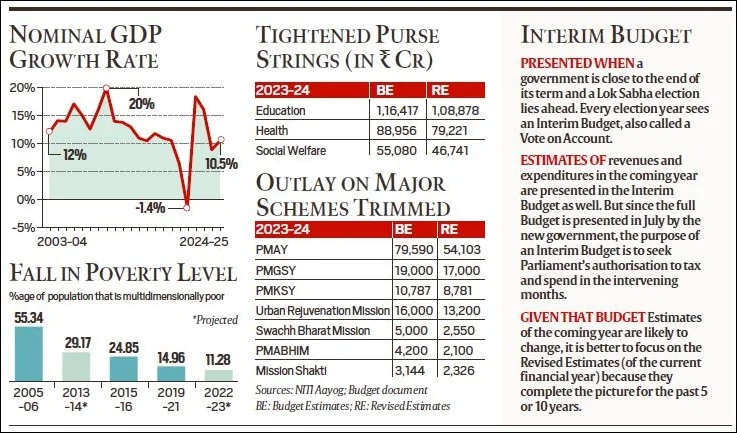
Interim Budget, unlike the Annual Budget, is presented during an election year to cover the transition period until a new government is established.
Key Highlights of the speech:
Outlook on GDP Growth
- Nominal GDP, a crucial economic indicator, is set to grow by just 10.5% in 2024-25, indicating a potential GDP growth rate of 6% to 6.5%.
- Nominal GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced in a given time period less the value of those made during the production process.
- Slow nominal GDP growth raises concerns about the real growth rate and may impact India’s economic trajectory.
- Fiscal deficit performance was better than expected, and was revised to 5.8% for the current fiscal year.
- Anticipated fiscal deficit target for FY25 is 5.1% of GDP, showcasing prudent fiscal management.
Housing Initiatives:
- The expansion of housing schemes, including an additional 2 crore houses over the next 5 years, will take place.
- The efforts to tackle the housing crisis by focusing on rural and middle-class housing needs.
Viksit Bharat Mission:
- The ‘Viksit Bharat’ is a mission to transform India into a developed country by 2047.
- The mission aligns with the vision of sustained economic growth but poses challenges in achieving the required GDP growth rate.
Reduction in Fiscal Deficit:
- Despite targets for capital expenditure (capex), the government fell short, achieving Rs 9.5 lakh crore against the set Rs 10 lakh crore in the current year.
- This shortfall may impact overall economic growth momentum and raises questions about fiscal management.
Interim Budget vs Union Budget:
- An interim budget is presented in an election year, focusing on funds required for the transition period until a new government is in place.
- Article 116 of the Constitution allows the Lower House to make any grant in advance for the estimated expenditure for part of any financial year by voting and passing such a legislation, i.e. vote on account.
- Unlike a full Union Budget, an interim budget cannot make major scheme announcements and is primarily a stopgap solution.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is an interim budget?
An interim budget is presented in an election year, focusing on funds required for the transition period until a new government is in place.
What article of the Constitution allows for an interim budget?
Article 116 of the Constitution allows the Lower House to make any grant in advance for the estimated expenditure for part of any financial year by voting and passing such legislation, i.e., vote on account.
Can an interim budget announce major new schemes?
Unlike a full Union Budget, an interim budget cannot make major scheme announcements and is primarily a stopgap solution.
What was the anticipated fiscal deficit target for FY25 mentioned in the interim budget?
The anticipated fiscal deficit target for FY25 is 5.1% of GDP, showcasing prudent fiscal management.