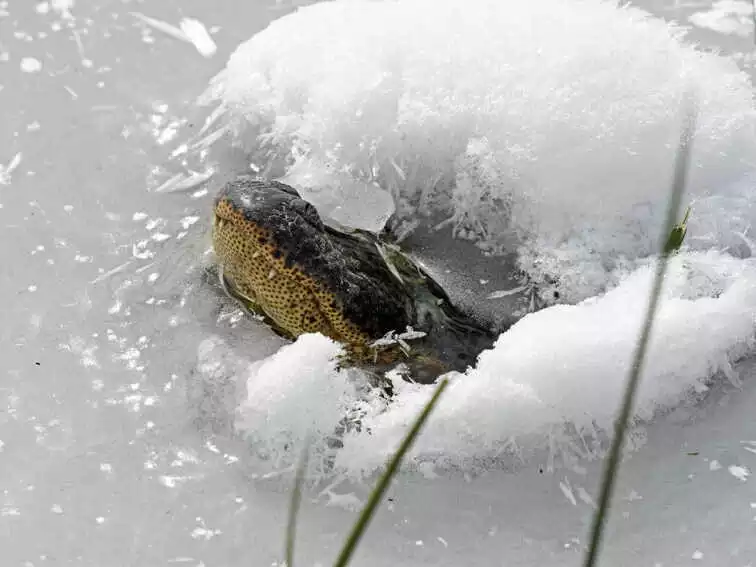
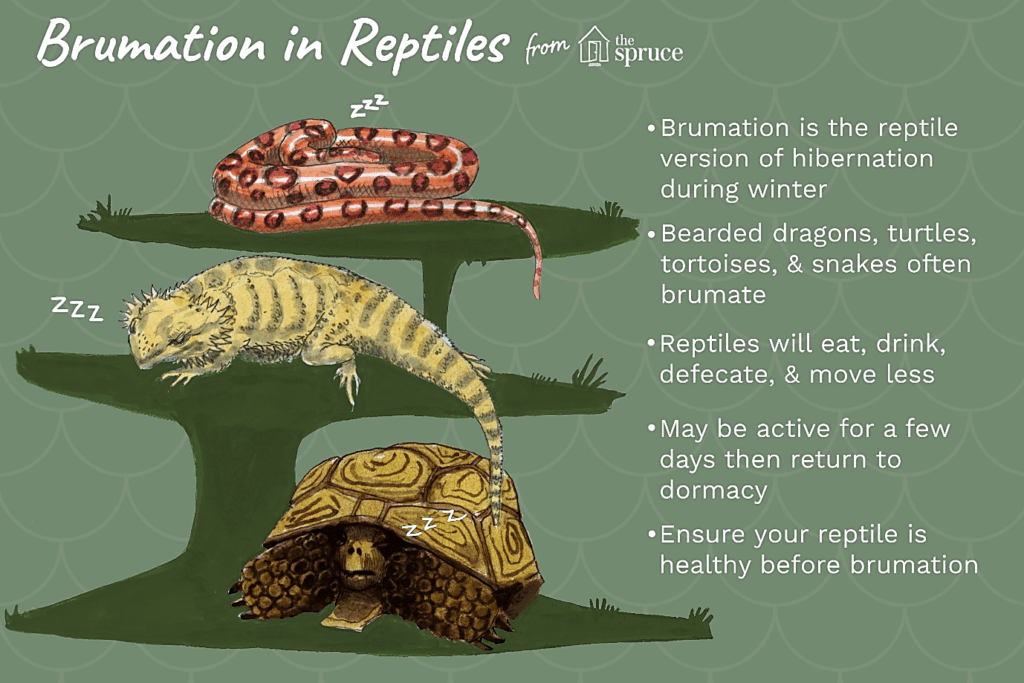
Alligators and other cold-blooded animals, such as snakes, turtles, salamanders, frogs, and lizards, enter a state of either hibernation or brumation to survive winter.
About the Brumation:
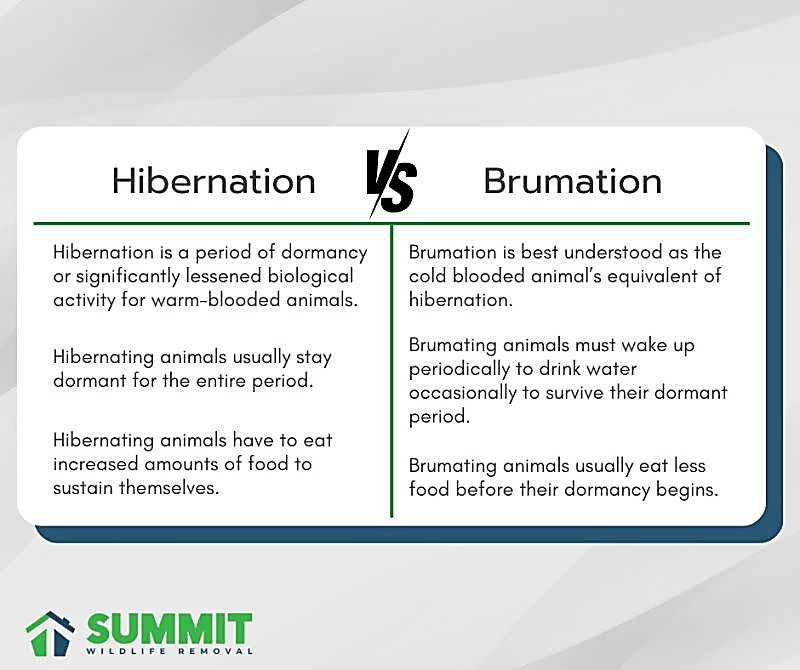
- TheBrumation is a process similar to hibernation but involves dormancy due to changes in temperature and light cycles.
- It leads to lethargy, decreased metabolism and body temperature, and reduced activity and food intake.
- Unlike hibernating animals, they occasionally emerge to drink water, keeping their body temperature close to the ambient temperature.
- During winter, alligators brumate in water, exposing only their snouts for breathing, a behavior known as “icing behavior,” and stay in “mud holes” without moving until temperatures rise.
About the Hibernation:
- The Hibernation is a state of minimal activity to conserve energy during extreme cold or scarce food availability, where the animals rely on fat reserves, and experience a drop-in heart rate, body temperature, and cessation of eating or drinking.
- Examples: bears, bats, and hedgehogs.
Hibernation vs Brumation:
Other forms of dormancy:
- Torpor: A temporary and less intense form of hibernation.
- Estivation: To survive hot and dry conditions.
- Diapause: A halt in growth or reproduction in many insects during hibernation or estivation.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |