Hepatitis A vaccine, named Havisure, India’s first indigenously developed, has recently been launched by Indian Immunologicals Ltd (IIL), a subsidiary of the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB).
About the Havisure:
- The Havisure is a 2-dose vaccine recommended for routine immunization, with the 1st dose being administered above 12 months of age and the 2nd dose being administered at least 6 months later.
- Beyond routine immunization, the vaccine is advised for individuals at risk of exposure or travelling to regions with high Hepatitis A prevalence.
- It is also recommended for those with the occupational infection risks and chronic liver diseases.
About the Hepatitis A:
- The Hepatitis is an inflammatory condition of the liver caused by the viral infections, alcohol consumption, health conditions, and medications.
- Causes of non-infectious Hepatitis–
- Alcohol and Toxins: Excessive alcohol, medication misuse, and exposure to toxins.
- Autoimmune Response: Immune system attacking the liver, more common in women.
- Common Symptoms of Hepatitis includes- Fatigue, flu-like symptoms, dark urine, pale stool, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, jaundice.
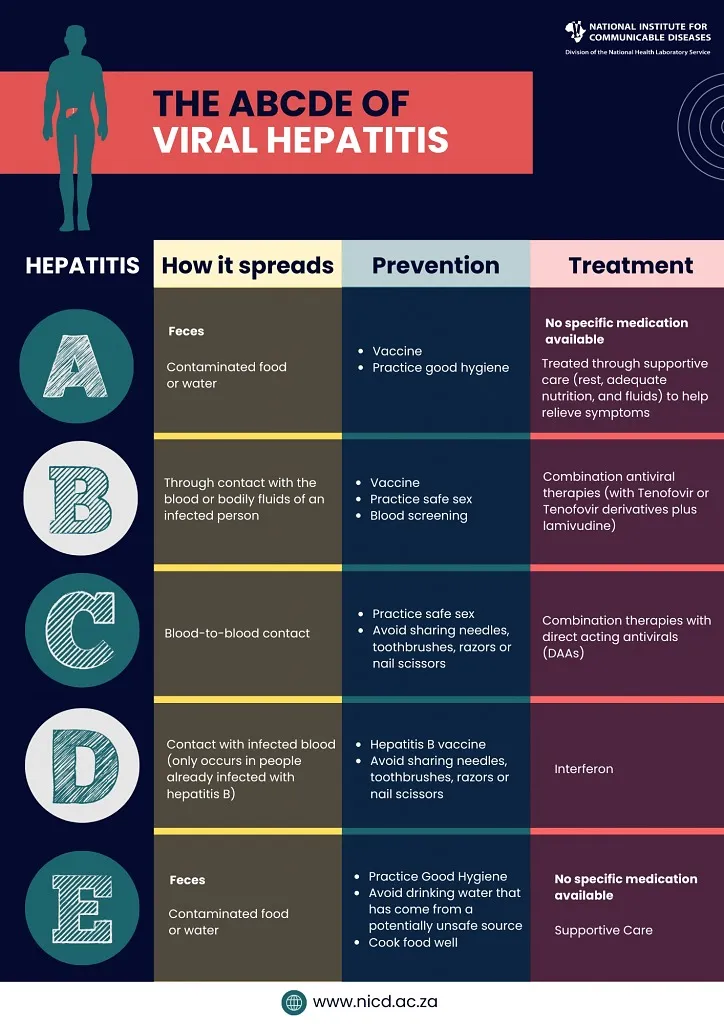
Types of Hepatitis:
- Viral Classifications: A, B, C, D, and E.
Diagnosis:
- Measure liver efficiency through blood samples.
Treatment of Hepatitis:
- Chronic cases of Hepatitis B can be treated with the antiviral medications.
- Hepatitis C can be treated with the antiviral medications for both acute and chronic cases and liver transplant for severe conditions.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis can be treated with the Corticosteroids and immune-suppressing drugs such as Azathioprine (Imuran) can be used.
- Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when the body’s infection-fighting system (immune system) attacks the liver cells of the body.
Vaccines:
- Hepatitis A: 2-dose series, recommended for children and adults.
- Hepatitis B: 3-dose series for newborns and for healthcare personnel.
- No Vaccines for Hepatitis C and E.
Complications of Hepatitis:
- Chronic Hepatitis B or C can lead to severe health problems including complications such as chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure.
- Avoidance of alcohol and careful consideration of medications is crucial for those with chronic Hepatitis B or C.
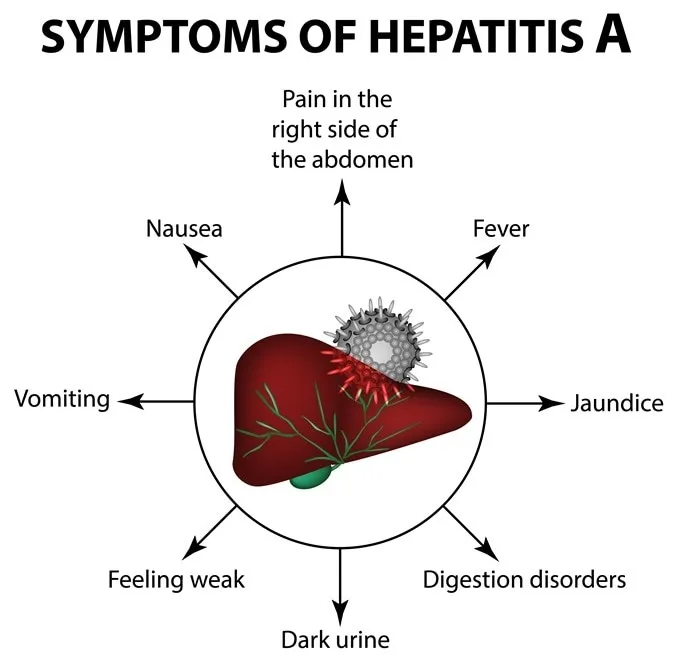
About the Hepatitis A:
- Hepatitis A virus (HAV) is a highly contagious liver infection that poses a substantial public health challenge primarily transmitted through the faecal-oral route via contaminated food or water.
- While most recover fully with lifelong immunity against the virus, a small percentage may experience severe, sometimes fatal, outcomes.
- The incubation period of virus is 14–28 days.
- The symptoms range from mild to severe and include fever, malaise, jaundice, and abdominal discomfort.
- Diagnosis of HAV involves detecting HAV-specific immunoglobulin G (IgM) antibodies in the blood.
- There is no specific treatment and the recovery may take weeks or months.
- Hospitalization is not required unless acute liver failure occurs.
- Currently, there is no vaccine available for children under 1 year.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |