In a recent study, researchers from the University of Liege have identified the oldest known microstructures in fossil cells, known as thylakoid membranes, dating back an astonishing 1.75 billion years.
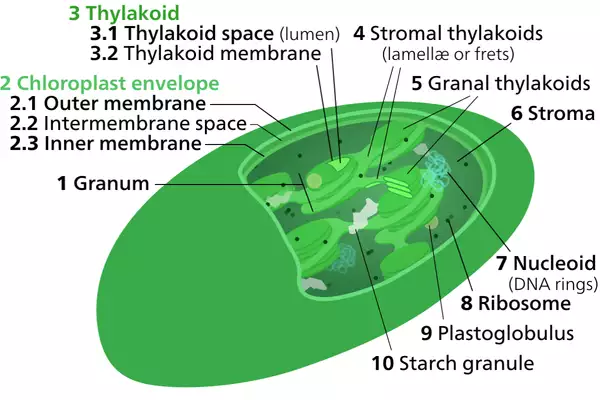
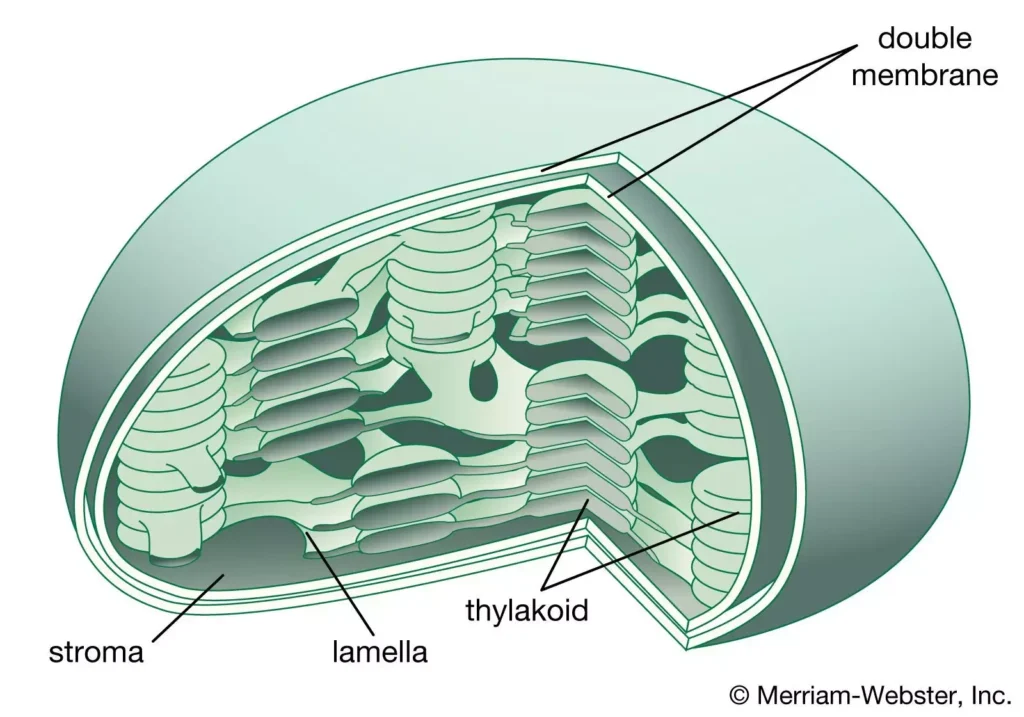
About Thylakoid membranes:
- Thylakoids are little pouches located in the chloroplasts of plants.
- They store chlorophyll, the substance in plant that reacts to sunlight and triggers photosynthesis.
- They are found in ancient, light-sensitive bacteria called cyanobacteria.
- Billions of years ago, cyanobacteria multiplied in the oceans and are believed to be responsible for the significant amounts of oxygen found in the atmosphere, making them a precursor to life as known presently.
- Recent understanding suggests that thylakoid membranes in cyanobacteria were instrumental in enabling these organisms to harness sunlight for energy production and release oxygen.
About the discovery:
- The oldest known fossil thylakoids date back to around 550 million years, but recent discoveries by researcher’s reveal microstructures in fossil cells that are 1.75 billion years old.
- These thus become the oldest thylakoid membranes, ever found.
- The discovery of ancient thylakoids in microfossils called N. Majensis along the coasts of Australia provides direct evidence of a minimum age of around 1.75 billion years for the divergence between cyanobacteria with thylakoids and without thylakoids.
- The presence of these ancient thylakoids raises the possibility of finding even older thylakoids in cyanobacterial microfossils and testing the hypothesis that thylakoids played a significant role in the ‘Great Oxygenation’ of the early Earth around 2.4 billion years ago.
About Great Oxidation Event:
- During the Great Oxidation Event, cyanobacteria released oxygen into the ocean, leading to oxygen-rich waters.
- Over time, oxygen escaped into the atmosphere, reacting with methane and displacing it, resulting in oxygen becoming a major component of the Earth’s atmosphere.
- The ‘Great Oxidation Event’ marked a crucial transition in Earth’s atmosphere, as the increasing oxygen levels had a profound impact on the composition and conditions of the planet.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |