Recent studies have highlighted a correlation between night-time light pollution and an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease, presenting new insights into environmental influences on this condition.
About Light Pollution:
- Definition: Light pollution refers to the excessive or inappropriate use of artificial outdoor lighting.
Components of Light Pollution:
- Glare: Excessive brightness causing visual discomfort.
- Sky Glow: Brightening of the night sky over populated areas.
- Light Trespass: Light falling where it is not intended or needed.
- Clutter: Excessive and confusing groupings of light sources.
Adverse Effects:
- Observational Impact: Hinders the ability to observe stars and celestial objects.
- Health Impact: Disrupts natural circadian rhythms and sleep patterns, increasing susceptibility to various health issues.
- Environmental Impact: Affects wildlife behaviour and ecosystems.
Connection to Alzheimer’s Disease (AD):
- Disruption of Circadian Rhythms: Night-time light pollution disrupts the body’s natural circadian rhythms, leading to impaired sleep.
- Increased Risk: The study links disrupted sleep patterns due to light pollution with a heightened risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Environmental Impact
- Migratory Species: Light pollution confuses migratory birds and sea turtles, disrupting their navigation and often resulting in fatalities.
- Insect Mortality: Artificial lights attract insects, which are then killed upon contact. This affects the food chain for birds and other animals.
- Bird Behavior: Studies show that city birds, exposed to artificial night lighting, become active earlier than those in natural areas. For example, blackbirds in Germany sing up to five hours earlier in cities compared to rural areas.
- Marine Life: Underwater artificial lighting affects marine ecosystems. Studies show fewer filter-feeding animals near lighted panels, indicating potential disruption of marine habitats.
About Alzheimer’s Disease (AD):
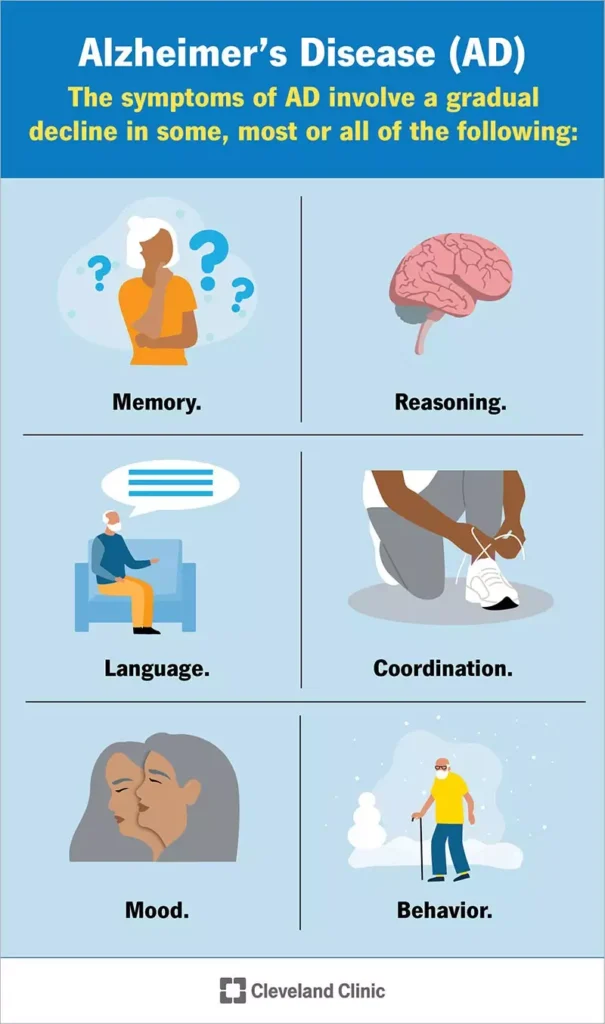
- Definition: Alzheimer’s disease is a common type of dementia characterized by a progressive decline in cognitive functions, including memory, thinking, learning, and organizing skills.
- Affected Brain Areas: Involves regions of the brain responsible for thought, memory, and language.
Risk Factors:
- Genetics and Medical Conditions: Genetic predispositions and medical conditions play a role.
- Environmental Stresses: Factors such as light pollution contribute to the risk.
- Symptoms: Early symptoms include forgetfulness, confusion, disorientation, and difficulties with planning and completing tasks.
Progression:
- Begins with mild memory loss.
- May advance to severe cognitive impairment, including loss of the ability to converse and respond to the environment.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
What are the components of light pollution?
Components include glare, sky glow, light trespass, and clutter, all of which cause visual and environmental disturbances.
How does light pollution affect health?
It disrupts natural circadian rhythms and sleep patterns, increasing susceptibility to health issues such as Alzheimer’s disease.
How is light pollution linked to Alzheimer’s disease?
Studies suggest that disrupted circadian rhythms caused by light pollution may increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
What impact does light pollution have on wildlife?
Light pollution disrupts the behavior of migratory birds, marine life, and insects, often leading to fatalities and ecosystem imbalance.