The Allahabad High Court recently ruled that the Government cannot disbelieve Apostille documents Issued by the countries signatory to the Apostille Convention.
About the judgement:
- The case of Naromattie Devi Ganpat vs. Union of India, checked the eligibility of a foreign citizen of Indian origin for an Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) Card.
- The respondents cannot compel the petitioner to produce a Nativity Certificate, in case of failure to maintain it by the government authorities.
- The court highlighted India as a signatory to the Hague Convention, citing the Ministry of External Affairs recognized ‘Apostille’ documents as legally valid.
- The court directed for processing the petitioner’s OCI Card application under Section 7A of the Citizenship Act, 1955.
- It mandated the conversion of the petitioner’s visa to expedite the issuance of the OCI Card.
About Apostille Convention:
- It is known as The Convention of Abolishing the Requirement of Legalisation for Foreign Public Documents.
- This is an international treaty drafted by the Hague Conference on Private International Law (HCCH), and signed on 5 October 1961.
- It is intended to simplify the procedure through which a document, issued in one of the contracting states, can be certified for legal purposes in the other contracting states.
- A certification under the Convention is called an apostille or Hague apostille.
- An apostille is an international certification comparable to a notarisation, and may supplement a local notarisation of the document.
Purpose and Procedure:
- An apostille issued by the state of origin is sufficient to certify the document, and removes the need for further certification by the destination state.
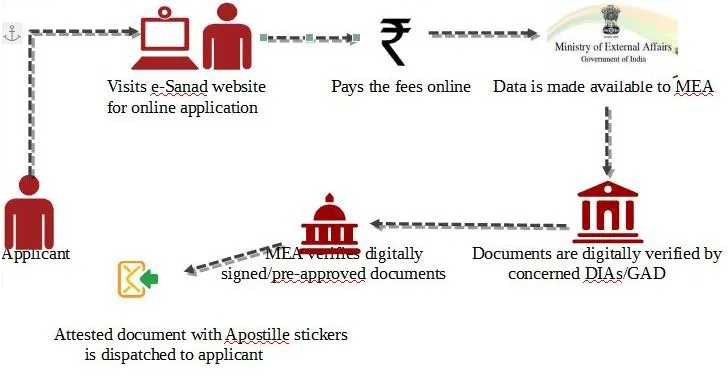
- Apostille is done for personal documents (Birth & death, marriage certificates, Affidavits, Power of Attorney) and educational documents (degree, diploma, secondary certificates).
- As India is a member of the Hague Apostille Convention, 1961, no further attestation or legalization of a document apostilled by a member country, should be required.
- An apostilled document should be treated as a legalized document for all purposes in India by all concerned, under the international obligation under the Convention.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |