Researchers have developed an early warning indicator for the potential collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a crucial ocean current system that regulates global climate and weather patterns.
About AMOC:
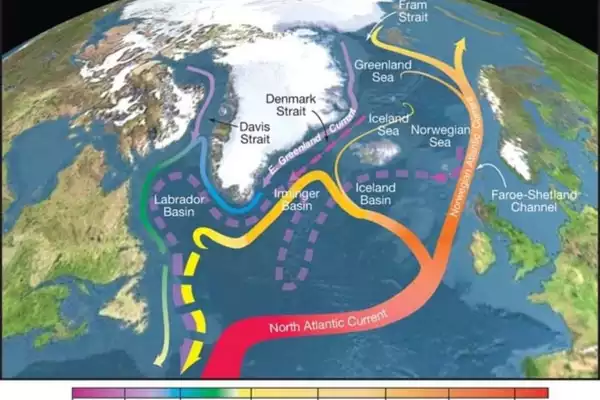
- The AMOC is a major ocean current system critical for regulating climate and weather patterns globally.
- It transports warm ocean water from the tropics to the northern Atlantic.
- It plays a key role in moderating the climate of Europe and North America and influencing Equatorial temperatures.
- It acts like a heat conveyor belt by warming northern latitudes and cooling southern latitudes.
- It has been slowing down due to added fresh, cold water from increased precipitation and rapid melting of the Greenland ice sheet, reducing salinity and density in the North Atlantic.
- It is at its slowest in 1,600 years, with about a 15% reduction in speed over the last few decades.
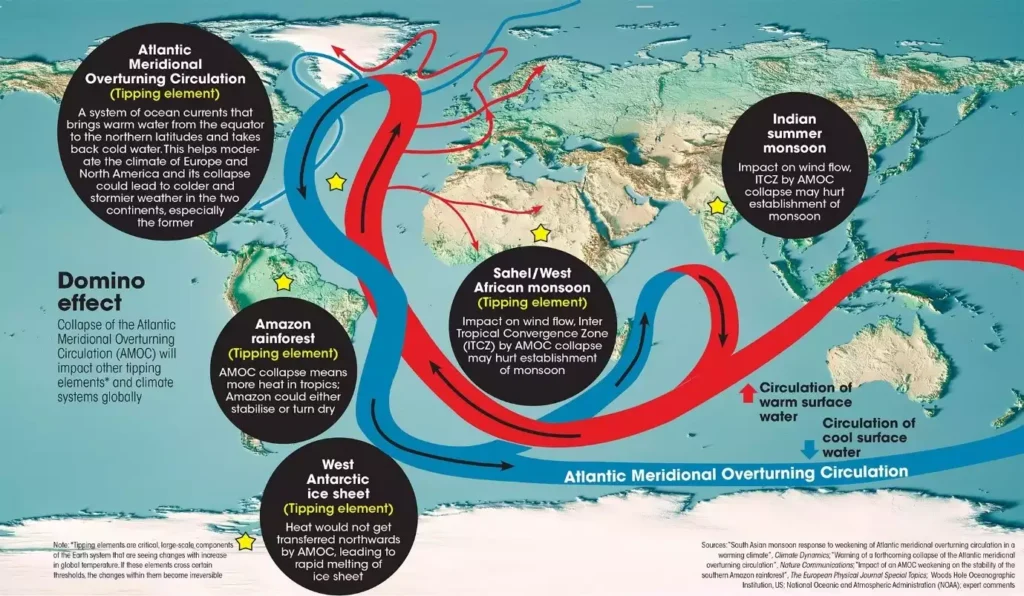
- Its collapse of AMOC could be irreversible and may trigger cascading effects on other climate-tipping elements and systems.
Key Findings of the Study:
- AMOC could collapse between 2025 and 2095, likely in the 2050s, with 95% confidence based on current emissions rates.
- AMOC is potentially the first of the 16 climate-tipping elements to be breached.
- The 2023 study assesses sea surface temperatures in the Subpolar gyre region as early warnings of AMOC’s collapse.
- Historical data link AMOC’s collapse to abrupt warming events preceding ice ages, known as Dansgaard-Oeschger events.
- AMOC has lost stability over the last century and may switch between fast/strong and slow/weak states within decades.
- Uncertainties in current models, such as overestimation of AMOC’s stability and poor representation of cold deep-water currents and salinity.
- Impact of Collapse:
- Cooling in the Northern Hemisphere,
- Altered precipitation patterns affecting food production, and
- Disrupt other climate systems like the Amazon rainforest, West Antarctic ice sheet, and various monsoons.
- The exact timing and nature of AMOC’s collapse depend on global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, with reductions likely postponing the collapse.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |