The Bonn Convention or the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS), is a treaty of the United Nations. The CMS provides a global platform for the conservation and sustainable use of migratory animals and their habitats. The CMS brings together the States through which migratory animals pass, the Range States, and lays the legal foundation for internationally coordinated conservation measures throughout a migratory range.
Convention on Migratory Species (CMS) will be helpful for UPSC IAS Exam preparation. GS Paper-3 Environment.
Table of Content
- What is a Migratory Species?
- What are Flyways?
- What is Central Asian Flyway (CAF)?
- What is Bonn Convention on Migratory Species?
- Members of the Bonn Convention on Migratory Species
- Appendices of the Bonn Convention on Migratory Species
- India and Convention on Migratory Species (CMS)
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Migratory Species?
- Definition: The Migratory Species is a species or lower taxon of wild animals of which the entire population or any geographically separate part of the population cyclically and predictably cross one or more national jurisdictional boundaries.
- The word ‘cyclically’ relates to a cycle of any nature, such as astronomical (circadian, annual etc.), life or climatic, and of any frequency.
- The word ‘predictably’ implies that a phenomenon can be anticipated to recur in a given set of circumstances, though not necessarily regularly in time.
What are Flyways?
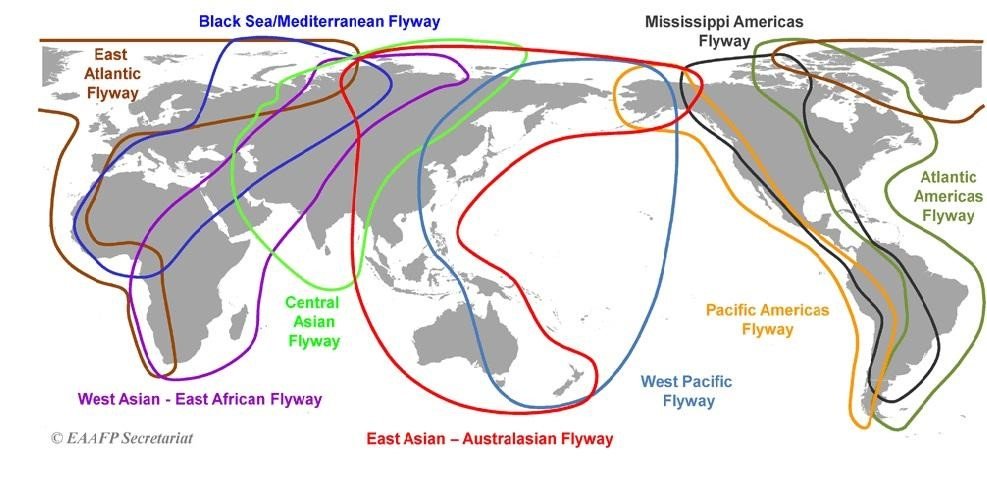
- Definition: The flyway is a flight path used by large numbers of birds while migrating between their breeding grounds and their overwintering quarters.
- Globally 9 major flyways are identified by the CMS Secretariat with respect to bird migration.
What is Central Asian Flyway (CAF)?
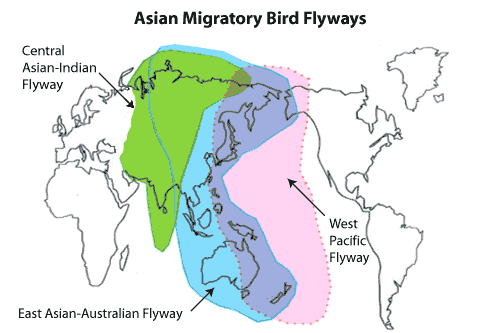
- The CAF covers a large continental area of Eurasia between the Arctic and Indian Oceans and the associated island chains.
- The CAF comprises several important migration routes of waterbirds, most of which extend from the northernmost breeding grounds in the Russian Federation (Siberia) to the southernmost non-breeding (wintering) grounds in West and South Asia, the Maldives and the British Indian Ocean Territory.
- The flyway region covers 30 countries of North, Central and South Asia and Trans-Caucasus.
What is Bonn Convention on Migratory Species?
- The Convention on Migratory Species (CMS) or the Bonn Convention, is an international agreement that aims to conserve migratory species throughout their ranges.
- The CMS was signed under the auspices of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- The agreement is known as the ‘Bonn Convention’ because it was signed in 1979 at Bonn, West Germany.
- It brings together the States through which migratory animals pass, the Range States, and lays the legal foundation for internationally coordinated conservation measures throughout a migratory range.
- It is the only global, and United Nations-based, intergovernmental organization that works exclusively for the conservation and management of terrestrial, aquatic and avian migratory species.
Members of the Bonn Convention on Migratory Species
- Total Parties: The Convention on Migratory Species has 133 Parties as of 1 March 2022.
- One country, Jamaica, has signed the original Convention but has yet to ratify it so is not a Party.
Appendices of the Bonn Convention on Migratory Species
Appendix I – Threatened migratory species
- Appendix I of the convention includes migratory species threatened with extinction.
- Parties that are range states to Appendix I species are obliged to afford them strict protection.
- Parties strive towards strictly protecting these animals, conserving or restoring the places where they live, mitigating obstacles to migration and controlling other factors that might endanger them.
- The CMS promotes strong action among the range states of many of these species.
Appendix II – Migratory species requiring international cooperation
- Appendix II of the convention lists migratory species that would significantly benefit from international cooperation.
- These species are the basis for establishing regional or global instruments under CMS.
- Because of this, the CMS promotes the range states to conclude global or regional agreements.
India and Convention on Migratory Species (CMS)
- India became a party of the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS) in 1983.
- The Indian sub-continent is also part of the major bird flyway network, i.e., the Central Asian Flyway (CAF)
- Bird flyway network includes the areas between the Arctic and Indian Oceans.
- The country has also launched the National Action Plan for the conservation of migratory species under the Central Asian Flyway.
- India and CMS had non-legally binding MoUs on the conservation and management of Iberian Cranes, Marine Turtles, Dugongs, and Raptors.
COP (Conference of Parties) 13 to the Convention on migratory species (CMS)
- COP13 was organised in 2020 at Gandhinagar, Gujarat, India.
- Theme: “Migratory species connect the planet and we welcome them home.”
- Mascot: Gibi – The Great Indian Bustard
Conclusion
The CMS acts as a framework Convention. The agreements may range from legally binding treaties to less formal instruments, such as the Memoranda of Understanding (MOU), and can be adapted to the requirements of particular regions
ref;Source-1
| Other Articles in Environment & Disaster Management | |
| Wildlife Protection Act 1972 | Wildlife trust of India |
| In-situ conservation | Kyoto protocol |
| Ex situ conservation | Rotterdam Convention |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When was the Bonn Convention established?
The Convention on Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS) was adopted in 1979 at Bonn, Germany and it came into effect on November 1, 1983.
Is India party to CMS?
Yes, India is a party to the CMS since 1983.