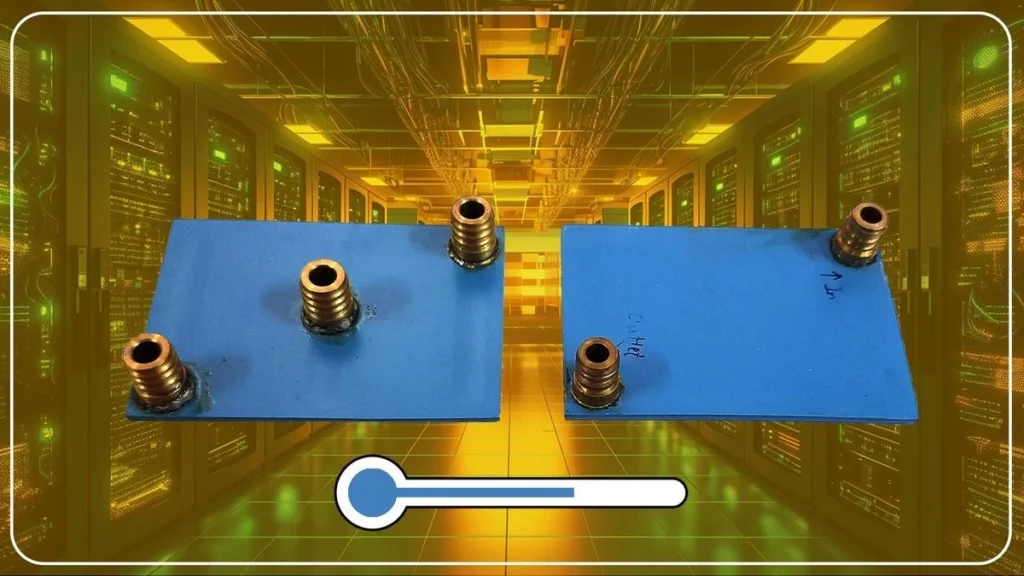
Researchers have identified Low-Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (LTCC) as a viable substitute for copper in supercomputer cooling technology.
Current Cooling Technology in Supercomputers:
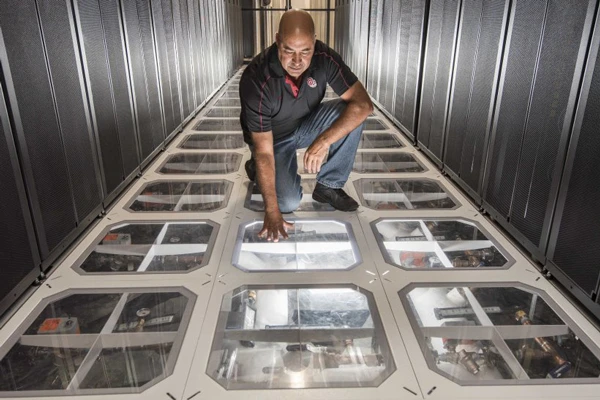
- Supercomputers utilize advanced cooling technologies to manage heat. The current standard involves using copper cold plates due to its high thermal conductivity.
- Role of Copper in Cooling: Copper cold plates in supercomputers act as heat sinks. They transfer heat from the supercomputer’s circuit components to the cooling liquid, typically deionized water, ensuring efficient heat removal.
- Emerging Technology – LTCC: Researchers are exploring Low-Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (LTCC) as a promising alternative to copper for cooling technology in supercomputers.
Benefits of LTCC Over Copper:
- LTCC is used in creating ceramic substrates essential for mounting electronic parts like resistors and inductors.
- It supports 3D circuit packaging, allowing for more compact and efficient designs than traditional Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs).
- LTCC could enhance the cooling efficiency of microprocessor chips in supercomputers, potentially boosting their overall performance.
About Supercomputers:
- Supercomputers are the most powerful computing systems, consisting of multiple CPUs organized into compute nodes.
- They are designed to process vast amounts of data at very high speeds.
- The capability of supercomputers is measured in Floating-Point Operations Per Second (FLOPS), reflecting their high-performance computing power.
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |