Crop diversification means growing more than one crop in an area. It can be done by adding a new crop species or different variety, or by changing the cropping system currently in use. Commonly it can mean adding more crops into an existing rotation. It can also be implemented to replace low-value commodities with high-value commodities, such as vegetables and fruits. Crop Diversification can also include an integration of crops and livestock, defined as mixed farming.
Crop Diversification will be helpful for UPSC IAS Exam preparation. GS Paper-3 Environment.
Table of Content
- What is Crop Diversification?
- Need for Crop Diversification
- Types of Crop Diversification
- What is Crop Diversification Programme (CDP)?
- Advantages of Crop Diversification
- Challenges to Crop Diversification
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Crop Diversification?
- Meaning: Crop diversification refers to the addition of new crops or cropping systems to agricultural production on a particular farm taking into account the different returns from value-added crops with complementary marketing opportunities.
- It aims to promote crop diversity through practices like crop rotation, multiple cropping, or intercropping.
- This approach enhances productivity, sustainability, and the ecological supply.
- It can be seen as a step towards creating more sustainable production systems, value chains for minor crops, and socioeconomic benefits.
- Examples of agricultural diversification strategies:
- Diverse crop rotations,
- Mixed cropping,
- Cultivation of grain legumes in predominantly cereal-based systems,
- Perennial leys or grassland, and
- Regionally adapted varieties or their combinations.
- In developing countries, crop diversification involves replacing one or more agricultural products with others.
- Agricultural diversification refers to reallocating farm resources like land, capital, equipment, and labor to new ventures.
- Diversification also includes transitioning from a less profitable cropping system to a more profitable one.
- Overall, crop diversification involves shifting from the dominance of a single crop to growing a variety of crops, meeting the increasing demand for cereals, pulses, oilseeds, fibres, fuel, and feed.
- It is a demand-driven and need-based approach that considers spatial and temporal aspects, value addition, resource complementarity, and a move away from less lucrative traditional crops.
Need for Crop Diversification
- Nutritional food security and quality of life can be improved through diversification in the food basket.
- Food security
- Poverty alleviation
- Employment generation
- Trade needs
- Protecting environmental degradation by reversing the declining trend in soil productivity and groundwater table.
- Income growth
- Ecological balance
- Sustainability of natural resources
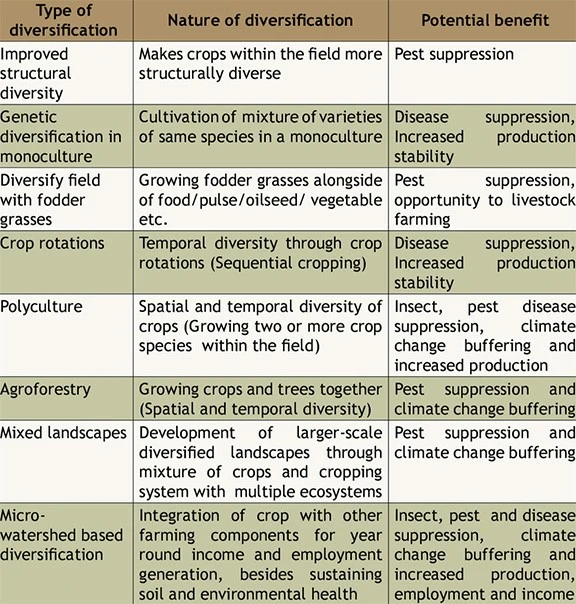
Types of Crop Diversification
Examples of crop diversification and potential benefits:
What is Crop Diversification Programme (CDP)?
- Crop Diversification Programme (CDP) is a sub-scheme of the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY).
- It is being implemented-
- In the Original Green Revolution States diverted the area of paddy crops to alternate crops and
- In tobacco-growing states encourage tobacco farmers to shift to alternate crops/cropping systems.
- Under CDP for replacing paddy crop, assistance is provided for four major interventions viz., alternate crop demonstrations, farm mechanization & value addition, site-specific activities & contingency for awareness, training, monitoring, etc.
- However, for replacing tobacco crops, tobacco-growing states have been given the flexibility to take suitable activities/interventions for growing alternative agricultural/horticultural crops.
Advantages of Crop Diversification
- Crop Diversification improves small farm holdings’ income.
- It is easier to withstand changes in commodity prices.
- It provides resistance to the highly erratic weather that climate change has brought about.
- By lowering the cost of production, it boosts profits.
- It provides more wholesome and varied food for both people and animals.
- It reduces the threat of pests like weeds, diseases, and insects.
- It boosts populations of helpful pollinators.
- It raises the soil’s quality.
- It contributes to more possibilities for employment.
- Crop yields and produce quality may both increase with diverse rotations.
Challenges to Crop Diversification
- Suboptimal and excessive use of resources, such as land and water, has a detrimental effect on the environment and the viability of agriculture.
- Inadequate availability of improved cultivars of plants and seeds.
- A cultivar is a species of plant that has been selectively bred for desired characteristics and is passed down from one generation to the next using techniques like grafting, tissue culture, or precisely managed seed production.
- Land holding fragmentation is less favourable to agriculture’s modernization and mechanisation.
- A lack of basic infrastructure, including power, transportation, and communications in rural areas.
- Inadequate post-harvest infrastructure and post-harvest technologies for handling perishable horticultural products.
- Agro-based industries are very weak.
- Untrained human resources as well as widespread and persistent illiteracy among farmers.
- Many pests and diseases that affect the majority of crop plants.
Conclusion
Diverse cropping systems reduce the possibility of widespread crop failures and pest pressure while enhancing soil quality and crop yields. To support healthy, sustainable, and profitable crop production, producers need to start looking for opportunities to incorporate new crop species into their existing rotation. This addition will help them overcome the challenges posed by climate change, particularly droughts and water usage issues. Additionally, policy changes that encourage crop diversity may be required to support efforts to ensure community food security.
Ref: Source-1
| Other Articles in Environment & Disaster Management | |
| Cropping systems | Vertical Farming |
| No-till farming | Liquid Nano Urea |
| Crop Diversification | Green GDP |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is Crop Diversification Index (CDI)?
CDI is an index with a base value of one, which represents the percentage of the total cultivated area devoted to a single crop. A higher index value means the crops are more diversified.
Why is crop diversification important in India? Or What is the importance of Crop Diversification?
Crop diversification helps divide the risk posed by fluctuating market prices. The farmer can sail through by the income brought in by the pulses that year even if one season the vegetables don’t perform well. In a situation where both crops get good prices, farmers have an opportunity to maximize their earnings.
What is crop combination?
Crop combination refers to the aggregate of various crops grown/cultivated in an area at a given point of time.
What is the difference between crop combinations and crop diversification?
Crop concentration is focused on the dominance of one crop over another in a particular research area. Whereas, Crop diversification refers to the different kinds of crops grown during a specific time period within the study area.