The irrational use of antibiotics, particularly broad-spectrum ones, can lead to dysbiosis and has adverse effects on the human microbiome.
About the Dysbiosis:
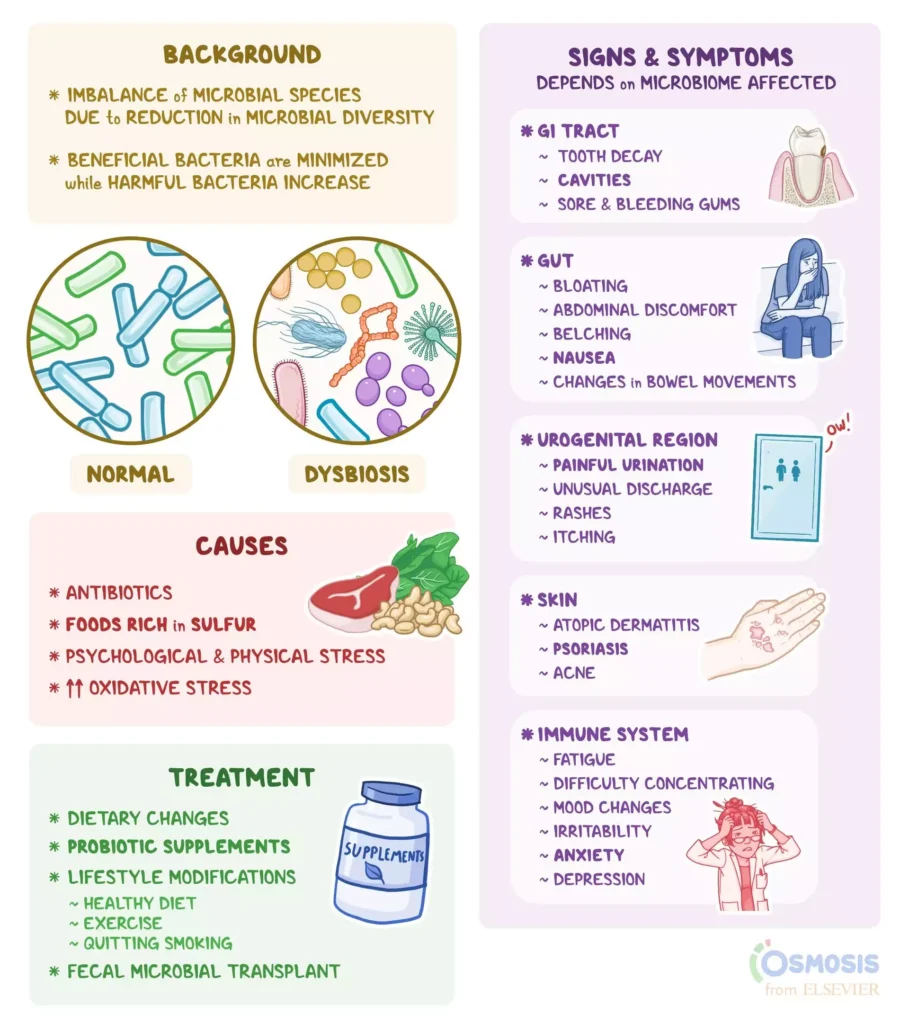
- The term for an imbalance in the microbial community, where beneficial bacteria are reduced and harmful bacteria increase.
- This condition can last for months or even years after a single course of antibiotics.
Health Consequences of Dysbiosis:
- Digestive Disorders: Dysbiosis can lead to inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome.
- Immune System: Disruption of the microbiome impairs immune function, increasing susceptibility to infections and autoimmune diseases.
- Metabolic Issues: Affected by the gut microbiome, dysbiosis can lead to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
- Gut-Organ Axes:
- Gut-Brain Axis: Dysbiosis can alter neurotransmitter levels, affecting mood, cognition, and mental health conditions like anxiety and depression.
- Gut-Liver Axis: Increased gut permeability (‘leaky gut’) can exacerbate liver conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Gut-Skin Axis: Dysbiosis can worsen skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
Broader Implications of Dysbiosis:
- Respiratory Tract: Antibiotic use can impact the respiratory microbiome, potentially leading to conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Genitourinary Tract: Dysbiosis in the vaginal and urinary microbiomes can cause bacterial vaginosis and urinary tract infections.
- Colonisation Resistance: Antibiotics can reduce the microbiome’s ability to protect against pathogenic microorganisms, increasing infection risks.
Other key facts:
- Antibiotics: Widely recognized for their ability to cure bacterial infections, antibiotics have revolutionized medical treatment. However, their misuse and overuse pose serious risks.
- Microbiome: The human body hosts ~38 trillion microbial cells, which outnumber human cells. The microbiome includes bacteria, fungi, and viruses, playing crucial roles in maintaining health.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
What is dysbiosis?
Dysbiosis is an imbalance in the microbial community, reducing beneficial bacteria and increasing harmful bacteria.
How long can dysbiosis last after a course of antibiotics?
Dysbiosis can last for months or even years after a single course of antibiotics.
What are some health consequences of dysbiosis?
Health consequences include digestive disorders, immune system impairment, metabolic issues, and alterations in the gut-brain and gut-liver axes.
How can dysbiosis affect the immune system?
Disruption of the microbiome can impair immune function, increasing susceptibility to infections and autoimmune diseases.
What role does dysbiosis play in metabolic issues?
Dysbiosis can lead to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome by affecting the gut microbiome.