Seismic waves, which are also called earthquake waves, are sound waves that travel through the Earth and other planets. These waves are produced by natural occurrences like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, as well as human activities. scientists examine them using specific tools.
Earthquake waves (Seismic Waves) will be helpful for UPSC IAS Exam preparation. GS Paper-1 Geography.
Table of Content
- What are Earthquake Waves (Seismic Waves)?
- Types of Earthquake Waves (Seismic Waves)
- What are Body Waves?
- What are Surface Waves?
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are Earthquake Waves (Seismic Waves)?
- Definition: A seismic wave or Earthquake Wave is an acoustic energy wave that travels through the Earth or other planetary bodies.
- These waves can be generated by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, magma movement, large landslides, and man-made explosions that produce low-frequency acoustic energy.
- Seismologists study seismic waves by recording them with seismometers, hydrophones (in water), or accelerometers.
- Seismic waves are distinct from seismic noise.
- Seismic Noise: It refers to persistent low-amplitude vibrations caused by various natural and human sources.
- The velocity of seismic wave propagation depends on the density, elasticity, and wave type of the medium it travels through.
- The velocity increases with depth in Earth’s crust and mantle but sharply decreases when transitioning from the mantle to the outer core.
- Earthquakes generate different types of waves with varying velocities and recording their travel times helps scientists locate the hypocenter of the quake.
- The refraction or reflection of seismic waves is used in geophysics to study the internal structure of the Earth.
- Scientists sometimes intentionally generate and measure vibrations to study shallow subsurface structures.
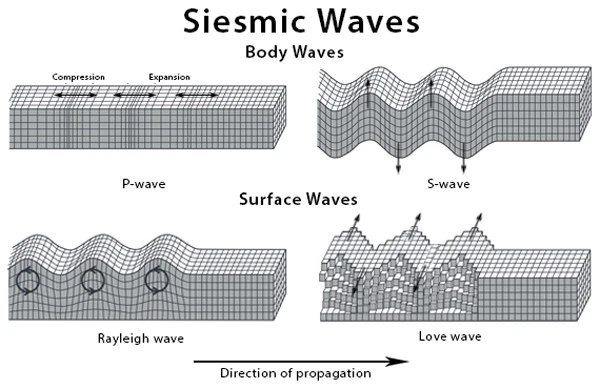
Types of Earthquake Waves (Seismic Waves)
- Seismic waves can be classified into two types:
- Body waves
- Surface waves.
- Body waves are energy waves that travel through the Earth’s inner layers.
- Surface waves are energy waves that travel along the surface of the Earth.
- During an earthquake, both body waves and surface waves are released.
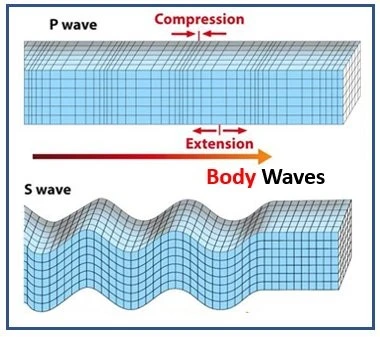
What are Body Waves?
- When an earthquake is recorded at a seismic station, body waves reach the destination before surface waves due to their higher speed.
- There are two types of body waves: P waves and S waves.
Difference between Primary Waves (P-Waves) and Secondary Waves (S-Waves)
| Primary Waves (P-Waves) | Secondary Waves (S-Waves) |
| The term P wave can refer to a pressure wave or a primary wave. | Following the initial waves, there are secondary waves known as S waves. |
| P waves are also known as primary waves or pressure waves. | S waves move at a slower pace compared to P waves. |
| They are a type of seismic wave in seismology. | These waves can only pass through solid substances like rocks and cannot travel through mediums such as fluids or subsurface water. |
| These waves have high velocity. | Scientists infer that the earth’s outer core is a liquid based on this characteristic of S waves. |
| They are formed by alternating compressions and rarefactions. | S waves propagate in various directions from their source and cause the ground to shake in a back-and-forth motion perpendicular to their own movement. |
| P waves are the fastest among seismic waves, making them the first to reach affected locations or seismographs during an earthquake. | |
| They can propagate through gases, liquids, and solids. |
What are Surface Waves?

- Unlike body waves, surface waves are limited to movement along the earth’s surface.
- They are restricted to the ground surface and cannot penetrate deeper.
- Surface waves are responsible for causing significant damage to the surface.
- There are two distinct types of surface waves: Love (L) waves and Rayleigh (R) waves.
Love (L) Waves
- L waves make the surface rocks move sideways, perpendicular to the wave’s direction.
- Their movement resembles a side-to-side motion.
Rayleigh (R) Waves
- R waves induce a vertical circular movement in surface rocks, similar to water in a sea wave.
- The rocks exhibit an up-and-down motion.
Conclusion
Seismic waves have a significant impact on comprehending the Earth’s inner structure. They can be categorized into body waves and surface waves, each having distinct properties and consequences. Through the study of these waves, researchers can pinpoint earthquake centres and acquire knowledge about the Earth’s makeup and behaviour.
Ref: Source-1
| Other Articles in Environment & Disaster Management | |
| P-Waves (Primary Waves) | Glacial Lake Outburst Flood |
| S-Waves (Secondary Waves) | Geomagnetic Storms |
| Disaster Management in India | Urban Flooding |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Name the three types of earthquake waves. Or How many types of earthquake waves are there?
There are three types of earthquake waves: P-waves, S-waves and surface waves.
Which earthquake wave is more destructive?
Surface waves (L-Waves) are the most destructive waves compared to Body Waves.
From where earthquake waves are generated?
The focus refers to the location within the Earth’s crust where an earthquake begins. Directly above the focus on the Earth’s surface lies the epicenter. Seismic waves radiate outward from the focus in all directions when energy is released.
Which instrument is used to measure the earthquake waves?
A seismometer is used to record the earthquake waves.
What is the medium of propagation of earthquake waves?
The medium of propagation of earthquake waves is Earth. It can be solid or liquid.
What types of waves are produced before the actual earthquake?
Low-frequency infrasound main shock waves are produced before the actual earthquake.
What is the source of earthquake waves?
Seismic waves are caused by the sudden movement of materials within the Earth, such as slip along a fault during an earthquake. Volcanic eruptions, explosions, landslides, avalanches, and even rushing rivers can also cause seismic waves.