Ecological pyramid serves as visual representations of the trophic levels in an ecosystem, offering insights into energy flow. These triangular pyramids categorize producers, herbivores, carnivores, and top carnivores, showcasing the diversity within ecosystems.
Ecological Pyramid will be helpful for UPSC IAS Exam preparation. GS Paper-3 Environment.
Table of Content
- What is Ecological Pyramid?
- Types of Ecological Pyramids
- Importance of Ecological Pyramids
- Limitations of Ecological Pyramids
- Conclusion
What is Ecological Pyramid?
- Ecological pyramids serve as visual representations of the various trophic levels within an ecosystem.
- These pyramids, shaped like triangles, can be categorized into three distinct types.
- The first level, known as the producers, forms the broad base of the pyramid, followed by subsequent tiers representing herbivores, carnivores, and top carnivores.
Types of Ecological Pyramids
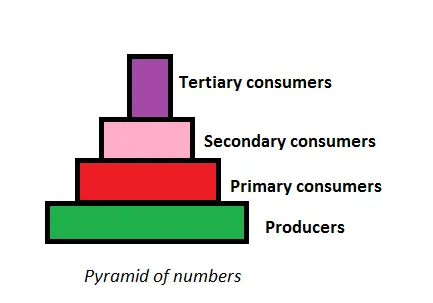
Pyramid of Number:
- The pyramid of number provides insights into the population count of organisms at each trophic level.
- For instance, in a grassland ecosystem, the number of grasses outweighs the number of herbivores feeding on them, and the number of herbivores, in turn, exceeds the number of carnivores.
- However, there are instances where the pyramid of number can be inverted.
- Example: the scenario where numerous caterpillars and insects rely on a single tree for sustenance.
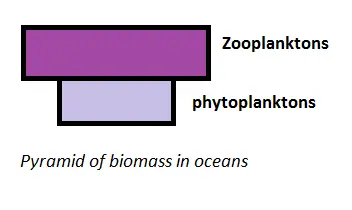
Pyramid of Biomass:
- The pyramid of biomass illustrates the overall standing crop biomass at each trophic level.
- Standing crop biomass refers to the amount of living matter present at a given time.
- It is commonly expressed in terms of grams per unit area or kilocalories per unit area.
- In terrestrial ecosystems, the pyramid of biomass typically maintains an upright shape but in aquatic ecosystems, it can be inverted.
- In a pond, phytoplankton serve as the primary producers, possessing short life cycles and high turnover rates.
- Their total biomass at any given moment may be lower than that of the herbivores dependent on them.
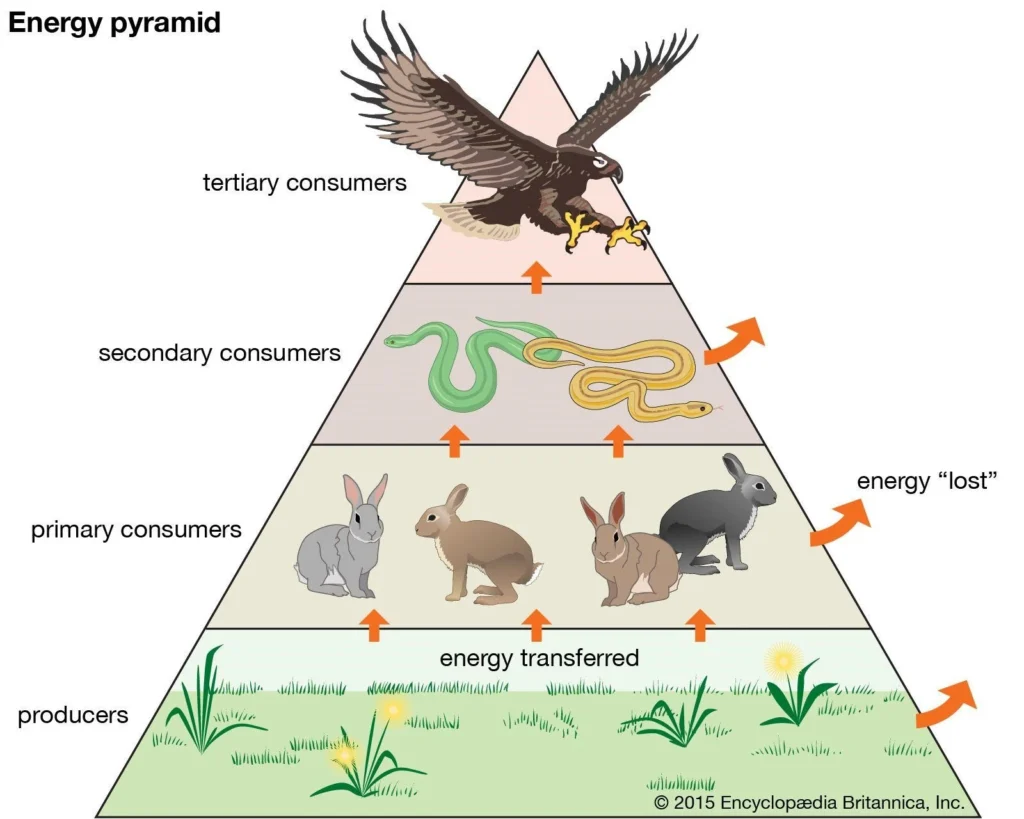
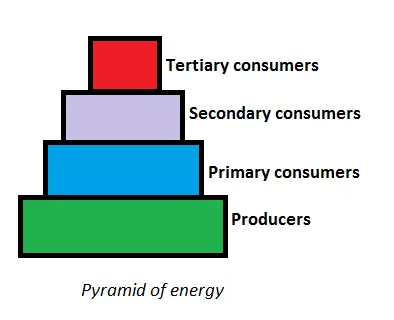
Pyramid of Energy:
- The pyramid of energy represents the overall energy content at each trophic level.
- Energy is measured in terms of rate, such as kilocalories per unit area per unit time or calories per unit area per unit time.
- Note: It is worth noting that energy pyramids never exhibit an inverted shape.
Importance of Ecological Pyramids
- Ecological pyramids play a crucial role in illustrating how organisms in diverse ecosystems obtain their food.
- They provide valuable insights into the flow of energy across different trophic levels within an ecosystem.
- They demonstrate the effectiveness of energy transfer, despite some energy being lost as heat to the surroundings.
- Closely monitoring Ecological Pyramids can contribute to the preservation of ecosystems.
Limitations of Ecological Pyramids
- Saprophytes or decomposers, despite their significance in the food chain, are often not assigned to a specific trophic level in the pyramid.
- The complexity of ecological pyramids leads to the exclusion of the intricate relationships depicted by the food web.
- Organisms of the same species cannot be placed at different trophic levels within a food pyramid.
- Ecological pyramids do not accurately represent seasonal variations and ongoing activities within the ecosystem.
- Their primary focus lies in depicting the food chain and its relationships.
Conclusion
While ecological pyramids are crucial for understanding energy transfer and preserving ecosystems, they have limitations. They overlook the role of decomposers, exclude intricate relationships depicted by food webs, and fail to represent seasonal variations and ongoing activities. Despite these challenges, ecological pyramids provide valuable information about the flow of energy and the interconnectedness of organisms within an ecosystem.
Ref: Source-1
| Other Articles in Environment & Disaster Management | |
| Food Chain | Oxygen Cycle |
| Food Web | Phosphorus Cycle |
| Energy Flow in Ecosystem | Food Crops |
FAQs (frequently asked question)
What is the definition of an Ecological Pyramid? Or
What do you mean by ecological pyramid?
An ecological pyramid is a visual representation created to illustrate the amount of biomass or bio-productivity present at different trophic levels within an ecosystem.
Who coined the concept of an Ecological Pyramid?
The concept of an ecological pyramid was developed by Charles Elton.
Which of the ecological pyramid is always upright?
The ecological pyramid that is always upright is the pyramid of Energy.
Give examples of ecological pyramids. Or
How many types of ecological pyramids are there?
The Pyramid of Energy, Pyramid of Biomass, and Pyramid of Number are 3 different examples of ecological pyramids.