Ecology is the study of relationship between the living organisms amongst each other and with their surroundings. In this article, you will learn ecology definition, concept of ecology, levels, principles and types of Ecology, providing key insights for GS Paper-III Environment and Ecology section of UPSC IAS Exam.
Table of Content
- What is Ecology?
- Introduction to Ecology
- Levels of Ecological Organization
- Principles of Ecology
- Types of Ecology
- Ecology examples
- Ecological factors
- Difference between Ecology and Environment
- Difference between Ecology and Ecosystem
- Importance of Ecology
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ecology?
- Ecology deals with the study of relationship between the living organisms amongst each other and with their surroundings.
- The word ecology is derived from the word “oikos” (means home) and “logos” (means study).
- The term ecology was coined by Ernst Haeckel in 1866 to describe the “economies” of living forms.
- Components of ecology are abiotic components or non-living elements and biotic components or living organisms.
- The scope of ecology is to primarily study the interrelationships between lifeforms and environmental factors, including thecomponents of ecology.
- Ecology deals with the examination of the population dynamics, communities, ecosystems, biomes and the biosphere.
- Eugene Odum is also known as the father of ecology or father of modern ecology.
- Ramdeo Misra is also known as the father of Indian ecology.
Introduction to Ecology:
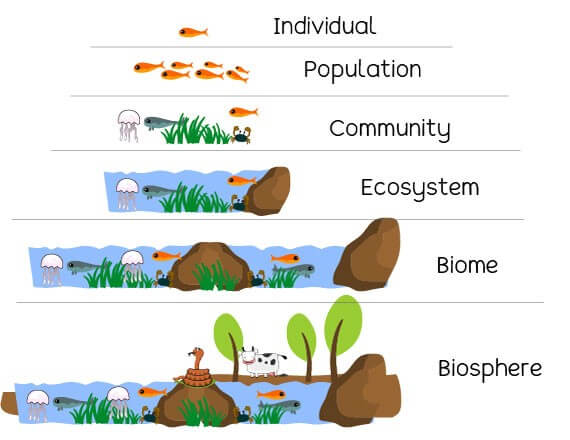
- Levels of Ecology: Individual; Population; Community; Ecosystem; Biome and Biosphere.
- Types of Ecology: Microbial Ecology; Behavioural Ecology; Population Ecology; Community Ecology; Ecosystem Ecology; Global Ecology.
- Examples of ecology studies how various types of ecology came into existence including Human ecology and ecological niche construction.
Levels of Ecological Organization:
- Individual: organisms that are the basic unit of study.
- Individual Ecology studies thephysiology, behavior, distribution and adaptation.
- Population: is group of individuals with samespecies that resides in a defined area and interact amongst each other.
- Population Ecology studies the interaction between members.
- Community: is group of populations with differentspecies that live in an area and interact amongst each other.
- Community Ecology studiesthe interactions between members and structure and composition of community.
- Ecosystem: is a combination of multiplecommunities of organisms with their physical environment.
- Theytogether interact as an ecological unit.
- Ecosystem Ecology studies the interactions between members, structure, nutrients cycling, climate, energy flow etc.
- Biome: is a combination of multiple ecosystems or a biogeographical unit characterized by a specific climate, that the types of plants and animals that live there has adapted to.
- Biosphere: it is the zone of life on earth where life exists and where different Biome interacts.
Principles of Ecology:
- First principle of Ecology: Ecological systems or Ecosystem are organized into hierarchies by evolution.
- Individual organisms form populations, which then form species.Species are grouped into higher taxa, such as genera and phyla.Each of these levels has abundance and ecological biodiversity (number of kinds) in a given ecosystem.
- Ecology helps understand how and why abundance and ecological biodiversity vary with time and space.
- Second principleofEcology: the Sun is the primarysource of energy for all ecosystems on Earth- it provides the sunlight that plants or phytoplanktons need to perform photosynthesis.
- This food is then consumed by other organisms, which use it for energy and to build new tissues.
- The energy from the sun also powers the water cycle, which is essential for all life on Earth.
- Third principleofEcology: Organisms are living systems that use energy to perform essential functions.
- The energy that organisms use comes from food.
- Without energy, organisms would not be able to survive.
- Fourth principle of Ecology: Chemical nutrients are constantly recycled within an ecosystem, while energy flows through it in a one-way direction.
- Energy can be used only once before they are lost to the universe.
- Fifth principle of Ecology: The change in the number of individuals in a population in a given area over time is determined by the ecological balance of births, deaths, and net migration.
- Sixth principle of Ecology: The rate of change in species diversity in an area is determined by the balance of three factors:
- Speciation: the process by which new species are created.
- Extinction: the process by which a whole species dies out.
- Migration: the movement of species into or out of an area.
- Individuals and species that are well-adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, and thus are more likely to persist in that environment.
- Seventh principle ofEcology: Organisms interact with each other in ways that can affect their abundance, including predation, competition, and mutualism.
- Predation is a type of interaction in which one organism– the predator, eats another organism- the prey.
- Competition is a type of interaction in which two or more organisms compete for the same resources.
- Mutualism is a type of interaction in which two or more organisms benefit from each other’s presence.
- The kind and strength of these interactions varies depending on the species involved and the environment in which they live.
- Eighth principle ofEcology: Ecosystems are organized into complex networks of interactions between organisms.
- The abundance of a population is affected by the relationships it has with other species in the same ecosystem.
- These relationships can be complex and difficult to predict, which makes it challenging to determine what patterns of abundance and diversity can be expected.
- Ninth principle of Ecology: Humans have a significant impact on other organisms, both positive and negative.
- Positive example: humans can plant trees to provide food and shelter for animals.
- Negative example: humans compete with wild animals for food and water.
- Tenth principle of Ecology: Ecosystems provide a variety of essential services to humans including: products; regenerating water and air quality; medicine through variety of medicinal plants and animals.
Types of Ecology:
- MicrobialEcology: is the study of at the fundamental levels of life or cellular organisms including Kingdom Monera and Kingdom Protista.
- Interactions between the microbes and their relationships with each other and their environments are studied.
- BehaviouralEcology: is the study of the organism at its fundamental levels including organism’s behaviours,their ecological adaptation and reasons of such adaptations.
- It is also known as organismic ecology.
- It also covers microbial ecology.
- Population Ecology: is the study of population including its size, structure, migration patterns, and the interaction with the organisms of the same species.
- Community Ecology: is the study of community including size, structure, interactions between different species and how one community affects the other community.
- Ecosystem Ecology: is the study of interaction between the abiotic and biotic factors and thus includes the overall aspects of the environment and how each factors interact.
- Global Ecology (Biosphere): is the study of all the ecosystems present on earth including interaction between all biomes and living organisms.
Ecology examples:
- Human ecology: is the study of the relationship between humans and their environment including Human’s behaviour and evolutionary reasons for certain traits.
- It helps to understand the impact that humans have on the environment and forces us develop sustainable ways of living that will not damage the environment.
- Niche construction: is a branch of ecology that studies how organisms alter their environment to their benefit including the benefit of other living things.
- It helps to understand how some organisms can overcome the environmental or habitat challenges that they face.
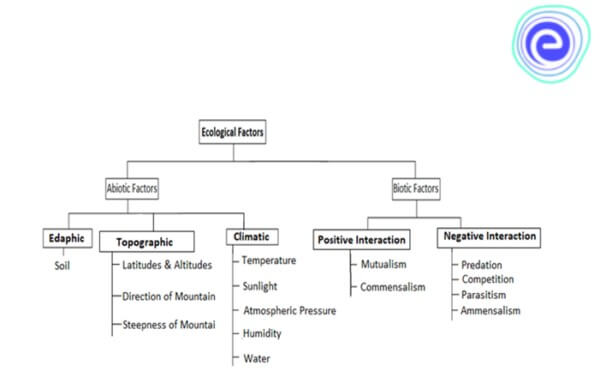
Ecological factors:
- Ecological factors are environmental variables that impact and influences organisms and leads changes in their behaviour.
Types of Ecological Factors:
Alt text: Types of Ecological Factors
Difference between Ecology and Environment:
| Environment | Ecology |
| The environment indicates the interaction between physical, chemical and biological components. | Ecology is the study of the relations between living things, the environment, and their interaction. |
| Environment includes issues like deforestation, pollution, global warming, and other major issues | Ecological issues include population size, diversity, biological distribution, and competition between them. |
| Environment is the study of internal and external factors that affect the environment. | Ecology aims to understand the processes of life, distribution, adaptation, and biodiversity. |
Difference between Ecology and Ecosystem:
| Ecology | Ecosystem | |
| Definition | The study of the relationships between organisms and the surrounding environment. | The ecosystem refers to the entire biological community in an area along with physical and chemical environment including abiotic components. |
| Correspondence | Study of all the ecosystems in a vast area. | Subset of ecology that focuses on a particular environment and its ecosystems. |
Importance of Ecology:
- Ecology provides knowledge of the interdependence between Human and nature.
- Ecology helps in conservation of Environment as it determines the impact of human actions on nature.
- Ecology helps in proper resource allocation by clearly demarcating various factors that are important for the Environment.
- Ecology helps in disease and pest control by determining the ways through which disease or pest can spread from one species to other species or communities.
Conclusion
Ecology plays a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the intricate relationships between organisms and their environments. It highlights the importance of biodiversity conservation, sustainable resource management, and addressing environmental challenges such as climate change and habitat loss. As we navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing world, integrating ecological principles into policymaking and societal actions is essential for fostering resilience and ensuring the long-term health of our planet and its inhabitants.
Ref:
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What do you mean by the term “ecology”?
Ecology deals with the study of relationship between the living organisms amongst each other and with their surroundings.
Who is the father of ecology?
Eugene Odum is also known as the father of ecology or father of modern ecology.
What is an Ecological Footprint?
The Ecological Footprint tracks the use of productive regions such as cropland, grazing land, fishing grounds, built-up land, forest area, and carbon demand on land.
Who coined the term ecology?
The term ecology was introduced by Ernst Haeckel in 1866.
What is deep ecology?
The Deep ecology is a philosophy that stresses on conservation of all living beings even if they have no utility to humans.
What is Urban ecology?
Urban ecology is the scientific study of the relation of living organisms with each other and their surroundings in an urban environment.
What is Restoration ecology?
Restoration ecology is the scientific study of restructuring disturbed ecosystems through human intervention.
What is Ecological Balance?
Ecological balance is a state of dynamic equilibrium within a community of organisms in which genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity remains relatively stable but are subjected to gradual changes through natural succession.
What is ecological niche?
Ecological niche is a position of a species within an ecosystem which describes the conditions required for the persistence of the species and its ecological role in the ecosystem.
What is Ecological System?
The ecological system refers to the entire biological community in an area along with physical and chemical environment including abiotic components.
What is Population Ecology?
Population Ecology is a sub–field of ecology that deals with the dynamics of species populations and how these populations interact with the environment, such as birth and death rates, and by immigration and emigration.
What is Community Ecology?
Community Ecology is the study of community including size, structure, interactions between different species and how one community affects the other community.