The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently awarded “breakthrough device” status to Neuralink’s Blindsight implant, an experimental vision-restoring implant.
About the Blindsight Implant:
- Purpose: Designed to restore vision in individuals who have lost their sight or were born blind.
- Initial Vision Quality: Early users may experience low-resolution vision similar to early video game graphics.
- Potential Advancements: Future improvements could enable users to perceive wavelengths beyond natural vision, including infrared, ultraviolet, and radar.
Significance of Breakthrough Device Designation
- Accelerated Development: This designation is intended to hasten the development of devices that offer promising new treatments or diagnostic capabilities for life-threatening conditions.
About Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs)
- BCIs enable users to communicate or control external devices using brain signals without physical movement.
- Functionality: Captures electrophysiological signals from the brain’s neurons and relays this information to external systems, enabling users to translate thoughts into actions.
Types of BCIs
- Invasive:
- Chips or sensors placed directly into the brain’s cortex (e.g., Neuralink’s implant).
- Provide high-definition signals due to proximity to neural networks.
- Suitable for patients with severe conditions like paralysis.
- Non-Invasive:
- Sensors positioned on the scalp.
- Produce weaker signals and are suitable for applications like gaming and augmented reality.
- Partially Invasive: Devices implanted inside the skull with external components.
How Do BCIs Work?
- Signal Capture: Electrodes detect voltage changes from neuron communication.
- Neural Decoding: Information is processed using algorithms to interpret brain intentions.
- Example: A BCI chip was implanted in a quadriplegic patient, allowing him to control a computer.
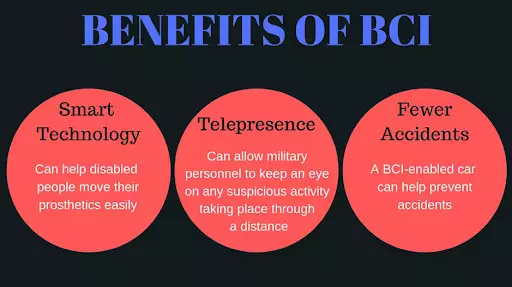
Benefits of BCIs:
- Restore Mobility: Direct control over exoskeletons and robotic limbs, bypassing injury sites.
- Mindwriting for Non-Verbal Individuals: Enable rapid communication through neural decoding.
- Treatment of Neurological Conditions: Potential to improve quality of life for patients with severe diagnoses.
- Mental Health Monitoring: Could help manage psychiatric conditions and promote wellness.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Allow users to train memory and processing speed through real-time feedback.
Applications of BCIs
- Medical:
- Restore lost functions (e.g., controlling prosthetic limbs).
- Aid patients with neurological disorders such as paralysis.
- Mental Wellness: Provide real-time feedback on mental well-being.
- Defense:
- Enhance awareness and management of autonomous systems in combat.
- Develop hands-free control for unmanned aerial vehicles.
- Gaming and Entertainment:
- Create immersive experiences through neural communication.
- Control apps and devices without physical movement.
Challenges and Concerns with BCIs:
- Cybersecurity Risks: Risks such as brain tapping, where signals from the brain can be intercepted.
- Ethical Concerns: Issues regarding informed consent.
- Safety Issues: Potential risks include tissue damage, seizures, and cognitive impairments.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
What is Neuralink’s Blindsight implant?
It is a brain-computer interface designed to restore vision in individuals who have lost their sight or were born blind.
How do BCIs like Blindsight work?
BCIs capture brain signals and relay them to external systems, enabling users to control devices or translate thoughts into actions.
What are the benefits of the Blindsight implant?
It can potentially restore vision, offering users low-resolution sight initially, with future advancements for improved perception.
What challenges are associated with brain-computer interfaces?
Potential risks include cybersecurity threats, ethical concerns, and safety issues like tissue damage or cognitive impairments.