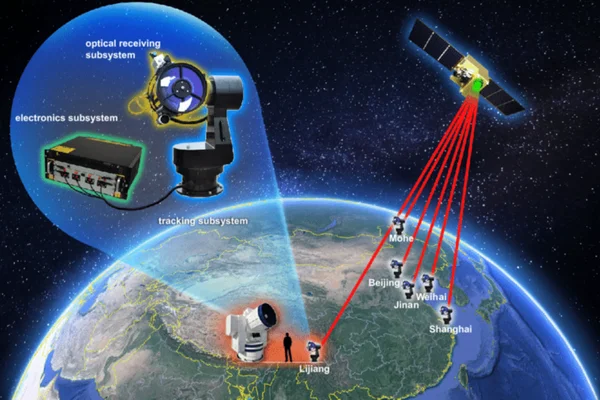
Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DOT) and Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) have successfully demonstrated the integration of C-DOT’s indigenous Fiber-based Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) system with PRL’s Free Space QKD system.
- This milestone establishes an end-to-end quantum communication link, combining both fiber and free space as transport mediums.
Quantum Computing Risks and Quantum Key Distribution (QKD):
- The surge in quantum computers and algorithms poses a threat to classical data security methods.
- Quantum computers’ immense computational power could compromise encryption keys’ secrecy.
- QKD, a branch of Quantum Communications, addresses this threat by ensuring fool-proof security even in the presence of quantum computers.
- Quantum Communication will play a critical role in sectors like defence, government communications, healthcare, finance, data centers, and telecommunications.
About Quantum key distribution (QKD):
- Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a secure communication method that employs principles of quantum mechanics in a cryptographic protocol.
- It allows two parties to generate a shared random secret key exclusive to them.
- The key is subsequently utilized for encrypting and decrypting messages, ensuring secure communication.
- QKD can be deployed through different mediums viz. optical fibre, free space as well as satellite to provide end to end security over the communication network.
Detecting third-party:
- A crucial and distinctive feature of quantum key distribution is its ability for the two communicating users to detect any third party attempting to gain knowledge of the key.
- This arises from a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics: the act of measuring a quantum system generally disrupts the system.
- Any attempt by a third party to eavesdrop on the key involves some form of measurement, thereby introducing detectable anomalies.
- By utilizing quantum superpositions or quantum entanglement and transmitting information in quantum states, a communication system can be established to identify eavesdropping.
- If the level of eavesdropping falls below a specific threshold, a secure key can be generated, ensuring that the eavesdropper has no information about it.
- Otherwise, if the level of eavesdropping exceeds the threshold, no secure key can be established, leading to the termination of communication.
Fiber-optic quantum key distribution QKD:
- Fiber-optic quantum key distribution (QKD) is a technique that uses quantum physics to create encryption keys between two parties.
- QKD systems transmit light particles, or photons, over fiber optic cables.
- The photons have random quantum states, and the stream of ones and zeros they create are called qubits.
Free space QKD:
- In the context of free space, QKD involves transmitting quantum information (usually encoded as quantum bits or qubits) between two parties through the air or outer space.
- Traditional fiber-based QKD systems are limited by the attenuation and loss of quantum signals in optical fibers.
- Free-space QKD overcomes these limitations by using free-space channels, such as the atmosphere, to transmit quantum information.
- The process typically involves the transmission of quantum states of particles (such as photons) between a sender and a receiver.
About Quantum communication:
- Quantum communication is a field of applied quantum physics that uses quantum mechanics to ensure secure communication.
- It constitutes one of the four verticals within Quantum Technology, alongside Quantum Computing, Quantum Sensors, and Quantum Materials.
- It involves creating ultra-secure communication networks that could form the basis of a quantum internet.
- It uses photons to transmit qubits between remote locations.
- Photons are well isolated from perturbations, which means they can propagate with low attenuation in optical fibers.
- It could be ideal for organizations that need to keep particularly valuable data secure.
- It leverages the unique properties of quantum systems, such as superposition and entanglement, to enable communication protocols that offer unprecedented levels of security and capabilities.
Initiative taken for quantum technology in India:
- National Mission on Quantum Technologies & Applications (NM-QTA): Launched in 2020, this five-year program aims to create a strong quantum technology ecosystem in India.
- The program’s goals include:
- Understanding and controlling quantum mechanical systems.
- Initiating work in quantum technology applications.
- National Quantum Mission (NQM): Nurture and scale up scientific and industrial research and development in quantum technology.
- Prime Minister’s Science and Technology Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC): Quantum Technologies & Applications is one of 9 missions of national importance
- Quantum Measurement and Control Laboratory (QuMaC): It is a research institute at TIFR that studies quantum phenomena in superconducting circuits.
- Quantum-Enabled Science and Technology (QuEST): A research program by the Government of India’s Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS): A program aims to transform ideas and concepts into products, and to boost new technologies.
About PRL:
- The PRL is a national research institute in Ahmedabad, India that studies space and related sciences.
- It was founded in 1947 by Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, a space and cosmic-ray scientist.
- The PRL is an autonomous unit of the Department of Space (DOS).
About C-DOT:
- C-DOT is an Indian government-owned company that develops telecommunications technology.
- It was established in 1984 by Sam Pitroda as an autonomous body.
Ref:Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |