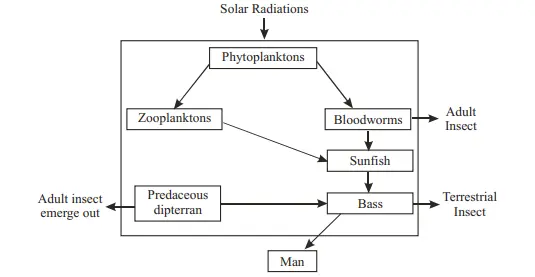
A food web is a network of interconnected food chains that illustrate the complex relationships among species in a community, demonstrating the flow of energy through interconnected trophic levels.
Food Web will be helpful for UPSC IAS Exam preparation. GS Paper-3 Environment.
Table of Content
- What is Food Web?
- Applications of Food Webs
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Food Web?
- Definition: A network of food chains that are interconnected at various trophic levels of the food chain to form a number of feeding connections is called a food web.
- In a food web one trophic level may be connected to more than one food chain.
- A snake can feed on frogs or rats or any other small rodent.
- In the figure given above sunfish consumes zooplanktons as well as bloodworms.
Applications of Food Webs
Direct Species Interactions
- Food webs serve as a tool to portray the nutritional relationships among species in a community.
- They are used to describe the connections between different species and their interactions within an ecosystem.
- Species in food webs can be categorized as basal (autotrophs like plants), intermediate (herbivores and intermediate-level carnivores such as grasshoppers and scorpions), or top predators (high-level carnivores like foxes).
Indirect Species Interactions
- Indirect interactions occur when two species do not directly interact but are influenced by a third species.
- Species can impact each other in various ways, such as through keystone predation.
- Robert Paine’s experiment in a rocky intertidal zone demonstrated keystone predation.
- Predation can influence competition within a food web.
- In the intertidal zone, starfish prey on invertebrate herbivores like mussels, barnacles, limpets, and chitons.
- Paine’s removal of starfish from experimental plots resulted in a decrease in prey species (a loss of 7 species) two years later, while the number of prey species in control plots remained the same.
- The absence of starfish allowed certain mussel and barnacle species, which were superior competitors, to dominate, leading to a reduction in overall diversity.
- This indirect interaction, known as keystone predation, demonstrates how the population dynamics of one species can impact the entire ecosystem.
Refer to the linked article to know more details about Energy Flow in Ecosystem, Ecological Pyramids and Food Chain.
Conclusion
Food webs play a important role in portraying the nutritional interactions within a community, categorizing species as basal, intermediate, or top predators. They also highlight indirect species interactions, such as keystone predation, which can influence competition and impact the diversity of an ecosystem. Understanding food webs help to comprehend the intricate dynamics of species and their interconnectedness within ecological communities.
Ref: Source-1
| Other Articles in Environment & Disaster Management | |
| Ecological Pyramid | Energy Flow in Ecosystem |
| Food Chain | Cropping systems |
| Food Crops | Crop Diversification |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the difference between food chain and food web?
A food chain shows the straight path of nutrients and energy as they move from one level of a food pyramid to another. Food webs are complex networks formed by multiple food chains operating at different levels within an ecosystem.
Which source is the primary source of energy in food webs?
The primary source of energy in a food web comes from the sun (Sunlight).