The Foreign Exchange Rate refers to the rate at which one currency is traded for another. This article discusses meaning pf foreign exchange rate, how foreign exchange rate is determined, and the types of global exchange rate systems – namely, the Fixed or Pegged, Flexible or Floating, and Managed Floating or Intermediate exchange rate systems. These systems each come with their own advantages and disadvantages, and countries opt for them based on their unique economic and political contexts. All of these are important topic for GS Paper-3 Economy Subject of UPSC IAS Exam. To explore other interesting Class 12 Economics concepts similar to foreign exchange rate, check out other articles of IASToppers.
Table of Content
- What is Exchange rate?
- Why the exchange rate is important?
- Factors affecting the foreign exchange rate
- Types of Foreign Exchange Rate
- Fixed or pegged exchange rate system
- Advantages of fixed exchange rate system
- Disadvantages of fixed exchange rate system
- Flexible or Floating exchange rate system
- Advantages of floating exchange rate system
- Disadvantages of floating exchange rate system
- Managed floating or Intermediate exchange rate system
- Conclusion
What is Foreign Exchange rate?
- Exchange rate, or foreign exchange rate, is the rate at which domestic currency is traded for a foreign currency.
- Similarly, it is the rate which shows the value of domestic currency in terms of other currencies.
Example of Exchange Rate
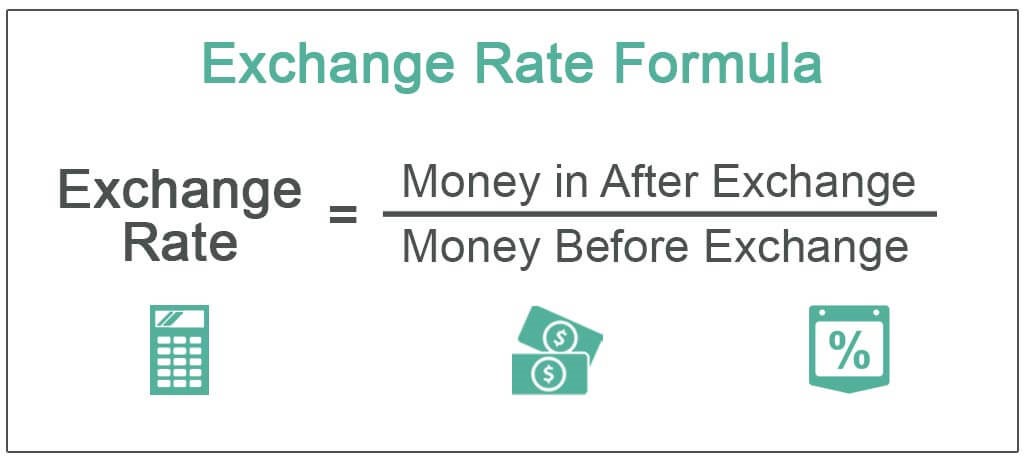
- Consider $1 = 80 INR (exchange rate), then if an Indian import wants to buy a watch worth of $100 in US, he/she has to pay 8000 INR (excluding other fees).
- If the foreign currency exchange rates move from$1 = 80 INR to $1 = 85 INR, the value of rupee will come downs as we need to give five more rupees to get one dollar.
Why the foreign exchange rate is important?
Because exchange rate fluctuation affect:
- Competitiveness of exports and cost for imports
- Currency value of debt payments
- Expenses of tourists
- Value of international investment portfolio
Because exchange rate fluctuation affects the decision of:
- Foreign investors
- Exports and importers
- Bankers, businesses, financial institutions
- Policymakers and people who are going abroad for various purposes etc.
Factors affecting the foreign exchange rate
- In a free-market economy, determination of foreign exchange rate is predominantly influenced by the supply and demand for rupees and dollars.
- However, in India, the foreign exchange rate is not fully determined by the market.
- From time to time, the RBI intervenes in the foreign exchange (forex) market to ensure that the rupee price does not fluctuate too much or that it doesn’t rise or fall too much all at once.
Other economic, political, and psychological elements, can also influence exchange rates.
- Economic factors include inflation, trade balances, and government policies.
- Political factors include domestic unrest or instability and any form of political conflict.
- Psychological factors include the mindset of participants involved in foreign exchange transactions.
Types of Foreign Exchange Rates
1. Fixed or pegged exchange rate system
- In Fixed or pegged exchange rate system, exchange rate of a weak currency is fixed at a particular rate with another stronger currency by the central bank.
- Two types of pegs:
- Hard peg: Exchange rate tightly fixed or pegged with hard currency and thus has no flexibility
- Soft peg: Exchange rate is fixed with some flexibility withing specific range
- Fixed exchange rate is determined by central bank of a country and thus market force cannot directly influence the exchange rate.
- Market forces refers toselling (supply) and buying (demand) of foreign currencies by various individuals and institutions.
- Presently, many developing countries are having fixed ERS.
How does central bank keep the ERS fixed?
- When value of domestic currency goes down,Central bank or government sell/supplies foreign currency to foreign exchange market.
- When value of domestic currency goes up, Central bank or government purchases foreign currency from foreign exchange market
- This buying and selling of foreign currency is called pegging, which is why the fixed exchange rate system is also known as the pegged exchange rate system.
Advantages of fixed foreign exchange rate system
- Removes uncertainty in incomes of exporters and the cost of imports of the importers.
- Risks associated with international trade and investment get minimised.
- Speculation in the foreign exchange market is reduced, discouraging capital flight.
- In underdeveloped countries, persistent balance of payment issues can be worsened by frequent exchange rate fluctuations; stable rates mitigate this problem.
- Precludes governments from employing reckless macroeconomic tactics, such as currency devaluation.
- Exchange rate stability may attract foreign investors and promote international trade.
- Avoiding currency depreciation through Fixed exchange rate maintains stable import prices and inflation rates.
Disadvantages of fixed foreign exchange rate system
- Government continually has to maintain foreign reserves to ensure economic stability.
- A rigid system like fixed rates may prevent a government’s ability to recover from economic shocks.
- Having a fixed exchange rate can interfere with other macroeconomic goals.
- Example: Falling currency value leads to higher interest rates, which curbs inflation but boosts hot money flows. This reduces demand and economic growth, potentially resulting in a recession.
- Adapting to temporary disturbances is challenging.
- Example: A rise in oil prices causes a worsening of balance of payments (BoP) of an oil importing nation, with no option to devalue and mitigate the deficit due to the fixed system.
- If a country faces huge BoP deficit, then the possibility of speculation increases.
- If the speculators can guess that BOP deficit will persist in near future and govt may go for a cut in foreign exchange rate then speculators will sell domestic currencies in the foreign exchange market for profit.
2. Flexible or Floating exchange rate system
- In this system, exchange rate is determined in the foreign exchange market by the operation of market forces.
- Central bank never intervenes in the foreign exchange market to stabilise the exchange rate.
- Most of the advanced countries are having floating ERS.
Advantages of floating foreign exchange rate system
- Government need not keep sizable foreign exchange reserves to maintain external balance.
- Government can concentrate on domestic economic policies by leaving the exchange rate system to market forces.
- Domestic economy remains insulated from external shocks and pressures. The threat of ‘importing inflation’ from outside the country is minimum.
- Market determines the exchange rate which reduces the need for a mechanism to ensure exchange rates stability. This also automatically solves the problem of international liquidity.
- BoP problem isautomatically adjusted through deprecation or appreciation of the currency.
Disadvantages of floating foreign exchange rate system
- The exchange rate may experience fluctuations, impacting the value of currency, and since the Forex market lacks regulation, currency values might soar or plummet within minutes.
- This system promotes currency speculation and results in huge capital movement in and out of the country, severely disrupting the national economy.
- Allocating resources becomes challenging for the economy due to fluctuating exchange rates.
- For instance, increased exchange rates favour imports, while decreased rates facilitate exports. Continuous fluctuations prevent the establishment of a long-term strategy.
- Economic discipline is necessary for freely floating currencies to provide independence.
- Governments might adopt unsuitable domestic policies (e.g., overly expansionary policies) without exchange rate constraints.
- It often discourages foreign investment as exchange rate becomes erratic and, hence, destabilising.
- Floating exchange rates may exacerbate existing economic problems in a country.
- Example: Depreciation of a currency already suffering from high inflation will cause inflation to increase further due to an increase in demand for goods.
3. Managed floating or Intermediate exchange rate system
- In this, exchange rate is determined in the foreign exchange market through the operation of market forces.
- But during extreme fluctuations, the central bank intervenes in the foreign exchange market.
- Thus, it is also known as intermediate exchange rate system as it is hybrid between fixed and floating ERS.
- India’s foreign exchange rate system is Intermediate exchange rate system.
- There is depreciation (decline in value of rupee) and appreciation (increase in value of rupee) of the domestic currency depending on the environment.
- Some governments impose bands within which the exchange rate can fluctuate, which is one of the reasons for calling this approach “dirty.”.
How to forecast foreign exchange rates?
Accurate predictions of foreign currency exchange rates help traders and business in strategizing better. There are three primary methods to forecast these rates: Parity in Buying Power, Comparative Economic Strength, and Statistical Forecasting Models.
- The Principle of Parity in Buying Power (PPP): This method is frequently employed for predicting foreign exchange rates and is commonly introduced in academic literature. The PPP concept scrutinizes the price of commodities in diverse nations.
- Comparative Economic Strength Approach: This approach focuses on evaluating and comparing the growth rates of different economies. This comparison helps in anticipating future currency exchange rates.
- Statistical Forecasting Models or Econometric Models: These are advanced techniques which utilize an extensive range of variables to decode and anticipate trends in foreign currency markets.
Conclusion
The exchange rate system plays a crucial role in a country’s economic stability and development. The choice between fixed, floating, and managed floating exchange rate systems depends on a nation’s unique economic and political circumstances. Moving forward, it is essential for India to continue monitoring its exchange rate policies and ensure they align with the nation’s long-term economic goals.
Ref: Source-1
| Other Articles in Economy | |
| Financial Market | Stock Exchange |
| G20 (Group of 20) | Ways and Means Advances |
| Marginal Cost of Funds based Lending Rate (MCLR) | Open Market Operations (OMO) |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
what do you mean by foreign exchange rate?
The foreign exchange rate is the value or rate at which one country’s currency can be traded for another country’s currency.
How does giving incentives for exports influence foreign exchange rate
When a country encourages exports, it creates more demand for its own currency. This can make its currency stronger in the foreign exchange market
What is the devaluation of foreign exchange rate?
Devaluation is when a country decides to lower the value of its own currency compared to the currencies of other countries
How can foreign currency exchange rate risk can be hedged?
Foreign exchange rate risk can be hedged through various financial instruments like futures, forwards, options, or swaps, ultimately securing a rate for future transactions
Which currency has highest foreign exchange rate with INR?
The Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD), the most valuable currency in the world owing to Kuwait’s economic stability, has highest foreign exchange rate with INR.
What is the relation between interest rates and foreign exchange rates?
Interest rates have a direct impact on the appeal of a country’s assets, impacting currency demand. A decline in interest rates can decrease speculative demand for a currency and thus decrease foreign investment, leading to a corresponding drop in currency strength. On the other hand, higher interest rates can strengthen the currency by drawing in more international capital. Thus, a higher interest rate is generally associated with increased foreign investment and a robust currency.




