
GAGAN (GPS-aided GEO augmented navigation) Satellite is a project developed by both Airports Authority of India (AAI) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) over 15 years. Its estimated cost is Rs 774 crores. It will benefit major airports in India which do not have the capacity to equip themselves with costly ground-based landing systems.
GAGAN (GPS-aided GEO augmented navigation) Satellite will be helpful for UPSC IAS Exam preparation. GS Paper-3 Science and Technology.
Table of Content
- What is GAGAN Satellite?
- Application of GAGAN
- Advantages of GAGAN
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is GAGAN Satellite?
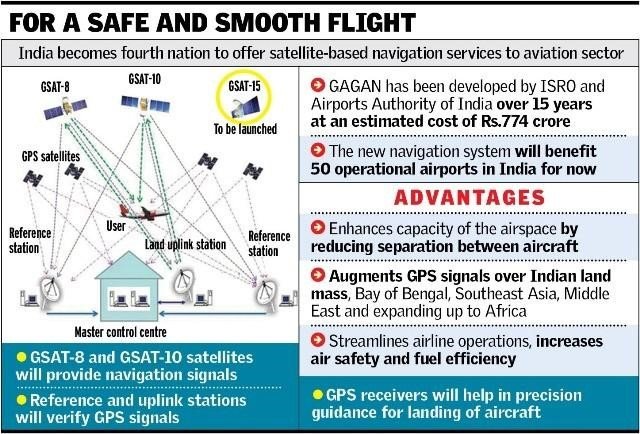
- The GAGAN (GPS-aided GEO augmented navigation) is an implementation of a regional satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) by the Government of India (GOI).
- Developed by: Airports Authority of India (AAI) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It is a part of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), which takes the input from the core GPS (Global Positioning System) constellation and augments navigation data through the GEO stationary satellites for providing better accuracy, integrity and continuity of service for its application in civil aviation.
- It uses a system of ground stations to provide necessary augmentations to the GPS standard positioning service (SPS) navigation signal.
Application of GAGAN
- Aviation Sector: GAGAN is operational and offers two levels of service; RNP 0.1 (Required Navigation Performance 0.1) over the Indian Flight Information region and APV I (Approach with Vertical Guidance, Level I) over a major part of Indian landmass, to its aviation users.
- It can support operations for all phases of flight including Oceanic, Approach, Terminal, and Surface.
- It helps in designing more efficient routes which can result in fuel savings.
- Disaster Management: The use of GAGAN message service (GMS), early Warning messages can be broadcast on the occurrence of natural disasters, calamities, and dangers for the safety of life within the GAGAN coverage area for Search and Rescue Messages, Relief and mitigation related messages, Meteorological information and other uses.
- Payment Applications: GAGAN can enhance safety, mobility, and regulation and enable payment applications.
- Road Sector: It can offer Smart mobility for lane guidance, better traffic management, speed control and traffic violation, and Real-time tracking of public transportation assets.
- With the use of GAGAN, initiation of alarm and barrier closure can be automated, and monitoring of train movements and automated train stopping can be achieved to reduce the risk of accidents.
- Navigation and Positioning: GAGAN can improve Navigation and Positioning in the Indian Subcontinent and Inland waterways by tracking the proximity of ships, enabling safe docking of ships at ports, enhancing coastal security and tracking ships.
Advantages of GAGAN
- It offers the same accuracy as a ground-based landing system, which comprises antennae and beacons that transmit signals to aircraft to help pilots land.
- It will enable aircraft to land even at smaller and regional airports, which are not equipped with expensive ground-based landing systems.
- GAGAN can benefit in saving fuel and equipment costs, flight safety, especially in adverse weather conditions and increased air space capacity.
Conclusion
After the implementation of GAGAN (GPS-aided GEO augmented navigation), India became 4th nation to offer a satellite-based navigation system to the aviation sector. which has GAGAN (GPS-aided GEO augmented navigation) Satellite is used mainly in the aviation sector but it has a wide range of potential which can be used in Disaster Management, Payment Applications, Road Sector, Navigation and Positioning etc.
What is the coverage area of GAGAN?
The coverage area of GAGAN expands from Africa to Australia and the GAGAN system can cater to 45 reference stations for expansion to neighbouring countries.
What is the full form of GAGAN?
The full form of the GAGAN satellite is GPS-aided GEO-augmented navigation.


