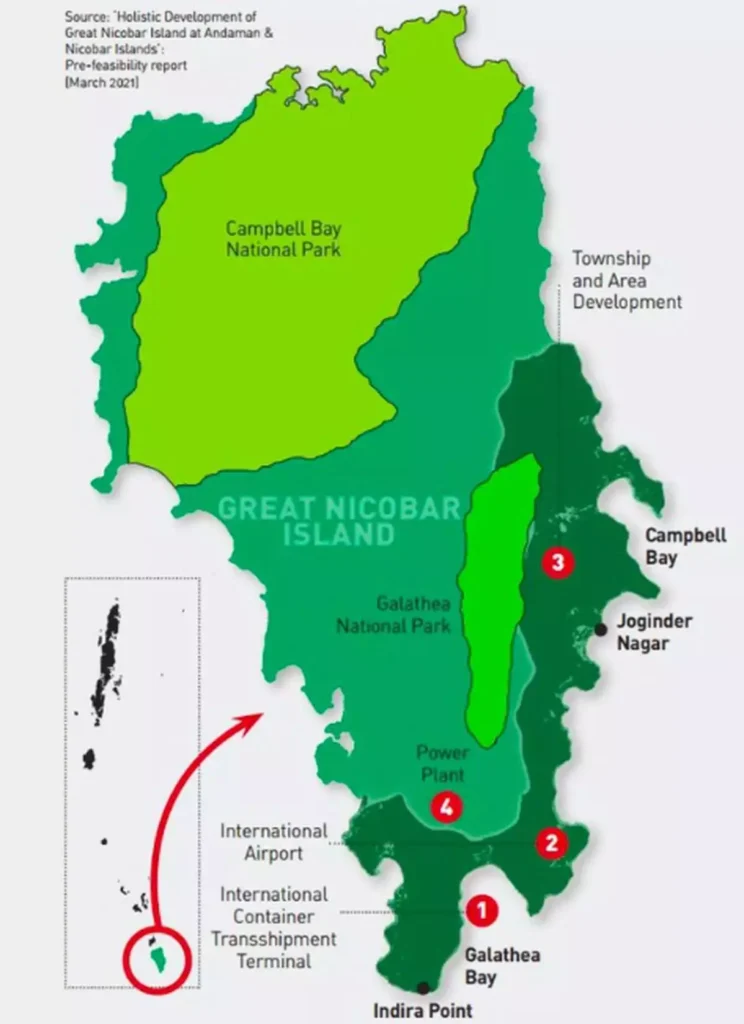
The Indian government has officially notified the Galathea Bay port in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands as a “Major Port.”
Key Highlights:
- This significant move is part of a Rs 44,000 crore project aimed at developing an International Container Transshipment Port (ICTP).
- This port will operate under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways and will receive central funding through a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- Once completed, this port is expected to capture a large share of transhipment cargo that currently goes through foreign ports like Colombo and Singapore.
- Phase 1 of the project is expected to be completed by 2028 with a capacity of 4 million TEUs, eventually growing to 16 million TEUs by 2058.
About Galathea Bay:
- Galathea Bay is located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and has been identified as the location for India’s next International Container Transshipment Port (ICTP).
- This strategic location places the port on a vital international shipping route, near the Malacca Strait, one of the world’s most critical choke points for global trade.
- The port’s proximity to the East-West shipping route will connect Europe, Africa, and Asia.
- The project is of both economic and strategic importance to India.
- It is expected to significantly increase economic activity at Indian ports and reduce the need for Indian transshipped cargo to be handled by foreign ports.
Importance of ICTP
- The International Container Transshipment Port (ICTP) is crucial for India’s foreign trade (EXIM trade).
- Currently, 75% of India’s transshipped cargo is handled at ports outside the country, such as Colombo, Singapore, and Klang. Developing the ICTP at Galathea Bay will help retain cargo handling within India, leading to foreign exchange savings and an increase in foreign direct investment.
- Additionally, it will enhance the overall efficiency of India’s shipping industry by offering quicker turnaround times and boosting economic activity across other Indian ports.
- Strategically, the port’s location near the Malacca Strait adds a security dimension, ensuring India’s control over a critical maritime route connecting the world’s largest continents.
Ports in India
- India boasts a total of 12 Major Ports and around 200 Non-Major Ports. The Major Ports are regulated under the Major Ports Authority Act, 2021, and fall under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways.
- The Non-Major Ports are regulated by State Maritime Boards and operate under state government regulations.
- Out of these non-major ports, 65 handle cargo, while others are used for activities like fishing and small ferry operations.
- In the future, India plans to develop three Mega Ports, including Vadhavan, Paradip, and Deendayal ports, all of which will have a capacity exceeding 300 million tonnes per annum (MTPA).
- Under the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047, four-port clusters with a capacity of more than 300 MTPA and two with more than 500 MTPA will be developed to boost India’s maritime infrastructure.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
Where is Galathea Bay located?
Galathea Bay is located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India.
What is a transshipment port?
A transshipment port is a facility where cargo is transferred from one vessel to another, often serving as a hub for international trade routes.
Why is the Malacca Strait strategically important?
The Malacca Strait is a crucial choke point in global shipping, connecting the Indian Ocean with the Pacific and serving as a key route for international trade.
What is the Major Ports Authority Act, 2021?
The Major Ports Authority Act, 2021 regulates India’s Major Ports, giving them greater autonomy and flexibility to enhance efficiency and competitiveness.
What is the Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047?
Maritime Amrit Kaal Vision 2047 is India’s long-term plan to develop port infrastructure, increase capacity, and enhance the country’s maritime trade capabilities by 2047.