Indian Immunologicals Limited (IIL) has recently introduced Havisure, India’s first indigenous Hepatitis A vaccine for paediatric use.
About Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis A is a highly contagious liver infection caused by the Hepatitis A virus.
- It primarily affects children and can lead to severe health complications.
- Transmission: The virus spreads primarily through the faecal-oral route, typically by ingesting contaminated food or water.
- Common Sources: Unsafe water, contaminated food, poor sanitation, inadequate hygiene, etc.
Geographical Distribution
- High-Income Countries: Lower infection rates due to good sanitation and hygiene. Outbreaks may occur in high-risk groups (e.g., drug users, men who have sex with men, travelers to endemic areas).
- Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Higher infection rates, especially among children, often without noticeable symptoms due to poor sanitary conditions.
Common Symptoms:
- Fever, malaise, loss of appetite, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal discomfort.
- Dark-colored urine and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
Treatment:
- Specific Treatment: No specific antiviral treatment for Hepatitis A.
- Vaccination is the most cost-effective method to prevent Hepatitis A.
About Hepatitis:
- Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by various infectious viruses and non-infectious agents.
- This condition can lead to severe health problems and, in some cases, be fatal.
Impact of Hepatitis:
- Types B and C are major causes of liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and hepatitis-related deaths.
- Vaccines: Currently, there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C.
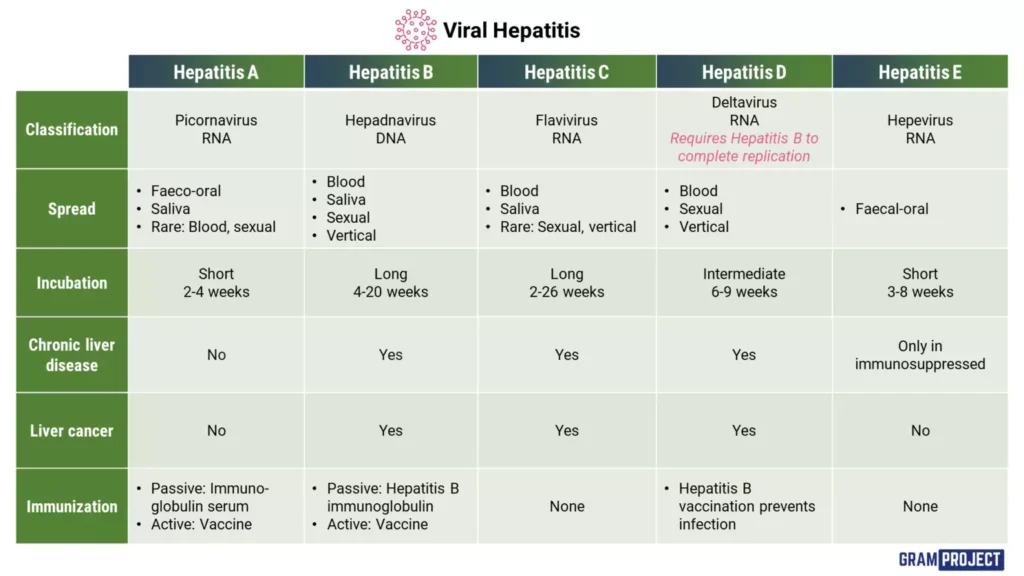
Types: Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E.
- Type A: Typically transmitted through contaminated food and water.
- Type B: Spread through contact with infectious body fluids, can lead to chronic disease.
- Type C: Transmitted mainly through blood-to-blood contact, often leads to chronic infection and liver cirrhosis.
- Type D: Occurs only in those infected with hepatitis B, exacerbates the severity of hepatitis B.
- Type E: Usually transmitted through contaminated water, often affects travellers.
Global Prevention and Control Efforts:
- WHO Global Hepatitis Strategy: Endorsed by all WHO Member States, this strategy aims to:
- Reduce New Infections: Target a 90% reduction in new hepatitis infections between 2016 and 2030.
- Decrease Deaths: Aim for a 65% reduction in hepatitis-related deaths by 2030.
National Initiatives:
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program 2019 aims to eliminate Hepatitis C by 2030, reduce Hepatitis B and C infections, and manage Hepatitis A and E.
- Mission Indradhanush provides vaccination against Hepatitis B along with seven other infections.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
What is Havisure?
Havisure is India’s first indigenous Hepatitis A vaccine developed by Indian Immunologicals Limited for pediatric use.
How is Hepatitis A transmitted?
Hepatitis A is primarily spread through the fecal-oral route, often via contaminated food or water.
What are the common symptoms of Hepatitis A?
Common symptoms include fever, loss of appetite, nausea, dark-colored urine, and jaundice.
Why is vaccination important for Hepatitis A?
Vaccination is the most cost-effective way to prevent Hepatitis A, as there is no specific antiviral treatment for the disease.
How does Hepatitis A affect high- and low-income countries differently?
High-income countries have lower infection rates due to better sanitation, while low- and middle-income countries experience higher rates, especially among children.