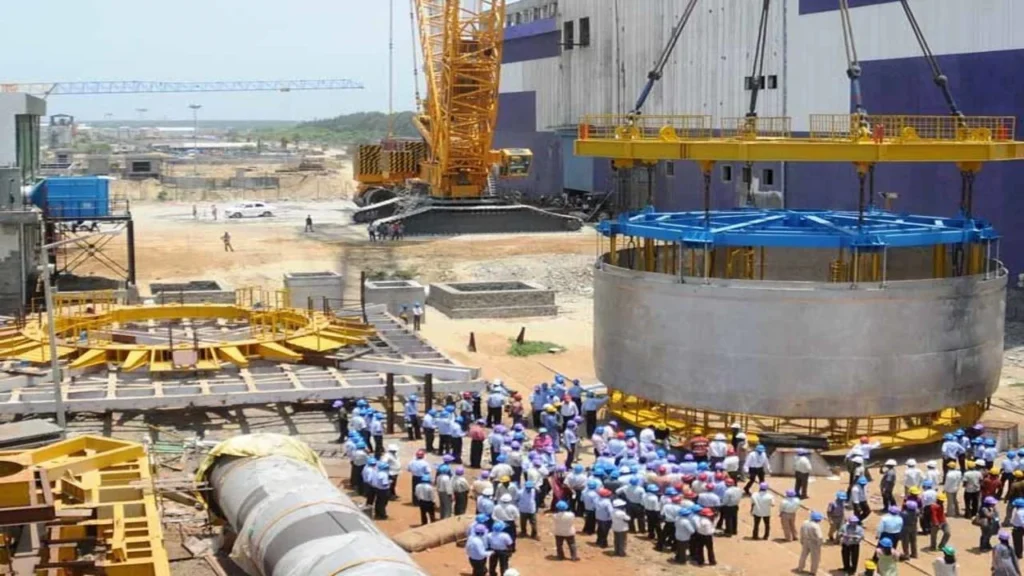
The Core Loading of India’s first indigenous Fast Breeder Reactor was commenced recently at Madras Atomic Power Station in Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu.
What is Prototype fast breeder reactor (PFBR)?
- The PFBR is a machine that produces more nuclear fuel than it consumes.
- The operationalization of the PFBR will mark the start of stage II of India’s nuclear powerprogram.
- This three-stage programme was designed by Dr. Homi J. Bhabha based on power needs and huge thorium reserves in India.
Stages of India’s Nuclear program:
- India used pressurized heavy water reactors (PHWRs) and natural uranium-238 (U-238), which contain minuscule amounts of U-235, as the fissile material.
- The heavy water in PHWR are water molecules containing the deuterium isotope of hydrogen, slows neutrons released by one fission reaction.
- It can be captured by other U-238 and U-235 nuclei and cause new fission.
- The heavy water is pressurized to keep it from boiling and produces plutonium-239 (Pu-239) and energy.
- Only U-235 can sustain a chain reaction but it is consumed fully in stage I.
- In stage II, India will use Pu-239 together with U-238 in the PFBR to produce energy, U-233, and more Pu-239.
- The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) set up a special-purpose vehicle in 2003 called Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam, Ltd. (BHAVINI) to implement stage II.
- In stage III, Pu-239 will be combined with thorium-232 (Th-232) in reactors to produce energy and U-233.
- The three stages are expected to allow the country complete self-sufficiency in nuclear energy.
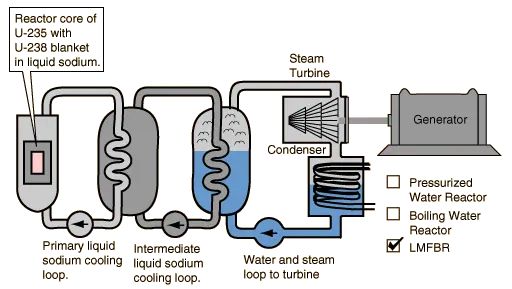
Prototype Fast Breeder Reactors:
- Fast breeder reactors employ fast neutrons that do not slow down, allowing them to efficiently trigger specific fission reactions.
- The PFBR, a fast breeder reactor, is designed to produce more Pu-239 than it consumes, thereby breeding additional fissile material for sustained energy production.
- The PFBR utilizes liquid sodium, a highly reactive substance, as a coolant in two separate circuits.
- In the primary circuit, sodium coolant enters the reactor core, absorbs heat and radioactivity, and exits to transfer heat to the secondary circuit.
- Heat is transferred to generators in the secondary circuit to produce electricity, while the liquid sodium is recirculated back to the primary circuit.
Challenges and Realities:
- Despite theoretical calculations and mock-up tests, the PFBR has faced challenges in its operationalization.
- Issues such as delayed preheating of the reactor vessel, underscore the complexities involved in translating theoretical designs into practical realities.
- Overcoming such challenges requires rigorous testing, continued research, and adaptive engineering to ensure the safe and efficient operation of breeder reactors.
- Breeder reactors hold promise for enhancing nuclear energy sustainability by utilizing abundant nuclear fuel resources more efficiently.
- Continued advancements in breeder reactor technology, and proactive problem-solving, can counter global energy needs.
About Kalpakkam Power station:
- Kalpakkam is known for its nuclear plants and affiliated research installations.
- These include the Madras Atomic Power Station (MAPS), a nuclear power plant, the Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR), and the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
- It is a comprehensive nuclear power production, fuel reprocessing, and waste treatment facility that includes plutonium fuel fabrication for fast breeder reactors (FBRs).
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |