Kármán line is a significant boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space, has gained importance in the recent times due to modernisation of space based weapons and satellite-based communications.
About the Kármán line:
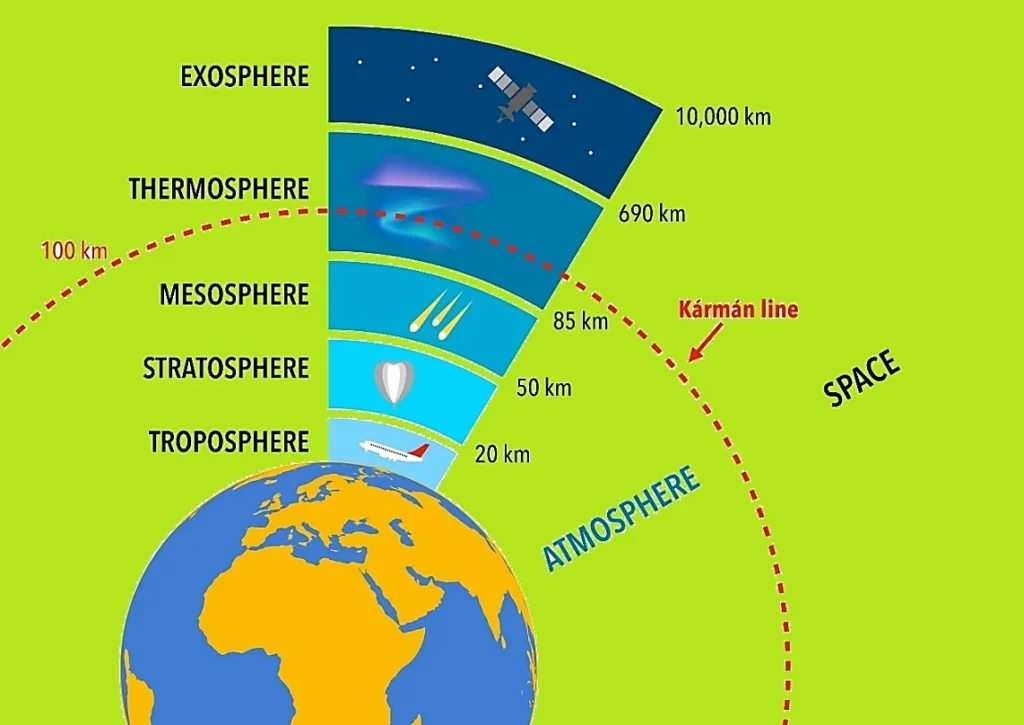
- The Kármán line is the theoretical boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space.
- It was established by Fédération aéronautique internationale (FAI).
- It is named after Theodore von Kármán, a Hungarian-American physicist and aerospace engineer who played a key role in the development of modern aerodynamics and astronautics.
- There is no specific national demarcation of the Kármán line, similar to international waters.
- It serves as a reference point for aerospace engineering and space-related activities.
- Beyond this boundary, conventional aircraft face challenges in terms of effective operation due to the diminishing atmospheric density.
- The Kármán line itself has no distinct physical characteristics.
- It is recognized at an altitude of 100 kilometers above mean sea level.
- This altitude is considered the point where the Earth’s atmosphere becomes too thin to support conventional aircraft, as they would require orbital velocity to generate lift.
Significance:
- It holds immense significance in the context of space defense and national security.
- It serves as a valuable reference to delineate Earth’s atmospheric limits.
- It influences jurisdiction and legislation applicable to aircraft and spacecraft.
- Reaching this altitude is considered a significant milestone for suborbital and orbital flights, as individuals who cross the Kármán line are often recognized as having entered space.
Why control over Kármán line possesses dangers?
- Anti-Satellite (ASAT) Weapons: Adversary control over Kármán line enables a nation to deploy satellites in Kármán line against enemy nations, who can disrupt or destruct critical communication links.
- Jamming and Interference: There is a potential for communication blackouts or degraded performance if ground or space-based systems disrupt satellite communications.
- Hacking and Cyber-attacks: Unauthorized access to satellites, can lead to data breaches or operational takeover.
- Physical Interception or Tampering: Adversaries can attempt to alter satellite orbits or damage critical components of a nation deployed on Kármán line.
- Space Debris and Kinetic Kill Vehicles: It deliberates creation of debris or deployment of kinetic kill vehicles near the Kármán line.
- Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP) Weapons: EMP can be used to disrupt or damage satellite electronics, potentially rendering them inoperable.
- Denial of Access to Space: Adversarial control over Kármán line restricts access for certain entities such as limiting the deployment, maintenance, or replacement of satellites.
- Spoofing and Deception: Satellite communication signals can be manipulated to mislead ground stations.
Historical Context of Kármán line:
- V-2 ballistic missile, developed by Nazi scientists, had breached Kármán line on June 20, 1944.
- It was a retaliation weapon used during World War II.
- By the 1960s, the U.S. and Soviet Union had established routine satellite deployments to dominate this imaginary line, Kármán line.
- Consequently, both superpowers initiated the development of anti-satellite weapons to destroy adversary satellites such as directed-energy weapons, kamikaze-style satellites, and orbital nuclear explosives.
- Later on, the Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBM) was created, which is capable of striking virtually any target on Earth within minutes.
India’s Space Defense Initiatives:
- India has developed robust launch capabilities and military satellites.
- RISAT (Radar Imaging Satellite) is a series of Indian radar imaging reconnaissance satellites, built by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), to provide information on situationalawareness, and communicationsatellites for coordination.
- It was initially designed in response to terrorist threats post the 2008 Mumbai attack.
- The Integrated Space Cell was established in 2010 to foster coordination between the Department of Space and the Indian Armed Forces and reduce any space-based threats.
- The Defence Space Agency was created in 2018 which is a tri-service agency of the Indian Armed Forces tasked with operating the space-warfare and Satellite Intelligence assets of India.
- It has a potential precursor to become a full-fledged aerospace command.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |