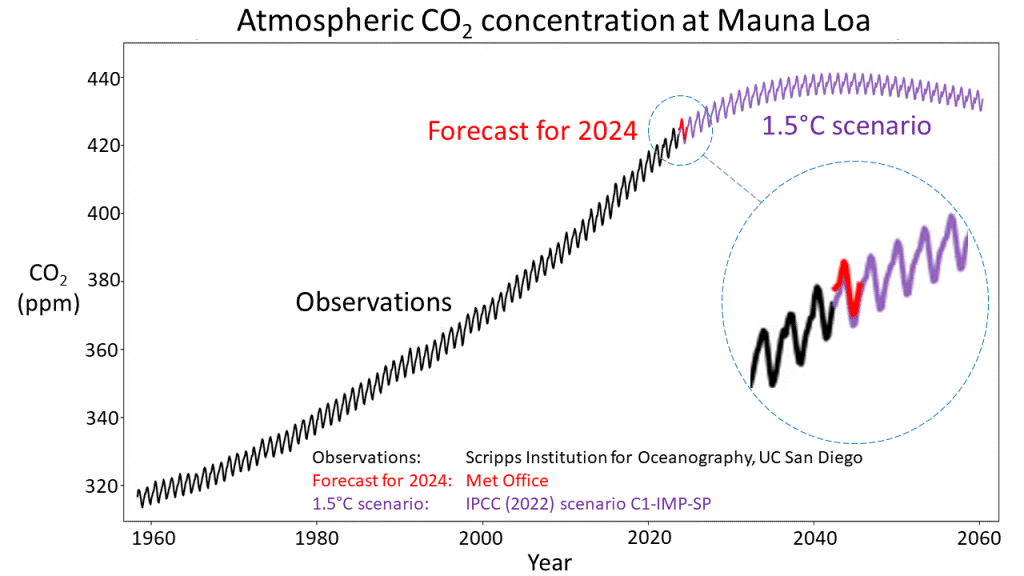
March 2024 saw a significant jump in the Keeling Curve with a global average carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration of 4.7 parts per million (ppm), greater than March 2023.

About Keeling Curve:
- The Keeling Curve is a graph that shows the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in Earth’s atmosphere since 1958, created by Dr. Charles David Keeling.
- Measurements are taken at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii.
Key Findings
- The Keeling Curve reveals both seasonal and long-term increases in atmospheric CO2.
- Seasonal variations show higher CO2 levels in spring and lower in autumn due to plant photosynthesis and respiration cycles.
- Long-term data indicates a consistent rise in CO2 levels, attributed to fossil fuel combustion.
Significance
- It provides the longest uninterrupted record of atmospheric CO2 levels, crucial for understanding climate change.
- The data shows a clear upward trend, illustrating the impact of human activities on global CO2 levels.
- The curve is instrumental in climate science, offering evidence for the greenhouse effect and informing climate models.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |