North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was established in 1949. Its aim was countering Soviet expansion in post-World War II Europe. NATO’s roots can be stretched back to the Treaty of Dunkirk. The Treaty of Dunkirk was signed by the United Kingdom and France in 1947. NATO serves as a political and military alliance. It is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) will be helpful for UPSC IAS Exam preparation. GS Paper-2 International Relations.
Table of Content
- What is North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)?
- Why NATO was formed?
- Members of NATO
- Purpose of NATO
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)?
- The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was established in 1949.
- Aim: to serve as a deterrent against Soviet expansion in post-World War II Europe.
- The roots of NATO can be traced back to the Treaty of Dunkirk in 1947.
- Treaty of Dunkirk was signed by the United Kingdom and France to counter the potential threat of a German attack.
- 12 founding members: United States, United Kingdom, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, and Portugal.
- Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium.
- Headquarters of Allied Command Operations: Mons, Belgium.
- NATO’s protection does not extend to members’ civil wars or internal coups.
- Funds: It is funded by its members.
- United States contributes roughly three-fourths of NATO’s budget.
Article 4 of the NATO Charter (Washington Treaty)
- NATO’s Article 4 allows member countries to raise concerns, particularly regarding the security of any member nation, for discussion within the North Atlantic Council.
- Throughout NATO’s existence since 1949, there have been seven instances where Article 4 has been invoked.
Article 5 of the NATO Charter (Washington Treaty)
- Article 5 of the NATO charter is about the collective defence clause.
- It is at the very heart of NATO’s founding treaty.
- Collective defence means that an attack against one Ally is considered as an attack against all Allies.
- Article 5 has been only invoked once by the United States, in the wake of the 9/11 attacks in 2001.
Why NATO was formed?
- After World War II, western Europe faced economic exhaustion and military weakness.
- In contrast, the Soviet Union emerged from the war as the dominant force in central and eastern Europe.
- The term “Iron Curtain” was used to describe the division between Western and Eastern Europe.
- Cooperation between the Western Allies and the Soviets broke down, leading to the division of Germany into democratic and communist states.
- The United States launched the Marshall Plan in 1948, it providing economic aid to Western and Southern European countries on the condition of cooperation and joint planning.
- The Western European Union was formed under the Brussels Treaty.
- The union aimed to ensure collective defence among the United Kingdom, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg.
- Recognizing the need for a stronger alliance, Britain, Canada, and the United States engaged in secret talks on security arrangements as an alternative to the United Nations.
- In March 1948, discussions began on a multilateral collective-defence scheme.
- These discussions were eventually joined by France, the Low Countries, and Norway and in April 1949 resulted in the North Atlantic Treaty.
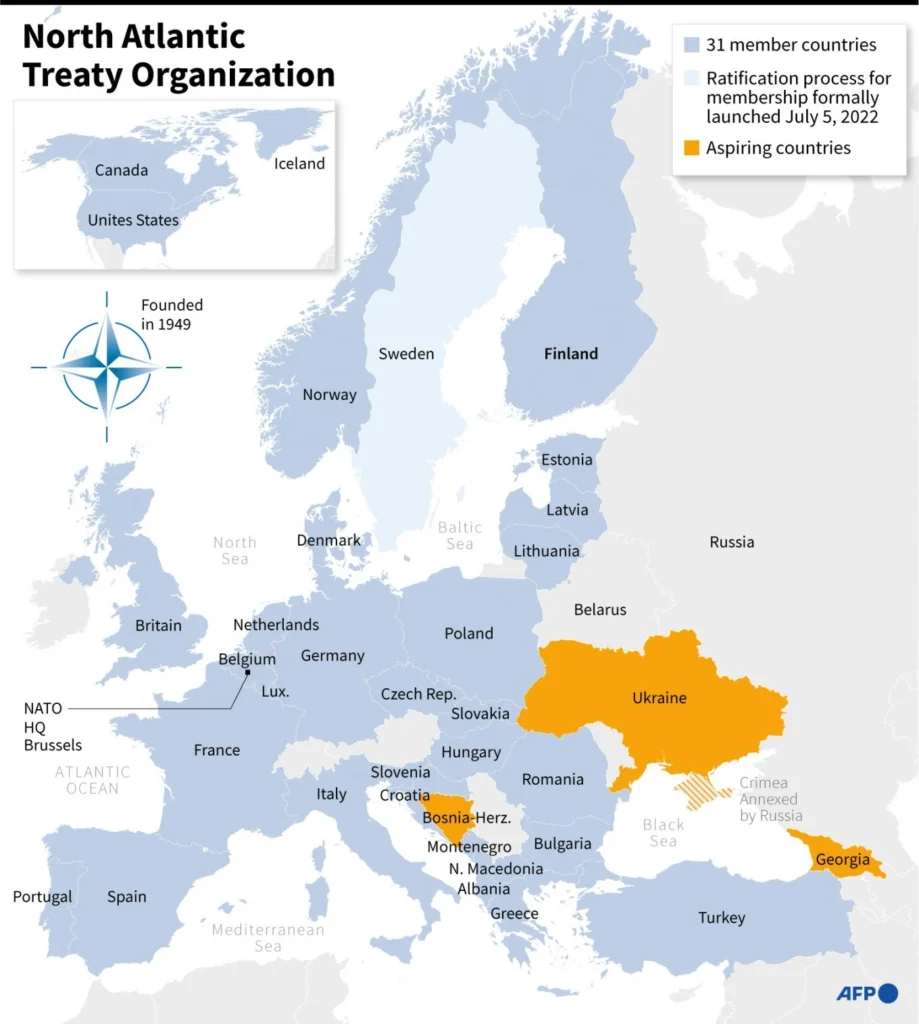
Members of NATO
- Currently, NATO has 31 member countries with Finland as its newest member. It became a part of NATO in 2023.
| NATO Member Countries | ||
| BELGIUM (1949) | UNITED STATES (1949) | LITHUANIA (2004) |
| CANADA (1949) | GREECE (1952) | ROMANIA (2004) |
| DENMARK (1949) | TÜRKIYE (1952) | SLOVAKIA (2004) |
| FRANCE (1949) | GERMANY (1955) | SLOVENIA (2004) |
| ICELAND (1949) | SPAIN (1982) | ALBANIA (2009) |
| ITALY (1949) | CZECHIA (1999) | CROATIA (2009) |
| LUXEMBOURG (1949) | HUNGARY (1999) | MONTENEGRO (2017) |
| NETHERLANDS (1949) | POLAND (1999) | NORTH MACEDONIA (2020) |
| NORWAY (1949) | BULGARIA (2004) | FINLAND (2023) |
| PORTUGAL (1949) | ESTONIA (2004) | |
| UNITED KINGDOM (1949) | LATVIA (2004) | |
Purpose of NATO
Political:
- NATO’s primary goal is to uphold democratic values and foster collaboration among member states in addressing defence and security challenges.
- This approach aims to resolve issues, foster trust, and ultimately prevent conflicts.
Military:
- NATO is dedicated to resolving disputes through peaceful means.
- However, if diplomatic efforts prove unsuccessful, NATO possesses the military capability to undertake crisis-management operations.
- These operations are conducted by the collective defence provision outlined in NATO’s founding treaty, known as Article 5 of the Washington Treaty.
- Additionally, NATO may engage in operations under a United Nations mandate.
- It can engage either independently or in collaboration with other nations and international organizations.
Conclusion
Article 4 of the NATO Charter enables member countries to discuss security concerns within the North Atlantic Council. It has been invoked seven times since NATO’s inception. Article 5 of the NATO Charter is about the collective defence clause. The clause states that an attack on one member will be considered an attack on all. It was invoked once following the 9/11 attacks in 2001. NATO’s primary purpose is to promote democratic values, facilitate collaboration on defence and security, and engage in crisis-management operations when diplomatic efforts fail.
Ref: Source-1
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a full form of NATO?
NATO stands for North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
When was NATO formed?
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was formed in the year 1949.
How many countries are there in NATO?
As of June 2023, there are total 31 member countries in NATO.
Is India part of NATO?
No, India is not a member of NATO.
How many official languages does NATO have?
NATO has two official languages: French and English.
What is NATO Plus?
NATO Plusis a grouping of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and five countries. It includes Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Israel, and South Korea. It works toward boosting global defence cooperation.