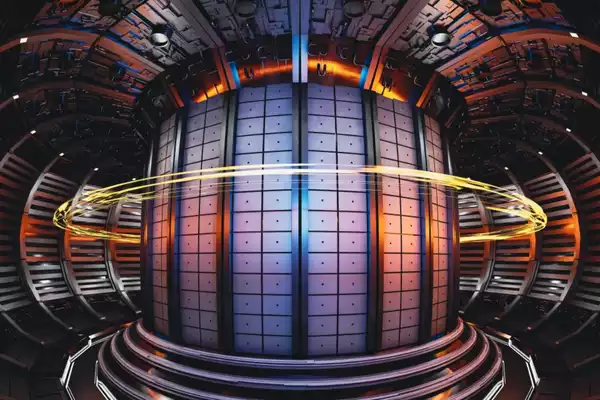
Nuclear Fusion researchers have set a new record in producing more power using the technology than ever before.
About Joint European Torus (JET):
- It is a large tokamak that was the first device to produce controlled fusion power with deuterium and tritium situated in the United Kingdom.
- A tokamak is a machine that confines a plasma using magnetic fields in a doughnut shape.
What is Nuclear fusion?
- It is a reaction that occurs when two or more atomic nuclei combine to form one or more different atomic nuclei.
- It is the opposite of nuclear fission, where heavy elements diffuse and form lighter elements.
- It occurs in elements that have a low atomic number, such as hydrogen.
- It is the process by which the sun and the stars get their powers.
- In this reaction, two atoms of hydrogen combine to form an atom of helium.
- Some of the mass of the hydrogen is converted into energy.
- Nuclear fusion releases an enormous amount of energy, much greater than the energy released during the nuclear fission reaction.
Some types of nuclear fusion include:
- Magnetic-Confinement Fusion (MCF)
- Inertial-Confinement Fusion (ICF)
- Magnetized Target Fusion (MTF)
- Field-Reversed Configuration (FRC)
- Stellarator
Advantages of Nuclear Fusion:
- Abundant Fuel Supply: Fusion uses isotopes of hydrogen, which are abundant and widely available, ensuring a long-term and sustainable fuel supply.
- Minimal Radioactive Waste: Fusion produces minimal long-lived radioactive waste compared to fission, reducing environmental and safety concerns.
- Inherent Safety: Fusion reactions are inherently safer than fission reactions, as they cannot undergo a runaway chain reaction and have no risk of meltdown.
- High Energy Density: Fusion has the potential to provide a high energy density, making it a compact and efficient source of power.
- No Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Fusion does not produce greenhouse gas emissions during its operation, contributing to a cleaner and environmentally friendly energy source.
Challenges of Nuclear Fusion:
- Technical Complexity: Achieving controlled nuclear fusion requires overcoming immense technical challenges, such as maintaining high temperatures and pressures for an extended period.
- Energy Input vs Output: The energy required to initiate and sustain fusion reactions often exceeds the energy produced, making it difficult to achieve a net positive energy gain.
- Material Constraints: The harsh conditions inside a fusion reactor can damage and degrade materials over time, requiring constant research into materials that can withstand the extreme environment.
- Tritium Supply: Tritium, an essential fuel for fusion, is not naturally abundant and poses challenges in terms of production, handling, and containment.
- Safety Concerns: While fusion is considered safer than fission, potential risks still exist, including radioactive waste and the possibility of accidents or system failures.
Nuclear Fission vs Nuclear Fusion:
| Feature | Nuclear Fission | Nuclear Fusion |
| Process | The nucleus of an atom splits | Nuclei of two atoms combine |
| Energy Release | Releases energy | Releases a larger amount of energy |
| Reaction Type | Chain reaction | Not chain reaction |
| Fuel | Usually heavy elements like uranium or plutonium | Light elements like hydrogen isotopes (deuterium and tritium) |
| Reaction Control | Can be controlled | Difficult to control |
| Reaction in Stars | Not the primary process in stars | Primary process in stars (including the sun) |
| Radioactive Waste | Produces radioactive waste | Generates less radioactive waste |
| Temperature Required | Operates at lower temperatures | Requires extremely high temperatures (millions of degrees Celsius) |
| Advantages | Established technology with power generation capabilities | Potential for clean and abundant energy, no greenhouse gas production |
| Disadvantages | Radioactive waste and safety concerns | Technologically challenging and currently not commercially viable |
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |