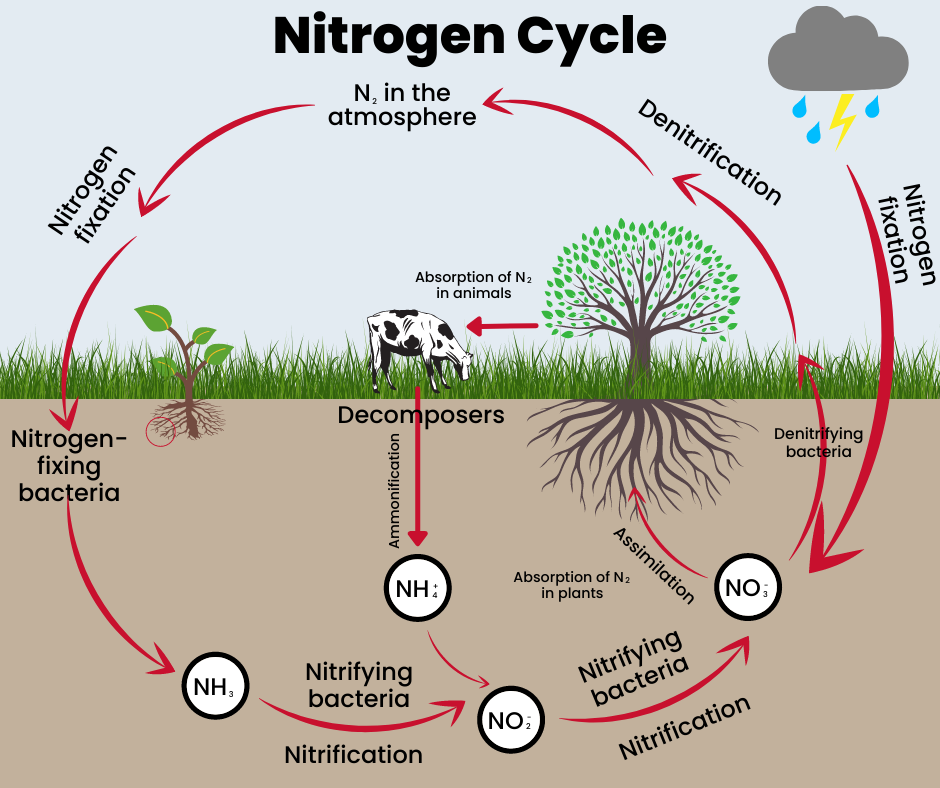
Nitrogen cycle is a crucial biogeochemical process that involves the transformation of nitrogen into different forms as it circulates through the Earth’s ecosystems, including the atmosphere, land, and oceans.
Nitrogen Cycle will be helpful for UPSC IAS Exam preparation. GS Paper-3 Environment.
Table of Content
- What is Nitrogen Cycle?
- Steps of Nitrogen Cycle
- Impact of human activities on the nitrogen cycle
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Nitrogen Cycle?
- Definition: The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into various chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems.
- Nitrogen in the atmosphere: Nitrogen is the largest component of the atmosphere, making up about 78% of the air.
- Nitrogen in organic compounds: Organic compounds often contain nitrogen, which plays a crucial role in the composition of essential substances like proteins, nucleic acids, and vitamins.
Refer to the linked articles to know about Phosphorus Cycle and Carbon Cycle.
Steps of Nitrogen Cycle
Steps of Nitrogen cycle process:
Nitrogen fixation:
- Nitrogen fixation is the natural process through which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is transformed into ammonia (NH3).
- This process is carried out by a variety of organisms, including bacteria, archaea, and lightning.
Nitrification:
- Nitrification is the process by which ammonia is converted into nitrites (NO2-) and then nitrates (NO3-).
- Nitrification is carried out by bacteria in the soil.
Assimilation:
- Assimilation is the process by which plants take up nitrates from the soil and use them to make proteins.
Denitrification:
- Denitrification is the process by which nitrates are converted back into nitrogen gas (N2).
- Denitrification is carried out by bacteria in anaerobic environments, such as wetlands and the bottom of the ocean.
Nitrogen deposition:
- Nitrogen deposition is the process by which nitrogen is returned to the atmosphere.
- Nitrogen deposition can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including volatilization, denitrification, and plant respiration.
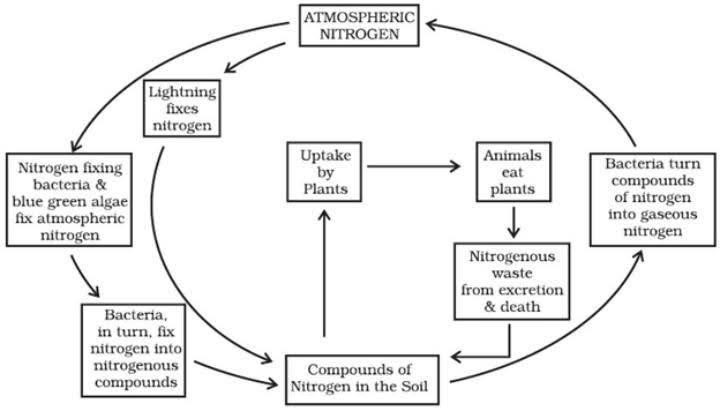
Impact of human activities on the nitrogen cycle
Increased use of nitrogen fertilizers:
- The use of nitrogen fertilizers in agriculture has increased dramatically in recent decades.
- As a result, there has been a rise in the nitrogen levels within the environment, leading to various adverse effects including water pollution and the occurrence of algal blooms.
Deforestation:
- Deforestation can also harm the nitrogen cycle.
- Trees play an important role in the nitrogen cycle by fixing nitrogen from the atmosphere.
- When trees are cut down, this process is disrupted, which can decrease the amount of nitrogen available to plants and animals.
Burning fossil fuels:
- Burning fossil fuels releases nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere.
- These gases can react with other pollutants to form smog, which can cause respiratory problems and other health problems.
Livestock production:
- Livestock production also contributes to the nitrogen cycle.
- Animals produce nitrogenous waste, which can contaminate water supplies and contribute to algal blooms.
Conclusion
Nitrogen cycle maintains the balance of nitrogen in the environment. However, the human impact on nitrogen cycle through the use of fertilizers, deforestation, burning of fossil fuels, and livestock production has disrupted this cycle. It is important to atop the disruption of this cycle otherwise it will cause environmental issues such as water pollution, algal blooms, and air pollution
What is the main difference between the carbon and nitrogen cycle?
The main difference between the carbon and nitrogen cycle is that the carbon cycle is involved in the recycling of carbon whereas the nitrogen cycle is involved in the recycling of nitrogen. Both cycles start and end with gases.