A recent study has discovered that anti-nephrin autoantibodies serve as a biomarker to monitor progression in kidney disorders with nephrotic syndrome.
About Nephrotic syndrome:
- Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by high levels of protein in the urine and is linked to kidney disorders including membranous nephropathy (MN), primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), and minimal change disease (MCD).
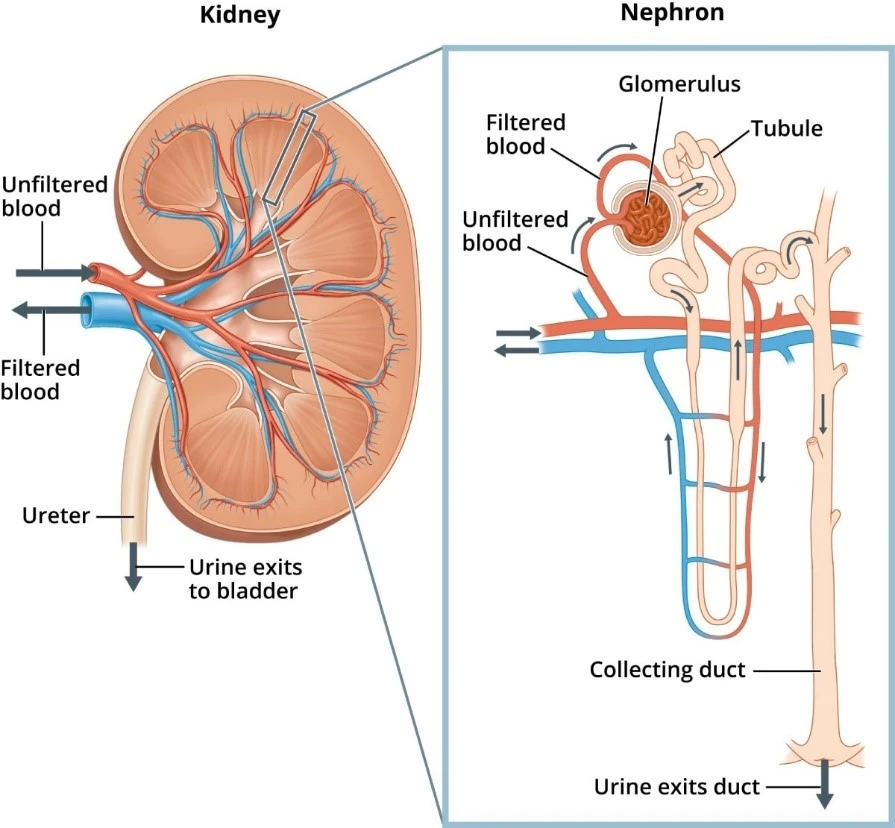
- The condition primarily results from damage to podocytes, the kidney’s filtering cells, leading to protein leakage into the urine.
- In children, idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) is often diagnosed due to unknown causes and the infrequent use of kidney biopsies.
Challenges in Diagnosis:
- Diagnosing nephrotic syndrome-related conditions is challenging due to overlapping histological features and hesitancy to perform invasive kidney biopsies, especially in children.
- Anti-nephrin autoantibodies have been found in some patients with MCD and FSGS, but their role in disease progression was unclear.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |