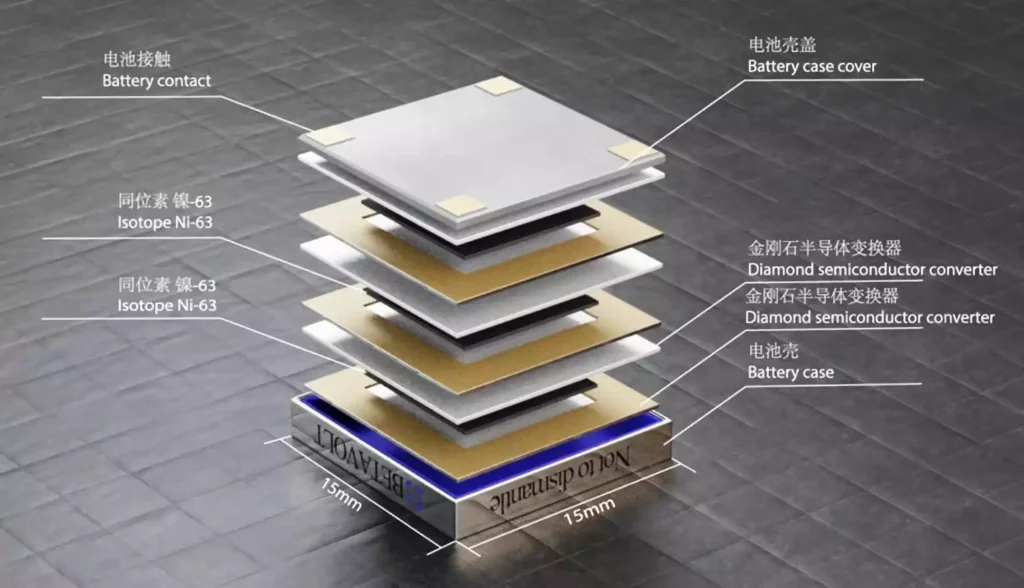
China has recently created a nuclear-powered BV100 battery that has a long lifespan and robust performance.
About the Nuclear-powered BV100:
- The Nuclear-powered BV100 has a 50-year lifespan that does not require recharge.
- It can operate safely under extreme temperatures and are resistant to physical damage.
- It is classified as betavoltaic.
- Betavoltaic battery is a form of nuclear technology that utilizes the decay energy of β-emitting radioisotopes to produce electrical power.
- It generates an electric current directly from beta particles (electrons), using semiconductor junctions, emitted from a radioactive source.
Features:
- It harnesses energy from nuclear decay of nuclear isotopes, specifically from nickel-63.
- It employs a unique single-crystal diamond semiconductor for energy conversion.
- It can achieve an 8.8% energy conversion efficiency.
- It is based on isotope technology first proposed in 1913.
Working mechanism:
- Unlike nuclear fission or fusion, nuclear decay is a spontaneous process in which isotopes emit radiation, leading to more stable new atoms.
- Scientists encapsulate these isotopes, and converts the energy emitted into usable electrical power.
- The BV100 uses a modular structure, as it sandwiches a nickel-63 layer between 2 thick diamond semiconductors, forming a power-generating unit.
- The beta particles released during the decay of nickel-63 are irradiated on the diamond semiconductor to form an electric field and achieve electrical energy output when connected to the circuit.
Benefits and Applications:
- It is designed to be safe and stable, posing minimal pollution threat.
- Integrating multi-stage batteries often leads to efficiency losses, and hence utilisation of Nuclear-powered BV100 can be beneficial.
- It has potential to power devices like smartphones and drones indefinitely.
- It can be used in continuous operation of military drones and deep-sea monitoring devices.
- It can also be used in submarine navigation beacons, heart pacemakers, among others.
Challenges:
- There are concerns like nuclear safety, radiation protection, and efficiency losses.
- It will increase dependency on imported isotopes for manufacturing.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |