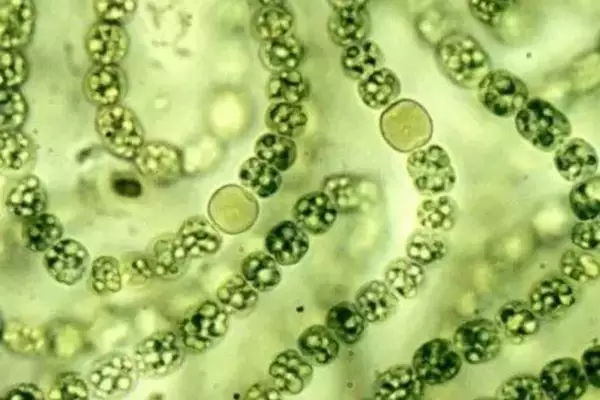
Prokaryotes are proving to be remarkably resilient to climate change and may dominate marine environments.
About Prokaryotes:
- Prokaryotes are microscopic, single-celled organisms, including bacteria and blue-green algae.
- They lack a defined nuclear region and membrane-bound organelles.
- Prokaryotic cells have a single chromosome.
- Functions typically performed by organelles in eukaryotic cells are carried out by poorly organized parts of the cytoplasm in prokaryotes.
- In photosynthetic prokaryotes, chlorophyll is associated with membranous vesicles rather than plastids.
About Eukaryotes:
- Eukaryotes include plants, animals, and fungi.
- They possess a well-defined nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells can be unicellular or multicellular.
- These cells have multiple chromosomes.
- Plant cells differ from animal cells as they have cell walls, plastids, and a large central vacuole, which are absent in animal cells.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
What are prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms like bacteria that lack a defined nuclear region and membrane-bound organelles.
How are eukaryotes different from prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes have a well-defined nucleus, multiple chromosomes, and membrane-bound organelles, unlike prokaryotes.
What are the main characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are characterized by their lack of a defined nucleus, a single chromosome, and the absence of membrane-bound organelles.
What organisms are considered eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes include plants, animals, fungi, and some unicellular organisms, all of which have complex cell structures.