The report on short-selling by Hindenburg recently prompted the Supreme Court to instruct the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to use its investigative powers to determine if these actions constituted a legal violation and harmed investors.
What is Short-selling?
- Short selling, also known as “shorting,” “selling short,” or “going short,” involves the sale of a security or financial instrument that the seller has borrowed.
- The short seller anticipates that the borrowed security’s price will decrease, allowing them to repurchase it at a lower price and profit from the difference.
- The profit or loss for a short seller is determined by the difference between the price at which the security was sold and the price at which it was repurchased.
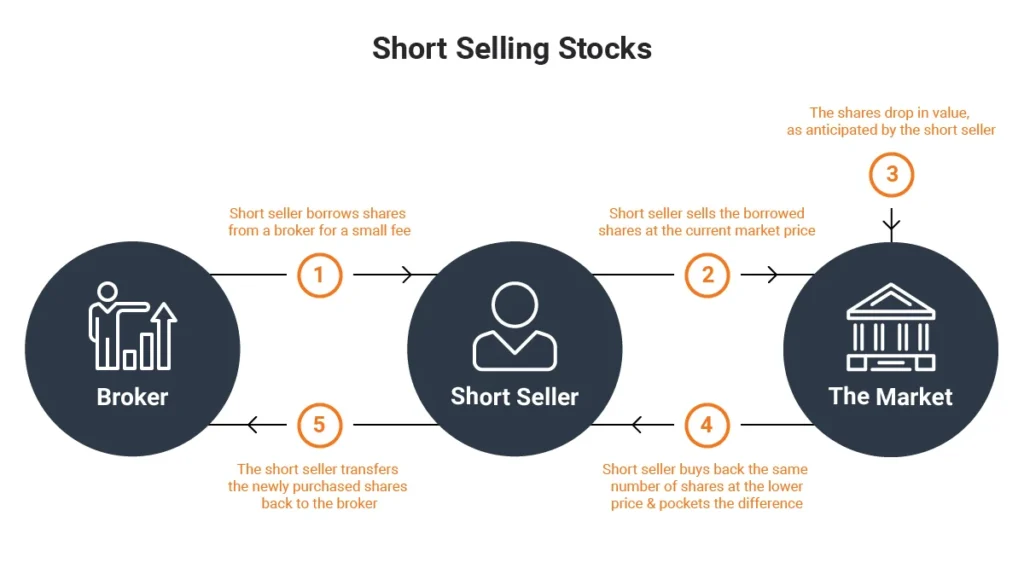
How short-selling works:
- Borrowing: The investor borrows a certain quantity of an asset (such as stocks) from a broker or another investor.
- The borrowed assets are typically sold in the market, generating cash for the investor.
- Selling: The investor sells the borrowed assets at the current market price.
- Waiting for Price Decline: The investor waits for the price of the borrowed assets to fall.
- Repurchasing (Covering): Once the price has dropped to a desired level, the investor buys back the same quantity of assets in the open market.
- Returning the Borrowed Assets: The investor returns the assets to the lender.
- Profit or Loss: The profit or loss is calculated based on the difference between the selling price and the repurchase price.
- If the repurchase price is lower than the selling price, the investor makes a profit.
- If it’s higher, the investor incurs a loss.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |