Soil Pollution occurs when substances that are added to the soil have a negative impact on its quality and fertility. In this article, you will get information of soul pollution, its definition, analysis, prevention, reasons, causes and effects of soil pollution, solution, examples, providing key insights for GS Paper-III Environment and ecology section of UPSC IAS Exam.
Table of Content
- What is pollution?
- What is soil pollution?
- Sources of soil pollution:
- Harmful effects of soil pollution
- Control measures of soil pollution
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Reference
What is pollution?
- Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that lead to adverse change in it.
- Types of pollution that exists in the environment are:
- Air pollution
- Noise pollution
- Water pollution
- Soil pollution
- Thermal pollution
- Radiation pollution
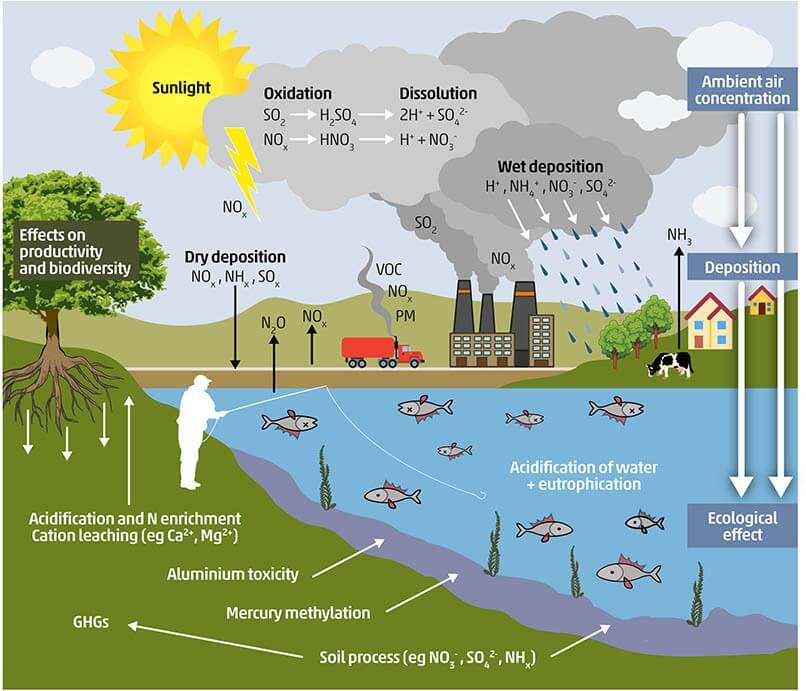
What is soil pollution?
- Soil pollution occurs when substances that are added to the soil have a negative impact on its quality and fertility through the accumulation of persistent toxic compounds, chemicals, salts, radioactive materials, or disease-causing agents in the soil.
- Soil is the thin layer of materials covering the Earth’s rocky surface, consists of both organic and inorganic components.
- Such substances may change the physical, chemical, and biological properties of the soil, leading to a reduction in its productivity.
- Types of Soil Pollution:
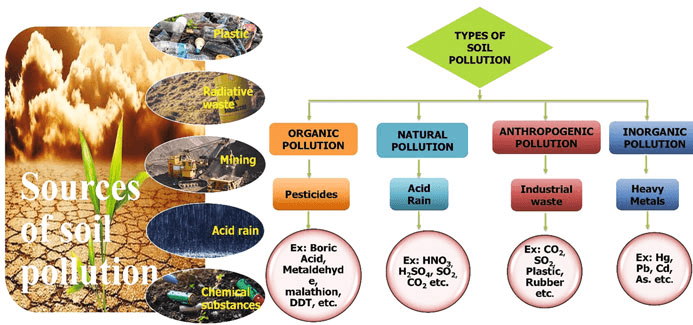
Sources of soil pollution:
- Chief source- Landfills and waste dumps: serve as dumping grounds for various types of hazardous wastes including municipal wastes, hospital wastes, and electronic wastes.
- Domestic Sources of Soil Pollution: wastes produced due to domestic activities such as food leftovers, peels of fruits and vegetables etc that are often dumped on the ground.
- These wastes alter the soil composition and make it bad for the growth and development of plants.
- Industrial Wastes: industrial wastes include chemicals such as Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs), mercury, lead, copper, zinc, cadmium, cynides, thiocynates, chromates, acids, alkalies, organic substances etc.
- It is mainly caused by the disposal of fly ash, dyes, acids, iron and steel slag.
- Mainly these chemicals are derived from sugar mills, pulp, e-Wastes, leather and rubber industries etc.
- Pesticides: Pesticides are chemicals that include insecticides, fungicides, algicides, rodenticides or weedicides sprayed to improve productivity of agriculture, forestry and horticulture.
- Fertilizers and manures: excessive use of chemical fertilizers reduces the population of soil borne organism and the structure of the soil, productivity of the soil and increasessalt content of the soil.
- Runofffrom such case can cause eutrophication, disrupting the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
- Irrigation practices: faulty irrigation practices cause water logging as water is evaporated in the sun leaving behind salts in the soil.
- Thus, soil gradually becomes saline and unfit for plant growth.
- Discarded materials: includes concrete, asphalt, rungs, leather, cans, plastics, glass, discarded food, paper and carcasses.
- Plastic bags mainly made from low–density polyethylene (LDPE) are a significant threat as they are indestructible in nature.
- Plastics are non-biodegradable, and when burned it releases highly toxic gases like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, phosgene, dioxin, and other chlorinated compounds.
- Radioactive wastes: Radioactive elements from mining and nuclear power plants, first enters water and then the soil.
- Mining operations particularly open-cast mining, contributes significantly to soil pollution as deforestation precedes mining activities which lead to the removal of topmostfertile soil and release of pollutants during transportation and processing.
- The extraction of minerals, such as iron ores, leads to soil pollution.
- Mining also pollutes water bodies with toxic metals and chemicals which is then percolated to the ground water.
- Tailings, slags, stones etc. that come out of mines are dumped in nearby areas causing further pollution.
- Pollutants: such as air pollutants (acid rain) and water pollutants thatbecome part of the soil.
- Weathering: the soil also receives some toxic chemicals during weathering of certain rocks aur due to municipal waste disposed through landfills.
- These wastes act as shelter of various types of insects and germs of diseases.
- Solid waste: generated from households, commercial establishments, and industries and consists of materials such as plastics, cloth, glass, metal, organic matter, sewage, sewage sludge, and building debris.
- Other reasons: deforestation, soil erosion and pollution due to urbanisation.
Open-cast mining:

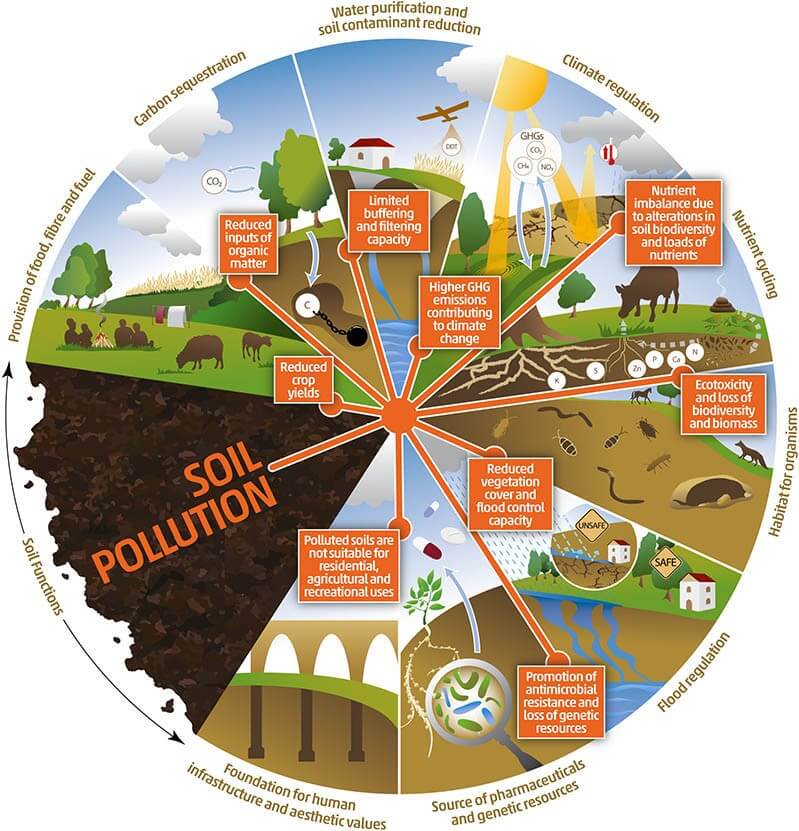
Harmful effects of soil pollution
- These substances adversely affect plant growth, health of humans and animals and biologicalbalance of organisms within the soil.
- Example: Pesticides cause respiratory problems, cancer, and even death to humans and animals.
- They can disrupt the natural balance of the soil’s organisms and have detrimental effects on its quality, texture, and mineral content.
- Agriculture: reduced soil fertility, crop yield, nitrogen fixation, increased erosion and salinity, loss of soil and nutrients, and deposition of silt in tanks and reservoirs.
- Health: when dangerous chemicals percolate through the underground water, radioactive rays arereleased and pollutantgases are released.
- Thisleads to bio magnification.
- Diseases caused by soil pollution includes cancer, arsenicosis, skeletal fluorosis, kidney and liver damage amongst others.
- Environment: it leads to reduced vegetation, ecological imbalance and imbalance in soil fauna and flora.
- Urban areas: it leads to clogging of drains, inundation of areas, foul smell and release of gases and waste management problems.
Control measures of soil pollution
- Refrain from indiscriminately disposing solid waste.
- Eliminate the use of plastic bags and instead opt for degradable alternatives like paper and cloth bags.
- Proper treatment of sewage should be carried out before utilizing it as a fertilizer or for landfills.
- Organic matter from household, agricultural, and other waste shall be separated and used for vermicomposting.
- Vermicomposting is a process that produces manure as a byproduct.
- Industrial waste shall undergo appropriate treatment to remove hazardous substances before its disposal.
- Facilitate solid waste treatment including physical, chemical and biological treatment.
- Biomedical waste must be collected separately and incinerated using proper incinerators.
- Reduce use of chemical fertilizer and pesticide by using bio pesticides, bio fertilizers andpromoting organic farming
- Prefer four R’s: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle
- Afforestation, reforestation and crop rotation: planting trees and grass cover on wastelands can control soil erosion and pollution.
- The practice of mixed cropping can help improve fertility of the land.
- Biodegradable material should be allowed to degrade under controlled conditions before being disposed.
Conclusion
Soil pollution poses a grave threat to the environment and human well-being. The contamination of soil by toxic substances adversely affects soil fertility, agricultural productivity, and ecosystem health. It is caused by various human activities, such as industrialization, improper waste disposal, and the excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers. Soil pollution in India will prove detrimental as India is an agrarian society. Hence, government must take appropriate steps to prevent such occurring.
Ref:
FAQs (Frequently Asked Question)
What do you mean by soil pollution?
Soil pollution occurs when substances that are added to the soil have a negative impact on its quality and fertility through the accumulation of persistent toxic compounds, chemicals, salts, radioactive materials, or disease-causing agents in the soil.
What are the causes of soil pollution?
Domestic Sources of Soil Pollution, industrial wastes, pesticides, weathering, mining etc. are the major reasons of soil pollution.
Explain how soil pollution and soil erosion could be prevented.
Refrain from indiscriminately disposing solid waste, eliminate the use of plastic bags and proper treatment of sewage should be carried out before utilizing it as a fertilizer or for landfills.
What are the effects of soil pollution on environment?
They can disrupt the natural balance of the soil’s organisms and have detrimental effects on its quality, texture, and mineral content.
What is the name of soil pollution caused by salt?
Soil salinization is the process that occurs when soluble salts are retained in the earth.
Name two soil pollutants.
The two pollutants of soil are mercury, lead, copper, zinc, cadmium, cynides, thiocynates, chromates, acids, alkalies, organic substances etc.


