Space weather, influenced by solar phenomena, has raised concerns about the vulnerability of LEO satellites, exemplified by the recent loss of Starlink satellites.
What is causing loss of satellites?
- A team from the IISER, Kolkata, in collaboration with NASA and Predictive Sciences Inc., was to determine the relationship between prevailing spaceweather conditions at LEO and the loss of Starlink satellites.
- The analysis conducted revealed that the loss of the satellites was not attributable to a single factor but rather a combination of several.
- These factors included the prevailing space weather conditions at the time, the insertion of the satellites into a relatively high-density LEO, and the possibility of enhanced drag due to orientation changes of the satellites.
About Spaceweather:
- Spaceweather are conditions and disturbances in space, particularly those influenced by the Sun, that can affect technological systems and infrastructure both in space and on Earth.
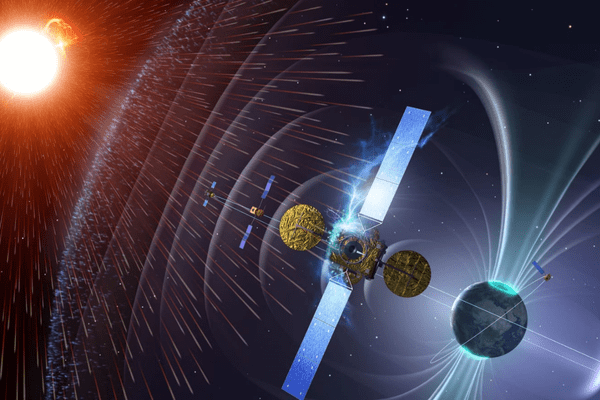
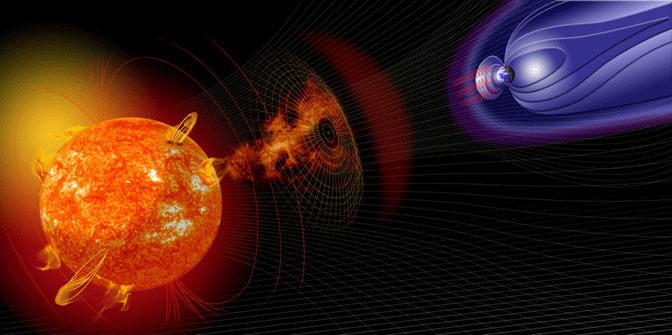
- Space weather is primarily caused by solar storm phenomena, which include: solar flares, solar particle events, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and solar wind.
- The Sun emits a constant stream of gas and charged particles into space known as the solar wind, originating from its hot outer atmosphere, the corona.
- A solar flare is an intense burst of radiation coming from the release of magnetic energy associated with sunspots.
- CMEs are large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona.
How space weather interacts with earth’s atmosphere?
- Earth possesses a magnetic field, an area of magnetic force activity, and is enveloped by a layer of gases known as the atmosphere.
- The magnetic field and atmosphere act like a shield, protecting earth from the majority of the solar wind blast.
- The majority of charged particles collide with Earth’s protective shield and bypass it.
- These particles compress and distort the side of the magnetic field facing the Sun, while the opposite side of the magnetic field extends into a long, trailing tail.
- Occasionally, charged particles manage to penetrate Earth’s shield.
- When these particles collide with the atmosphere, they create luminous displays known as auroras.
Impact of space weather on earth:
Radio Blackouts:
- Solar flares emit X-rays, among other electromagnetic energy.
- Increased X-ray emissions can scatter radio waves, causing radio blackouts on Earth due to disruptions in the ionosphere.
Solar Radiation Storms:
- Solar radiation storms result from solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
- These storms involve large bursts of protons and other particles from the Sun, which can elevate radiation levels near Earth to harmful levels.
- This poses health risks for astronauts at the International Space Station and, occasionally, for airline travelers in polar regions.
Geomagnetic Storms:
- A large coronal mass ejection can cause a strong gust of solar wind to reach Earth, transferring energy to Earth’s magnetic field and causing a geomagnetic storm.
- These storms can create intense currents in Earth’s magnetosphere and cause the ionosphere and upper thermosphere to heat up.
- The most common effect on Earth is spectacular auroras, but they can also disrupt radio signals and navigation systems, create drag for low-orbiting satellites, and harm power grids.
About Starlink:
- Starlink is a satellite internet constellation that provides high-speed internet to over 70 countries.
- It is the first and largest satellite constellation to use low Earth orbit, which allows it to provide internet that supports streaming, gaming, and video calls.
- Starlink is operated by Starlink Services, LLC, a subsidiary of SpaceX, an American aerospace company.
- SpaceX has been launching Starlink satellites since 2019.
Ref:Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |