UNESCO’s ‘State of Ocean Report, 2024’ reveals critical changes affecting global oceans due to climate change and human activities.
Key Findings of the Report:
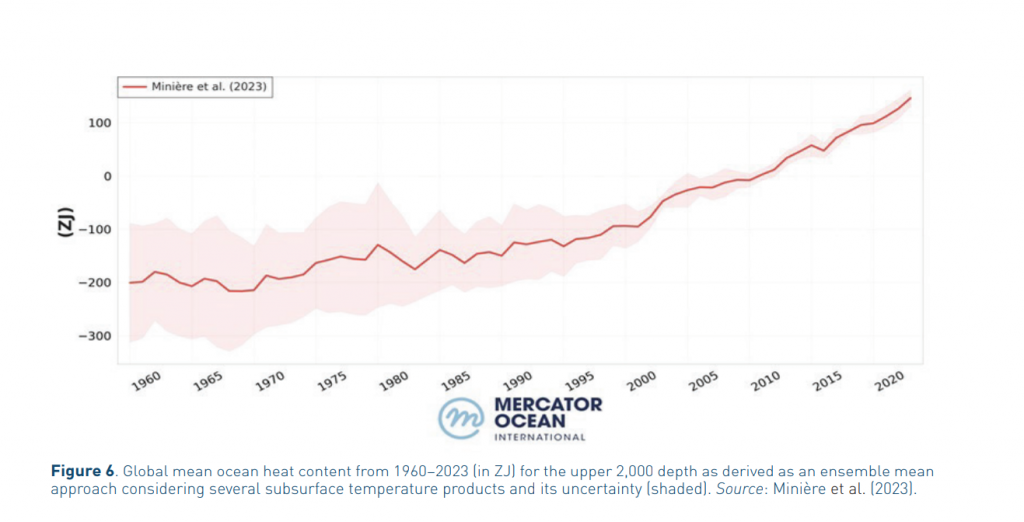
- Ocean warming has intensified, now at twice the rate from twenty years ago. Average temperatures have increased by 1.45°C. Hotspots in the Mediterranean, Tropical Atlantic Ocean, and Southern Oceans exceed 2°C.
- Rising sea levels are mainly due to accelerated ice mass loss from Greenland and West Antarctica. Increased ocean warming also contributes significantly.
- Ocean acidification has significantly increased. The oceans absorb about 25% of annual anthropogenic CO2, lowering the pH and potentially doubling acidification by the end of the century.
- Deoxygenation is worsening. Oxygen levels are decreasing, leading to more severe hypoxia across oceanic regions.
- However, the rate of acceleration due to increased ocean heat content remains uncertain.
- Coastal blue carbon ecosystems like mangroves, seagrasses, and tidal marshes play a crucial role in mitigating the effects of warming and acidification. They are significant carbon stores.
- However, 20–35% of these ecosystems have been lost since 1970, and their protection is still uncertain.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |