A recent study concluded that Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) can delay the tendency of statins to induce glucose intolerance and diabetes.
About Statins:
- Statins are cholesterol-lowering drugs commonly prescribed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- They are listed as essential medicines by the World Health Organization and are among the most sold drugs worldwide.
- Common statins include Atorvastatin, Fluvastatin, Lovastatin, Rosuvastatin, etc.
- Statins are recommended for individuals with high risk of heart attack or stroke, high LDL cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Statins block the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in the production of LDL cholesterol in the liver.
- They help draw cholesterol out of plaque in the arteries, reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Statins may also decrease triglyceride levels and increase HDL or good cholesterol.
- Their common side effects of statins include muscle damage, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, headache, dizziness, and fatigue.
- Studies suggest a potential risk of frank/pre-diabetes with statin use, but benefits often outweigh risks.
About Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA):
- UDCA, also known as ursodiol, is a secondary bile acid produced in the liver and by intestinal or gut bacteria.
- It is used to treat or prevent various liver or bile duct diseases.
About Cholesterol:
- Cholesterol is a vital substance in the body, crucial for cell function and hormone production.
- Imbalances in cholesterol levels can lead to health issues, including cardiovascular diseases.
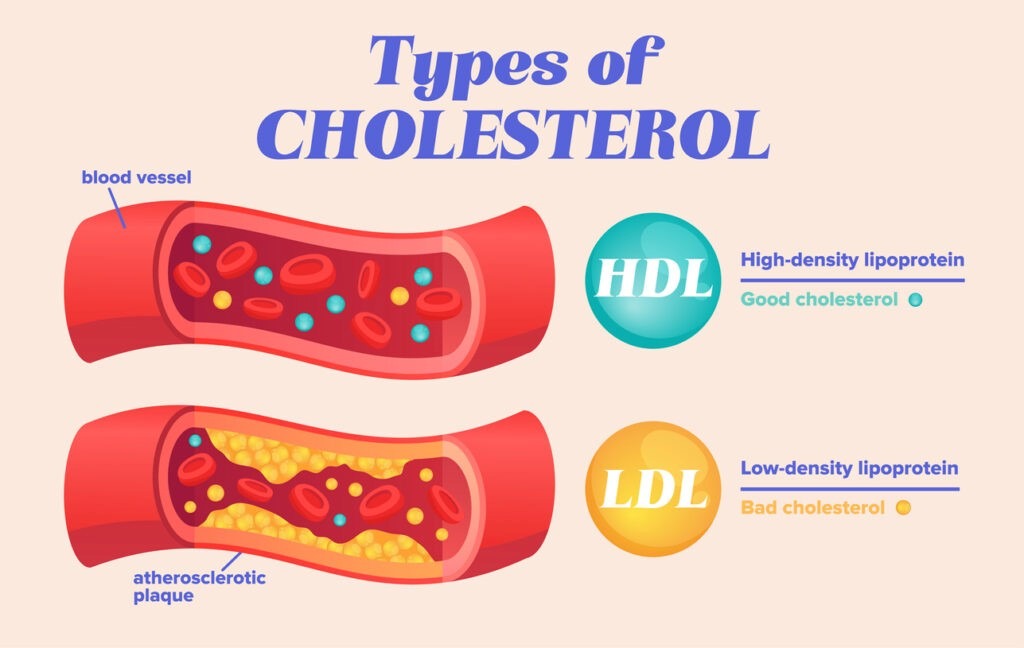
Types of Cholesterol:
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because it can build up on the walls of arteries.
- It forms plaque that can narrow and block blood vessels, leading to heart disease and stroke.
- High-density Lipoprotein (HDL) is known as “good” cholesterol as it helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
- It transports it to the liver where it can be broken down and excreted from the body.
Impacts and management of High Cholesterol:
- High cholesterol levels can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes.
- Cholesterol buildup can also lead to hypertension, peripheral artery disease, and the development of xanthomas (fatty deposits under the skin).
- Managing cholesterol levels involves adopting a healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats.
- Regular exercise can help boost HDL cholesterol levels.
- Medications such as statins may be prescribed to lower LDL cholesterol levels.
- Lifestyle modifications such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress are also important for cholesterol management.
Ref:Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |