Terrorism, an insidious phenomenon, manifests as the deliberate use of violence and intimidation to achieve political, ideological, or religious objectives. It poses a grave challenge to global peace and security, transcending borders and ideologies. In this article, you will learn about Terrorism, challenges related to Terrorism, Government Initiatives to control Terrorism, International Initiatives to Counter Terrorism, etc.
This article will provide key insights for GS Paper- III internal Security of UPSC IAS Exam.
Table of Content
- Terrorism
- Challenges Related to Terrorism in India
- Government Initiatives to control Terrorism in India
- International Initiatives to Counter Terrorism
- Methods to counter Terrorism
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Terrorism
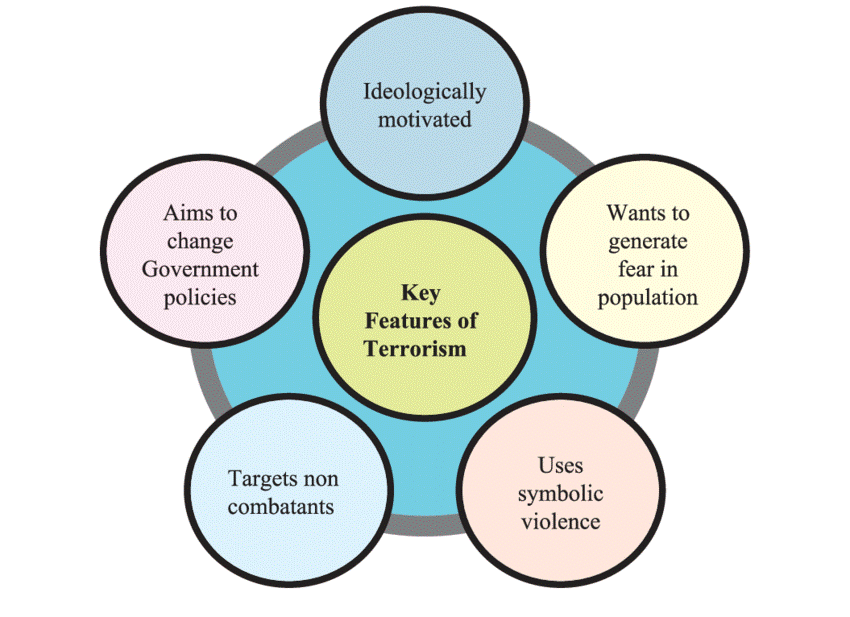
- Terrorism is the use of force or violence against persons or property in violation of the criminal laws for the purpose of intimidation, coercion, or ransom.
Challenges Related to Terrorism in India
- No Standard definition of Terrorism: There is no universally accepted definitions for what constitutes terrorism, so it is hard to classify a particular activity as a terrorist activity.
- Cross-Border Terrorism: India faces threats from terrorist groups operating from neighboring countries, particularly Pakistan. These groups, such as Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) and Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM), have been involved in several attacks on Indian soil.
- Insurgency and Naxalism: Internal conflicts, such as insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir and Naxalite movements in various states, often lead to violence and instability in affected regions.
- Cyber Terrorism: With the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure, cyber terrorism has emerged as a new threat. Terrorist groups use cyber-attacks to disrupt critical infrastructure and spread propaganda.
- Radicalization: The rise of radical ideologies, often propagated through social media and online platforms, has led to an increase in homegrown terrorism. Efforts to counter radicalization and prevent youth from being influenced by extremist ideologies are crucial.
- Terror Financing: Terrorist groups require funding and support to carry out their activities. Disrupting their financial networks and cutting off their sources of funding is a key challenge.
- Weak Border Security: India’s long and porous borders pose a challenge in terms of preventing the infiltration of terrorists and illegal arms and ammunition.
- Bio-Terrorism: Biotechnology can be misused as even small amounts of biotic agents can be hidden, transported and discharged into vulnerable populations.
- Lack of Coordination: Lack of coordination between various intelligence and security agencies can lead to gaps in security and intelligence sharing.
Government Initiatives to control Terrorism in India
- Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Amendment Act: It was enacted in 1967, to deal with the terrorism related crimes and has provisions different from ordinary legal procedures.
- National Investigation Agency: It is the Central Counter-Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency of India mandated to investigate all the offences affecting the sovereignty, security and integrity of India.
- National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID): It is the integrated intelligence grid connecting databases of core security agencies of India and will help set up an Entity Extraction, Visualization, and Analytics (EVA) system.
- National Security Guard: It is a counter-terrorism unit, operating under the Ministry of Home Affairs, that conducts counter-terrorist task such as counter hijacking, bomb disposal, post blast investigation, etc.
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO): It is a permanent acting agency of SCO that assists, coordinates and interacts with the competent agencies of SCO member states on fighting terrorism, separatism and extremism.
International Initiatives to Counter Terrorism
- United Nations Security Council’s Counter Terrorism Committee (CTC): It monitoring implementation of resolution 1373 which requested countries to implement measures to enhance their legal and institutional ability to counter terrorist activities.
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC): It is a United Nations office, mandated with the task of controlling trafficking and abuse of illicit drugs, crime prevention and criminal justice, international terrorism, and political corruption.
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF): It is the global money laundering and terrorist financing monitoring organisation set up in 1989 out of a G-7 meeting of developed nations in Paris.
Methods to counter Terrorism
- Legislative Measures: Enactment of robust anti-terrorism laws to define and criminalize terrorist acts and implement measures to freeze terrorist assets and restrict their financing.
- Security and Intelligence Operations: Strengthen security forces and intelligence agencies to detect and prevent terrorist activities and use of advanced technology for surveillance and monitoring of terrorist groups.
- Counter-Narratives and De-radicalization: Develop counter-narratives to challenge extremist ideologies and prevent radicalization and implement programs for the rehabilitation and reintegration of former terrorists.
- Border Security: Enhance border security measures to prevent the infiltration of terrorists and illegal arms and cooperate with neighboring countries to secure borders and exchange information.
- Development of Cyber-Defence Mechanism: Cyber-Defence Mechanism shall be developed to deal with cyber terrorism and the scope of countermeasures against cyber-attacks shall be extended.
- Reducing Exposure to Terrorism: The values of non-violence, peaceful coexistence and tolerance, must be incorporated since early childhood programs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, terrorism remains a persistent threat to global peace and security, requiring comprehensive and coordinated efforts from the international community. Addressing the root causes, such as socio-economic inequality, political grievances, and ideological extremism, is essential in combating terrorism effectively.
Furthermore, enhancing intelligence sharing, strengthening border security, and promoting dialogue and cooperation among nations are crucial steps in countering the menace of terrorism. Upholding human rights, promoting inclusive governance, and fostering tolerance and understanding among diverse communities are also vital in preventing radicalization and extremism
Ref: Source-1
| Other Related Articles in Social Issues | |
| Honour Killing | Abortion Laws in India |
| Healthcare Sector in India | Feminization of Agriculture |
| Euthanasia | Same Sex Marriage in India |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
When was the term terrorism first used?
The words terrorism and terrorist came to English as translations of words used in French during the period known as the Reign of Terror (1793-94), when the new government punished—usually by death—those people thought to be against the ongoing French Revolution.
What are the 5 components of terrorism?
The 5 components of terrorism- an involvement of an act of violence, an audience, the creation of a mood of fear, innocent victims, and political goals or motives.