Vertical Farming is a better alternative to traditional farming which will be enhanced with Industrial revolution 4.0 to leads towards future vertical farming. In this article, you will learn definition, types, features, etc.
This article will provide key insights for GS Paper-3 Environment and ecology section of UPSC IAS Exam.
Table of Content
- About Vertical farming
- Diagram of Vertical farming
- Features of Vertical farming technology
- Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
- Advantages of Vertical Farming
- Disadvantages of Vertical Farming
- Government initiatives for vertical farming in India
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
About Vertical farming:
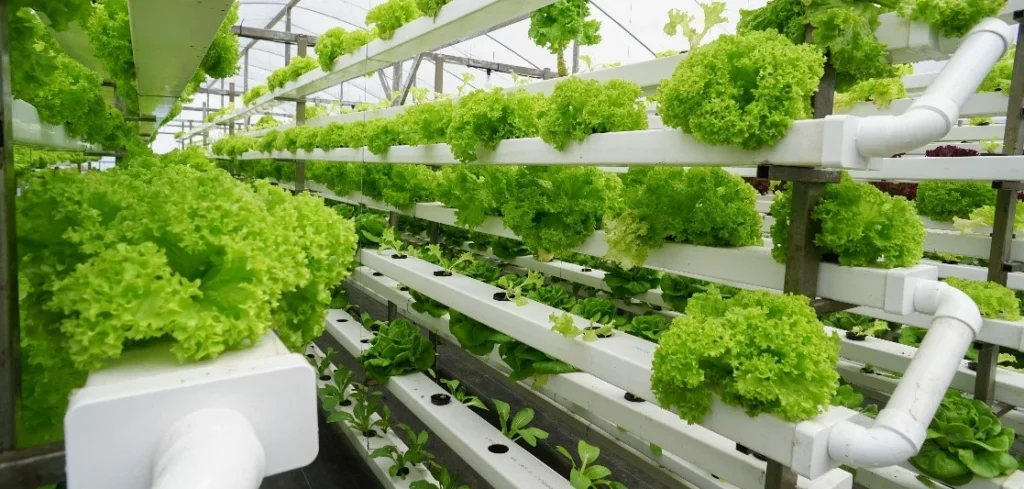
- It is the practice of farming plants in vertically stacked layers in a closed structure.
- It can use soil or any techniques like hydroponics or aeroponic growing methods that does not requires soil to grow.
- It aims to produce food in challenging environments, like where arable land is unavailable or water is insufficient to grow crops or for future where land will become scarce for agriculture.
- Japan was one of the early pioneers in vertical farming.
- Japan holds the largest share in the global vertical farming market.
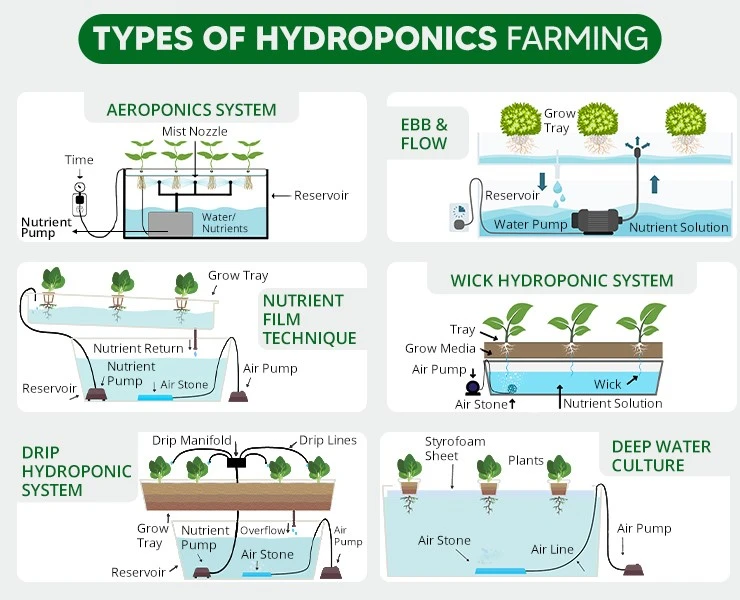
- Types of vertical farming: hydroponics vertical farming, aquaponics vertical farming, and growing-media based systems.
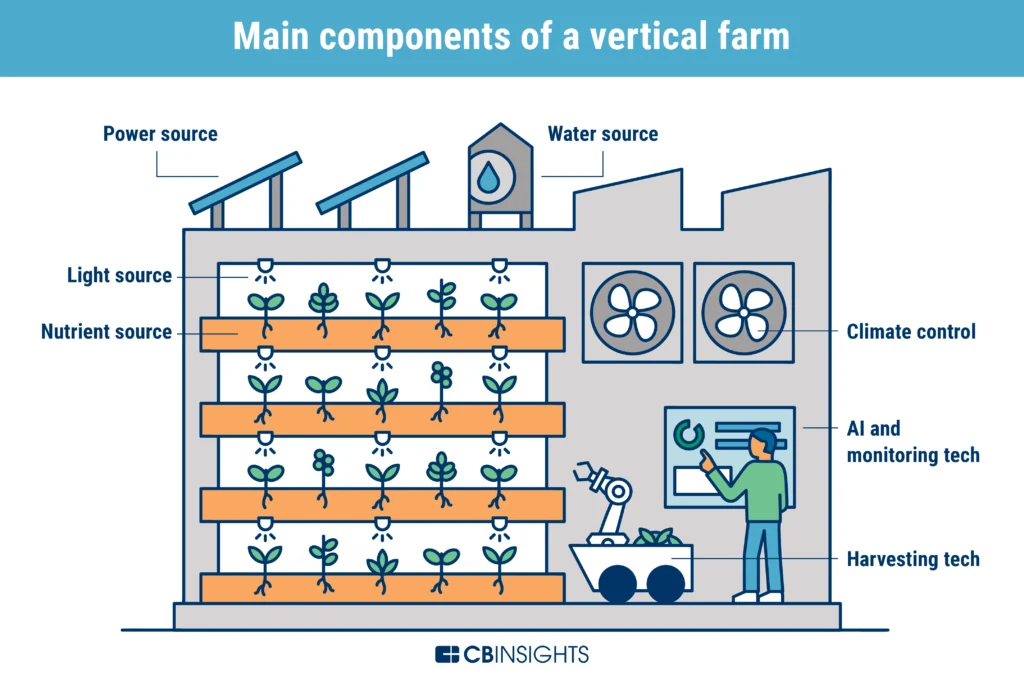
Diagram of Vertical farming:
Features of Vertical farming technology:
- Vertical net farming: It generally uses enclosed structures with produce being vertically stack either directly above each other or staggered for better natural light exposure.
- It uses a mixture of natural light and artificial light.
- Artificial light may use LED driven by a renewable power source.
- It requires balanced amount of humidity control and artificial temperature, checked through sensors.
- Failure to achieve this might lead to loss of the produce.
- It stresses on pesticide-free crops all year round by using sterilization and disinfection strategies from time to time.
Types of Hydroponics farming:
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA):
- It is a practice that is a part in Indoor vertical farming.
- It involves using technologies to provide optimal conditions for plants by controlling factors like temperature, lighting, and humidity.
- This allow farmers to grow plants that would otherwise not be suitable for the climate and weather.
Advantages of Vertical Farming:
- Hydroponic methods can save space as it doesn’t require soil as a growing medium, this accompanies reduced requirement for water.
- Aeroponics vertical farming methods reduces weight and water requirements, thus making it suitable to be grown in desert conditions.
- It would reduce the amount of farmland required, which then could decrease deforestation and pollution.
- It offers overall increased and consistent year-round production.
- It reduces human-animal (or vermin) conflict that is common in traditional farming.
- It reduces occupational hazards that might be faced by farmers while practicing traditional farming.
- It reduces the washing away of fertiliser by heavy rain associated with traditional farmingand thus reducing the possibility of algal bloom.
- Vertical farming at home will help in reducing carbon footprint of urban area along with making it self-sufficient in terms of food.
- This model is known as urban vertical farming.
- It reduces the chances of attacks by pathogens or worms common in traditional farming.
- Vertical farms when combined with CEA technology eliminates the need for chemical pesticides by keeping pests away from the plants since first day of farming.
Disadvantages of Vertical Farming:
- Most of its designs don’t efficiently deliver the necessary artificial light to keep the design green.
- Many vertical farms use heavy electricity that may not be renewable to produce good yields.
- The problem with agriculture is not a lack of farmable land but rather inefficient usage.
- Due to its high cost, many vulnerable countries and regions, who requires it the most, cannot afford it.
- Vertical farming crops includes herbs as it will help in recovering the cost invested. However, it is not a good option for growing staple crops.
Government initiatives for vertical farming in India:
- Vertical Garden Scheme: it is a scheme to promoteverticalfarming in Kerala by supporting the establishment of the vertical farming in urban areas for vegetable production with support from the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana.
- The Agriculture Infrastructure Fund provides long-term debt financing facilities for setting up vertical farms.
- India’s National Horticulture Board provides a credit-link subsidy for the development of commercial horticulture projects based on the Vertical Farming.
- Urban Horticulture Development Scheme: under this scheme Tamil Nadu government introduced a “do-it-yourself” kit for city dwellers to grow vegetables on rooftops.
- Bihar government has encouraged terrace gardening in 5 smart cities by providing subsidy for input cost.
Conclusion
Vertical Farming is a better alternative to traditional farming which will be enhanced with Industrial revolution 4.0 to leads towards future vertical farming. This type of farming has potential to offer many futuristic solutions to problems associated with the traditional farming, yet right steps must be taken to make its production viable so that it leads to inclusive growth including vulnerable farmers who cannot afford high costs associated with it. India must learn the successful vertical Farming model from the other countries such as Israel vertical farming, China vertical farming. Future prospects of vertical farming lies in innovations like using Internet of Things, 5G technology to offer higher production.
Ref: Source-1
| Other Articles in Environment & Disaster Management | |
| Miyawaki Method | Food Crops |
| No-till farming | Cropping systems |
| Crop Diversification | Green GDP |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is vertical farming?
Vertical Farming is the practice of farming plants in vertically stacked layers in a closed structure.
Is vertical farming eco-friendly?
Vertical Farming is eco-friendly as long as the energy used in it comes from the renewable sources.
What are the pros and cons of vertical farming?
Vertical Farming can help farming in urban spaces with low availability of the land but as it is costly it may not lead to an inclusive growth.
How vertical farming works?
Vertical Farming applies the method of the stacking the plants one over each other to reduce space and are placed in such a way that the plants receive their optimal photoperiod.
What is aquaponics vertical farming?
Aquaponics vertical farming is the combination of aquaculture and hydroponics to provide dual benefit of growing fishes as well as farming without using the soil.