Table of Content
- About Great Nicobar
- About the Great Nicobar Project
- Significance of the project
- Concerns with the Great Nicobar Project
- What has Government been doing to address these challenges?
About Great Nicobar:
- Great Nicobar is located at the southernmost tip of India, part of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Indira Point, earlier known as Pygmalion Point, lies at the tip of the Great Nicobar Island and is the southernmost point of the country.
- It is roughly equidistant from Colombo in Sri Lanka to the southwest and Port Klang (Malaysia) and Singapore to the southeast & located near the East-West international shipping corridor.
Ecology:
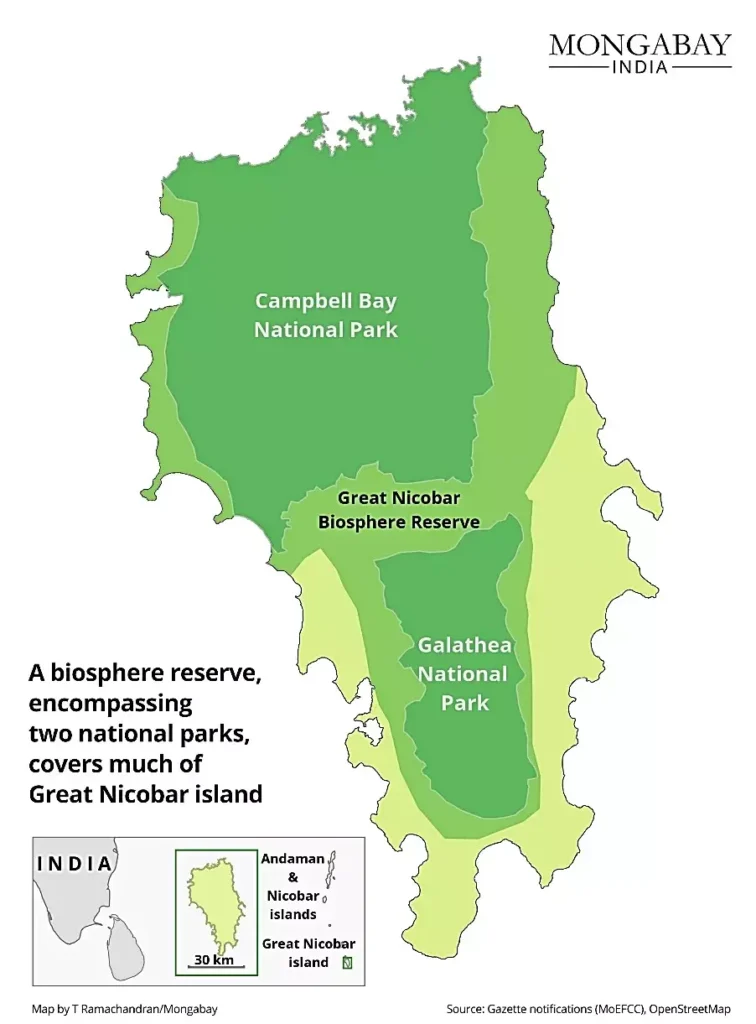
- It is a UNESCO biosphere reserve and part of the Sundaland biodiversity hotspot.
- It mainly consists of tropical rainforest, located in southeastern Bay of Bengal.
- The vegetation of the island is broadly divided into evergreen hill forest, tropical rainforest, littoral forest, and mangrove vegetation.
- The leatherback sea turtle is the island’s flagship species.
- Of the more than 2,500 species of fauna and flora found on the island, 17% are endemic.
About the Great Nicobar Project:
- It is a ₹72,000 crore development plan to develop Galathea Bay International Container Transhipment Terminal (GBICTT), Great Nicobar International Airport, Great Nicobar Gas and Solar Power Plant, and 2 new coastal cities the Great Nicobar.
- Itaims to make Great Nicobar a key player in global maritime trade and to promote tourism by enhancing the island’s infrastructure.
- The idea was first conceived in 2021, by NITI Aayog and is being developed by Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDC).
Details about each project:
- GBICTT: Its development will attract existing traffic of ports along the eastern coast of India, Bangladesh and Myanmar, as they form the primary catchment for transshipment terminal.
- Great Nicobar International Airport: It will be developed as a “joint military-civil, dual-use airport”, under the operational control of the Indian Navy and will cater to tourism as well.
- Township: It will be made up of commercial, industrial and residential zones, but a major part of land will be set apart for tourism projects and activities.
Significance of the project:
- Enhance global maritime trade: Located near the Malacca Strait, an important maritime route, the project will increase India’s participation in global maritime trade. Malacca Strait connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific Ocean.
- Strategic importance: It will help to counter the Chinese influence which wants to deploy maritime forces at the Indo-Pacific choke points, especially Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok.
- Tourism: Roads, public transport, water supply and waste management facilities, and several hotels have been planned to cater to tourists.
Concerns with the Great Nicobar Project:
Impact on Tribes:
- The project violates the rights of tribal communities living on the island such as Shompen, a PVTG (Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group) and Nicobarese tribal communities.
- Shompen tribes are at the risk of contracting diseases, due to being isolated for many years.
- The use of tribal lands without proper consent.
Ecological Concerns:
- It has many endemic species such as the giant leatherback turtle, the Nicobar megapode, the Great Nicobar crake, the Nicobar crab-eating macaque, etc.
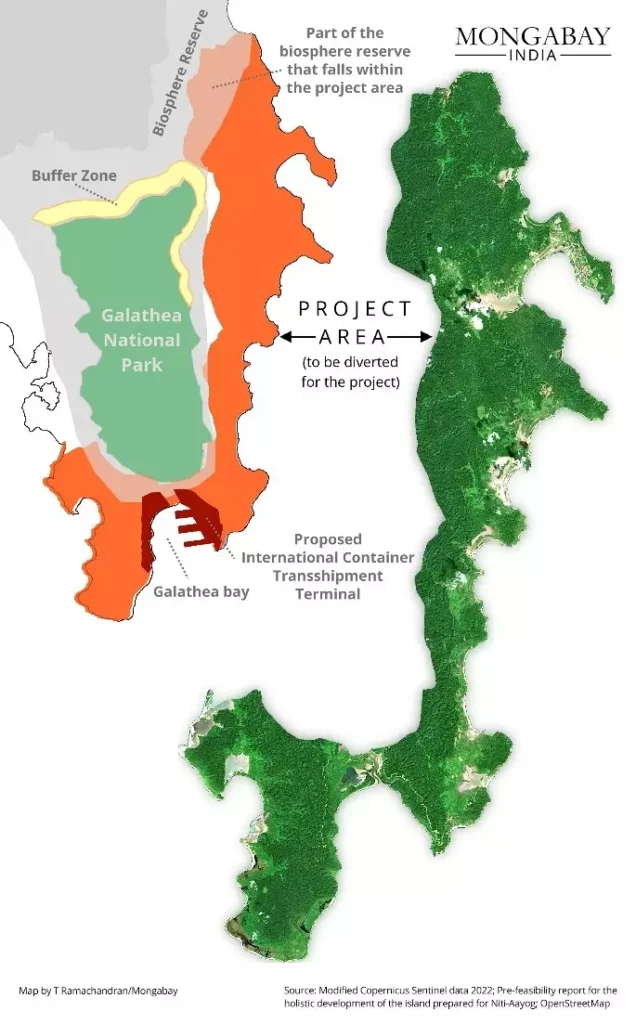
- The transshipment terminal will be developed at Galathea Bay, one of the world’s largest nesting sites for the giant leatherback turtle.
- The project will clear 130 sq. km of forest land and Galathea Bay wildlife sanctuary and the Megapode wildlife sanctuary were denotified for this purpose.
- The Government had released a ‘National Marine Turtle Action Plan’ that lists Galathea Bay as a marine turtle habitat in India.
- Coral reefs and the mangroves on the islands are particularly threatened.
Earthquakes:
- Great Nicobar is located in a seismically active zone “ring of fire,” which is prone to earthquakes. Thus, safety & feasibility of the project may be compromised.
- The area is in Category V: the geographical zone with the most seismic hazard.
What has Government been doing to address these challenges?
- Compensatory afforestation for the trees felled in the Great Nicobar has been planned, in the different ecological zone of Haryana.
- India has translocated a coral reef from the Gulf of Mannar to the Gulf of Kutch earlier.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Questions:
Where is Great Nicobar located and what is its significance?
Great Nicobar is at the southernmost tip of India and it is part of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Indira Point, the southernmost point of India, lies at the tip of the island, near the East-West international shipping corridor.
What is the ecology of Great Nicobar like?
Great Nicobar is a UNESCO biosphere reserve and part of the Sundaland biodiversity hotspot. It mainly consists of tropical rainforest with vegetation such as evergreen hill forest, tropical rainforest, littoral forest, and mangrove vegetation. The leatherback sea turtle is the flagship species of the island.
How many species are found on Great Nicobar and how many are endemic?
There are more than 2,500 species of fauna and flora found on the island, with 17% of them being endemic to Great Nicobar. The island’s diverse ecosystem is home to various unique and rare species.
What is the Great Nicobar Project and how much is it worth?
The Great Nicobar Project is a development plan with an estimated cost of ₹72,000 crore. This project aims to bring about economic development and infrastructure improvements to the island.