Scientists have created the world’s first 3D-printed brain tissue that behaves like natural brain tissue.
About 3D Printing:
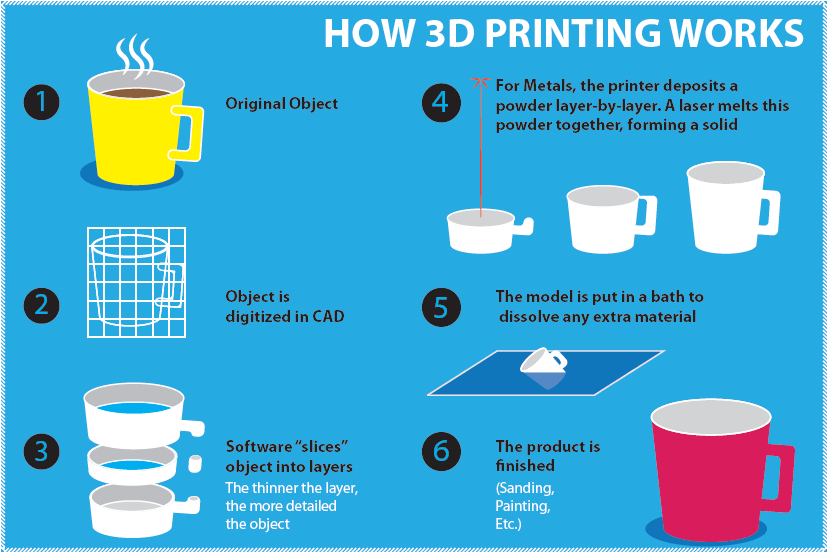
- 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the process of creating 3–dimensional objects from digital models by adding material layer by layer.
- Advantages Over Traditional Manufacturing:Efficient and customized production, overcoming limitations such as expense, slow pace, and errors associated with earlier technologies.
- It Utilizes computer-aided designing for prototyping or creating working models through additive manufacturing, employing materials like plastic, resin, thermoplastic, metal, fiber, or ceramic.
- National Strategy for Additive Manufacturing: Released in 2020 by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology to leverage the technology’s potential.
Benefits of 3D Printing:
- Facilitates quick and cost-effective prototyping, accelerating design iteration and reducing time-to-market for new products.
- Enables the creation of complex designs, previously challenging to achieve.
- Efficient material use, minimizing waste by using only the necessary materials for the object being printed.
- Reduces the need for large inventories, streamlining supply chains by producing parts on demand.
Applications of 3D Printing:
- Construction: India’s first 3D-printed post office in Bengaluru.
- World’s first 3D-printed pedestrian bridge was in Spain using micro-reinforced concrete.
- Medical and Dental: Patterns for casting metal dental crowns and manufacturing tools for creating dental aligners.
- Wider Application of 3D Printing:
- Extensively used across healthcare, automotive, aerospace, and more industries.
- Pandemic Response: Critical in manufacturing medical equipment like swabs, face shields, masks, and ventilator parts during the COVID-19 pandemic peak in 2020.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |