A committee recently voted against declaring the start of the Anthropocene epoch in the geologic time scale (GTS).
Key debates on the Anthropocene Epoch:
- The Anthropocene, or “Human Epoch,” proposal has been a subject of debate among scientists.
- Transition between these units is marked by significant geological events.
- The Holocene epoch began about 11,700 years ago, marking the end of the Last Glacial Period.
- The term “Anthropocene” reflects the profound influence of human actions on geological processes, such as climate change, deforestation, and biodiversity loss.
- The Anthropocene Working Group (AWG) proposed the start of the Anthropocene epoch in 1952.
- The proposal was voted against by the Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy (SQS), citing standards of chronostratigraphy.
- Critics argue against the recentness of the proposed start date and the magnitude of geological change required to define a new epoch.
- There are concerns about the clarity of defining boundaries and the permanency of the Anthropocene as an epoch.
- Some scientists propose viewing the Anthropocene as an “event” rather than a new epoch.
- The concept underscores the transformative impact of human activity on the planet, which is undeniable and recognized.
- While the proposal for the Anthropocene epoch was rejected, the debate underscores the recognition of human influence on Earth’s geological history.
- The concept remains relevant in understanding the profound impact of human activity on the planet.
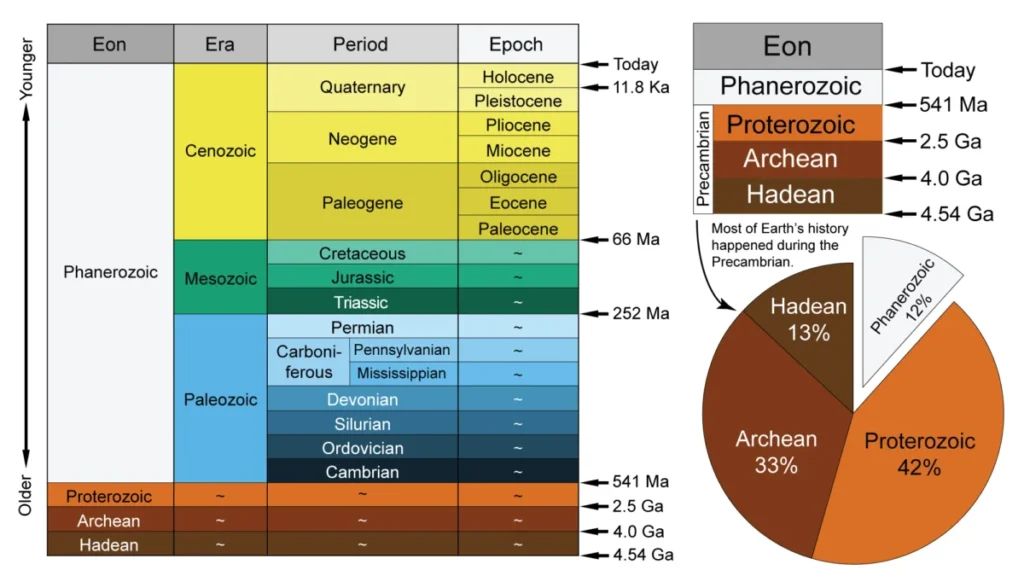
Geologic Time Scale (GTS):
- The GTS serves as a chronological framework for understanding the Earth’s history, providing a means to organize and categorize geological events spanning billions of years.
- It offers a systematic method to study the evolution of the planet, including the development of life forms, changes in climate, and geological processes.
- The GTS measures the history of the planet and is divided into aeons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages.
- The GTS is based on chronostratigraphic classification, which relates rock layers (or strata) to the measurement of geological time.
- This approach allows scientists to correlate rock formations across different regions and continents.
- Transitions between different units of the GTS are marked by significant geological events, such as mass extinctions, changes in climate, or shifts in tectonic activity.
- These events serve as critical markers for defining boundaries between geological time intervals.
- It aims for uniformity and standardization in terminology and classification to facilitate global communication and collaboration among geoscientists.
- International organizations like the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) oversee the development and maintenance of the GTS, ensuring consistency in its application.
Alt Text: Anthropocene Epoch
Description: Anthropocene Epoch is believed to be the New era, surpassing Holocene era in Geological Time Scale.
Ref:Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |



