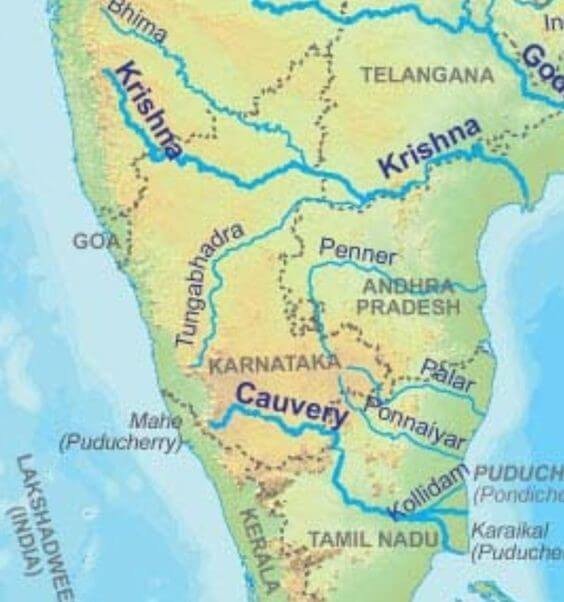
Cauvery River is the Ganga of the South that originates from TalaKaveri or TalaCauvery near the Brahmagiri range of hills in Karnataka’s Kodagu district. In this article, you will learn about Kaveri River system, Kaveri River’s origin, Kaveri River length, Kaveri tributaries, Cauvery river map, dams on Cauvery river, river Kaveri in India map, soil types, industries, rocks, minerals, climate etc, providing key insights for GS Paper- I Indian Geography section of UPSC IAS Exam.
Table of Content
- What is Cauvery River?
- Drainage of Cauvery River
- Kaveri river in India map:
- Features of Cauvery River basin
- Types of Soil in the Cauvery River basin
- Rocks and minerals in Cauvery River basin
- Waterfalls produced by Kaveri River
- Climate of the Cauvery Basin
- Precipitation levels in the Cauvery basin
- Tributaries of Kaveri River
- Forest coverage in the basin
- Main crops cultivated in the basin
- Projects on the Cauvery River
- Industries located near the Cauvery River
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Reference
What is Cauvery River?
- The Cauvery River is the Ganga of the South that originates from TalaKaveri or TalaCauvery near the Brahmagiri range of hills in Karnataka’s Kodagu district.
- The Cauvery River rises from an elevation of 1,341 meters.
- The Cauvery River is also known as the Kaveri River.
- The Godavari is referred to as Dakshin Ganga due to its size and Kaveri due to its spiritual significance.
Map of Cauvery river in India
Drainage of Cauvery River
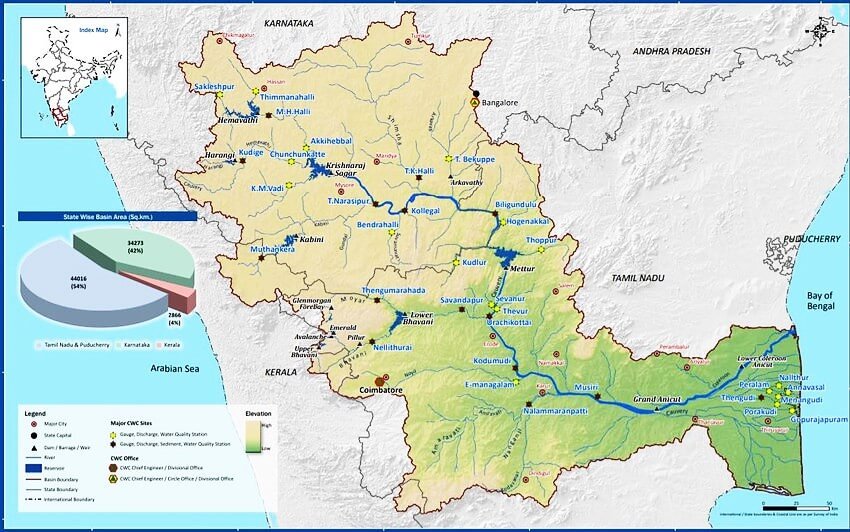
- The Cauvery River system covers a vast basin that spans across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- Percentage of water received by each state: Kerala (3%), Karnataka (41%), and Tamil Nadu (56%).
- The Cauvery River has length of 800 kilometers.
- The Kaveri River drains an area of approx. 81 thousand square kilometers.
- The Kaveri River is surrounded by the:
- Western Ghats on the west
- The Eastern Ghats on the east and south
- The ridges that separate it from the Krishna and Pennar basins on the north
Kaveri river in India map:
Features of Cauvery River basin
Division of basin:
- An extension of Nilgiris from the Western Ghats towards the Eastern Ghats divides the basin into two natural regions:
- The Karnataka plateau in the North
- The Tamil Nadu plateau in the South
- The Kaveri basin can be divided into three parts: the Western Ghats, the Plateau of Mysore, and the Delta.
Catchment area of basin:
- The catchment area of this basin can be classified into three sections:
- The upper catchment area is characterized by steep slopes
- The middle catchment area is mainly located in Tamil Nadu
- The lower catchment area is confined to the plains of Tamil Nadu
Shape of the Kaveri basin:
- In terms of flooding, the Cauvery River basin has a fan-shaped structure in Karnataka and a leaf–shaped structure in Tamil Nadu.
- Due to its shape, the basin does not experience rapid flooding as the runoff does not drain off quickly.
The Cauvery River basin map:
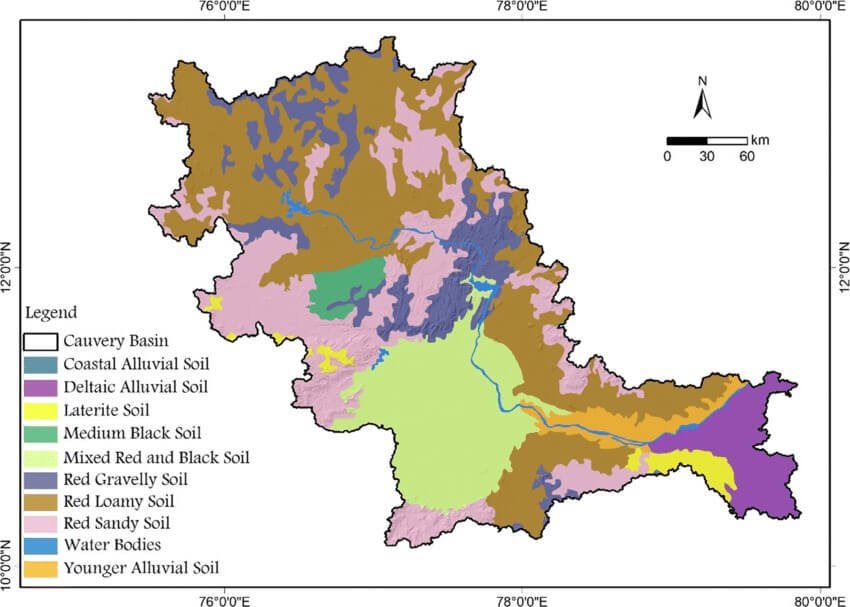
Types of Soil in the Cauvery River basin
- The Kaveri delta region is highly fertile.
- Soil types present in the Kaveri basin includes black soils, red soils, laterites, alluvial soils, forest soils, and mixed soils.
- Red soils are more widespread in the basin, followed by black soils.
- Alluvial soils being found in the delta areas.
- The highlands in Karnataka have lateritic soils that have a reddish-brown color.
- These shallow soils are slightly acidic to neutral and possesses fertility.
- The highlands in Kerala have redloam soils, with some areas containing fertile black soils.
- The fertile black soils are rich in organic matter and nitrogen, making them beneficial for agriculture.
- In the lowlands and plains of Karnataka, the soils have a neutral to acidic pH and good drainage with higher water retention capabilities.
- The soils in Tamil Nadu are have a high clay content, limited drainage capacity, low nitrate and phosphorus levels, and high potassium and lime content.
- In the south-eastern are of the basin, there are swampy areas with alluvial clay soils t.
Rocks and minerals in Cauvery River basin
- The Cauvery basin is part of the South Indian Shield, which consists of an ancient crust formed over 2500 million years ago.
- The Kaveri River route creates the basin that is rich in minerals such as cobalt, zinc, manganese and rare earth materials.
- The main rock types in the basin are metamorphic and igneous rocks.
- They both represent significant geological events such as volcanism, plutonism, metamorphism, and sedimentation.
- Archean era mineral rocks in the basin include scharnockites, high-grade schists, migmatites, greenstone belts, and consolidated gneisses.
- The southern region of the basin has laterized and ferruginous sandstone.
- Coastal areas may contain conglomeratic sandstone, coralline limestone, and shale.
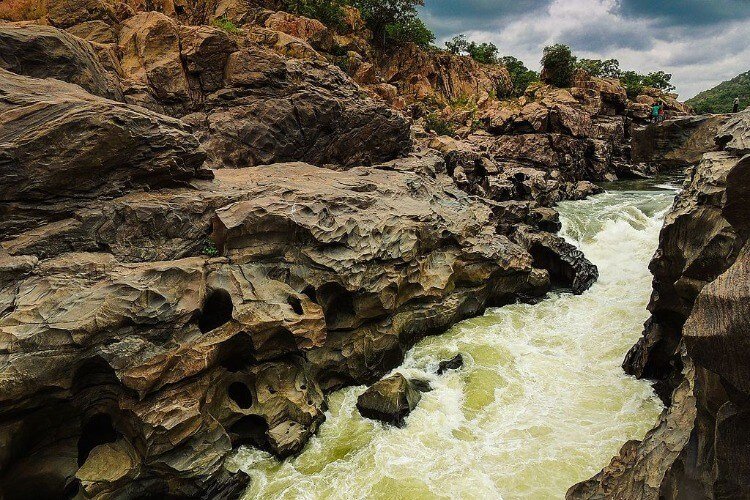
Waterfalls produced by Kaveri River
- The Kaveri River descends from the South Karnataka Plateau to the Tamil Nadu Plains.
- While entering the plains it forms the Shivanasamudram waterfalls.
- The Shivanasamudram waterfalls is approximately 101 meters high.
- At Shivanasamudram waterfalls, the river splits into two parts and cascades through a series of falls and rapids.
- This waterfall is utilized for power generation by the power station at Shivanasamudram.
- After the waterfalls, the two branches of the river reunite and flow through a wide gorge known as Mekedatu (Goats leap), where Mekedatu falls can be found.
- There was a Cauvery water dispute associated with the Mekedatu waterfalls between the state of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Union territory of Pondicherry for which Union Government has formed Cauvery Water Management Authority.
- The dispute is now resolved after Supreme Court’s judgement in 2018.
- Continuing its course, the Kaveri River takes a southern direction at Hogennekkal Falls and enters the Mettur Reservoir.
- Below the reservoir, the river widens and flows as Akhanda Cauvery with a sandy bed.
- In the final stage, the riversplits into two parts:
- The Northern branch is called ‘The Coleron’.
- The Southern branch is called Cauvery.
- This basin marks the beginning of the Cauvery Delta.
- After flowing for about 16 kilometers, the two branches- Coleron and Cauvery joins again to form ‘Srirangam Island.’
- On the Cauvery branch lies the “Grand Anicut,” that was constructed by a Chola King in the 1st Century A.D.
- Below the Grand Anicut, the Cauvery branch further divides into-Cauvery and Vennar.
- The river’s drainage network is extensive, later forming a delta at Trichinopoly.
Mekedatu water gorge:
Alt text: Cauvery river images
Climate of the Cauvery Basin
- The overall climate in the Cauvery basin tends to be dry, except during the monsoon months.
- The extreme northwestern region of the drainage basin has a moist climate, which gradually transitions eastward into humid, moderately moist, moderately dry, and semi-arid zones.
- As we move closer to the sea, the relative humidity increases once again.
- Across the catchment area, there is significant variation in the average daily maximum and minimum temperatures.
- The average daily maximum temperature ranges from 19.5 to 33.7 degrees Celsius.
- The average daily minimum temperature varies from 9.1 to 25.2 degrees Celsius.
- Wind patterns in the region are influenced by the monsoons which predominantly blows from the southwest to the northwest during the southwest monsoon season.
- The presence of clouds is associated with the monsoon activity, resulting in generally overcast skies during the monsoon period.
Precipitation levels in the Cauvery basin
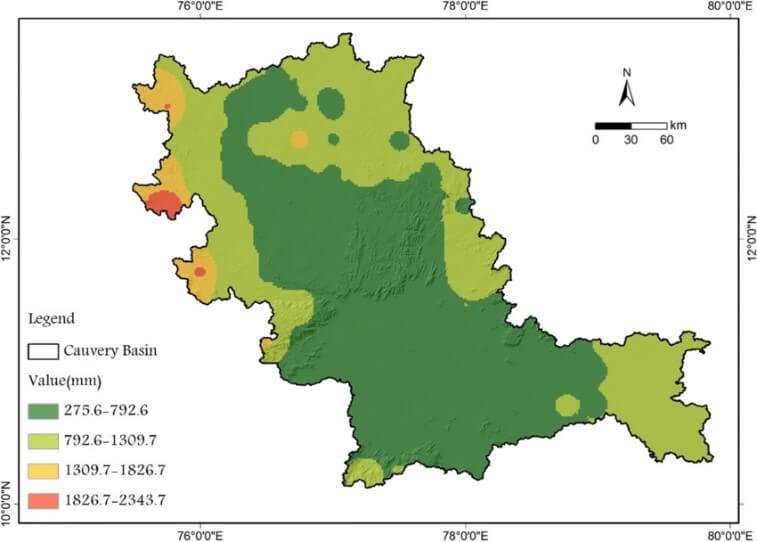
Alt text: Kaveri river cities
- The Karnataka region of the basin primarily receives rainfall from the South-West Monsoon, supplemented partially by the North-East Monsoon.
- The Tamil Nadu region receives significant water from the North-East Monsoon.
- The upper catchment area experiences summer rainfall from the South-West Monsoon, between June and September.
- August sees the highest rainfall.
- The lower catchment area experiences winter rainfall from the retreating North–East Monsoon between October and December.
- Approximately 50% of the totalrainfall occurs during the southwest monsoon, 33% during the northeast monsoon, 10% in the pre-monsoon season, and the remaining in the winter months.
- This makes Cauvery River almost perennial, with relatively stable flow fluctuations.
- For the rest of the year, rainfall is minimal with March being the driest month.
- Thus, Kaveri River is highly valuable for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation.
- The Kaveri River is so well-regulated that most of its irrigation and power production potential is already utilized.
Tributaries of Kaveri River
- The Left bank tributaries of Kaveri River includes- the Harangi, Hemavati, Shimsha, and Arkavati rivers.
- The Right bank tributaries of Kaveri River includes- Lakshmantirtha, Kabbani, Suvarnavati, Bhavani, Noyil, and Amaravati rivers.
| Tributary Name | Catchment Area (Sq.km) | Origin | Sub-Tributaries | State |
| Arakavathy | 4351 | Nandidurga | Kumaudavathy, Manihalla, Kuttehole, Vrishabhavathy | Karnataka and Tamil Nadu |
| Harangi | 717 | Pushpagiri Hills of Western Ghats | Karnataka | |
| Hemavathy | 5410 | Ballarayana Durga in Western Ghats | Karnataka | |
| Kabini | 7040 | Western Ghats in Kerala | Taraka, Hebballa, Nugu, Gundal | Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu |
| Lakshmana Thirtha | Western Ghats | Ramathirtha | Karnataka | |
| Shimsha | 8469 | Tumkur District | Veeravaishnavi, Kanihalla, Chickkhole, Habbahalla, Mullahalla, Kanva | Karnataka |
| Suvarnavathy | 1787 | Nasrur Ghat Range | Karnataka and Tamil Nadu Top of Form Bottom of Form |
Forest coverage in the basin
- Only 19.53% of the total basin area is covered by forests.
- In Karnataka, around 18% of the basin area has forest cover, while Tamil Nadu has around 19% of the basin area has forest cover.
- The forest cover in the Kerala part of the basin is higher, it constitutes a small portion of the overall basin area.
- Despite the forest cover being less than ideal, these forests are ecologically distinct and exceptionally diverse.
- They serve as habitats for unique flora and fauna, and the area is renowned for its numerous sanctuaries.
Main crops cultivated in the basin
- Majority of the basin’s population resides in rural areas and relies on agriculture as their primary occupation.
- Approximately 48% of the land in the basin is used in cultivation, with 24% of the area having some form of irrigation.
- Majorcrops grown are paddy, sugarcane, ragi, and jowar.
- Paddy cultivation is most prominent amongst them followed by Ragi.
- Ragi is cultivated most in Mysore plateau.
- Sugarcane is cultivated most in Tamil Nadu.
- Jowar is cultivated most in Mandya of Karnataka and Coimbatore and Dindigul in Tamil Nadu.
- Other crops grown are coffee, pepper, banana, betel vine, gingili, onion, cotton, and black gram.
Projects on the Cauvery River
- Dam across Cauvery River in Karnataka- Krishnarajasagar dam, Hemavati, Harangi, Kabini.
- Dam across Cauvery River in Tamil Nadu– Mettur dam, Lower Bhavani.
Industries located near the Cauvery River
- The cotton textile industry in Coimbatore and Mysore.
- The cement factories in Coimbatore and Trichinapally.
- The mineral and metal-based industries in Coimbatore and Trichinapally.
- The Salem steel plant and various engineering industries in Coimbatore and Trichinapally.
Conclusion
The Kaveri Water Dispute or Kaveri River Dispute was in between Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Union territory of Pondicherry. The Cauvery River water dispute has ended after Supreme Court has issued its final verdict by allocating more water to the state of Karnataka.
Ref:
FAQs (frequently asked question)
Through which states Kaveri River flows?
The river Cauvery flows from Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
Is Cauvery water hard water?
The contamination due to heavy metals makes the Cauvery water hard.
Between which two states does the Cauvery water dispute has existed?
The Cauvery River dispute was in between Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Union territory of Pondicherry.
What are the tributaries of Cauvery River?
The tributaries of Kaveri River are the Harangi, Hemavati, Shimsha, Arkavati rivers, Lakshmantirtha, Kabbani, Suvarnavati, Bhavani, Noyil, and Amaravati rivers.