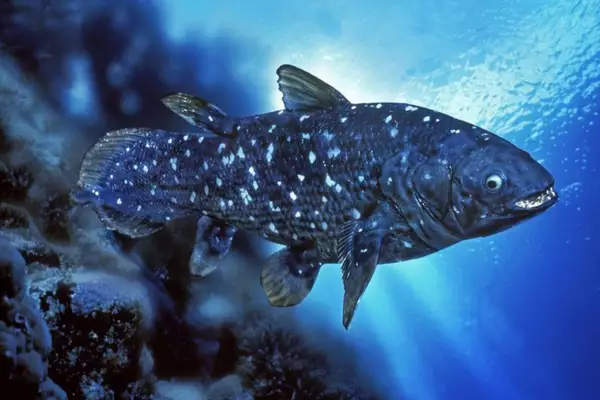
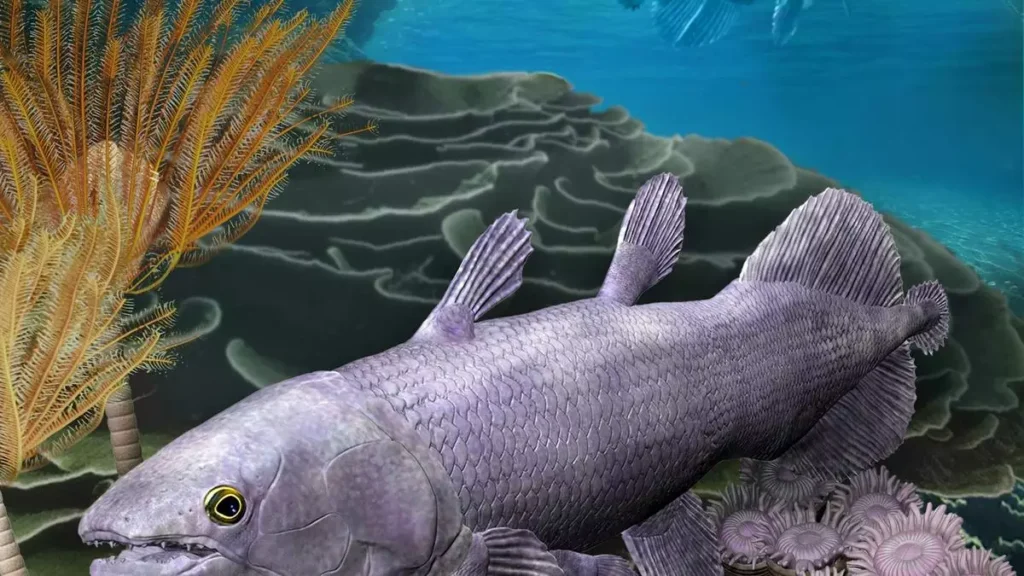
Researchers recently identified the best-preserved coelacanth fossil from the Devonian Period in northern Western Australia, named Ngamugawi wirngarri.
About Coelacanths:
- Coelacanths are deep-sea fish believed to have existed for over 410 million years, living off the coasts of southern Africa and Indonesia and can reach up to two metres in length.
- Once thought to be extinct, their rediscovery in 1938 marked them as “living fossils,” showcasing remarkable evolutionary stasis.
- Over 175 fossil species of coelacanths have been identified, with significant diversification occurring during the age of dinosaurs.
- Coelacanths have robust, limb-like fins, making them more closely related to tetrapods than to most fish.
- Two extant species exist, Latimeria chalumnae and Latimeria menadoensis, while they resemble ancient counterparts, genetic analysis indicates they are distinct.
Key findings on Recent Discoveries:
- It is the best-preserved coelacanth fossil ever found from the ancient period hundreds of millions of years ago when these ancient sea-dwellers first evolved.
- The fossil comes from the Gogo Formation on Gooniyandi Country in northern Western Australia, an area that was once a vibrant tropical reef.
- Contrary to expectations, tectonic activity was the primary driver of coelacanth evolution, rather than factors like ocean temperature or oxygen levels.
- Increased tectonic movement correlated with higher rates of new species emergence.
- While they have not developed new features, their body proportions and DNA exhibit slight variations over time.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
What are coelacanths?
Coelacanths are deep-sea fish that have existed for over 410 million years. They are primarily found off the coasts of southern Africa and Indonesia and can grow up to two meters in length.
Why are coelacanths called “living fossils”?
Coelacanths were once thought to be extinct until their rediscovery in 1938. Their ancient lineage and minimal evolutionary change over millions of years led to them being termed “living fossils.”
How many species of coelacanths are known?
More than 175 fossil species of coelacanths have been identified, currently, there are two extant species: Latimeria chalumnae and Latimeria menadoensis.
What makes coelacanths unique among fish?
Coelacanths have robust, limb-like fins that resemble the structure of tetrapod limbs, indicating a closer evolutionary relationship to land animals than to most fish.