The Fourth Annual Air Quality and Climate Bulletin on global PM2.5 air pollution trends and its connections to climate change was released by the United Nations’ World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
Key findings of the report:
- Global PM2.5 concentrations: Europe and China have seen reductions in PM2.5 levels, while North America and India experience rising emissions, primarily from human activities.
- PM2.5 hotspots: Agricultural regions in Central Africa, Pakistan, India, China, and Southeast Asia are identified as significant pollution zones.
- Impacts on agriculture: PM2.5 pollution reduces crop yields by up to 15%, hindering sunlight from reaching leaves and affecting plant functions.
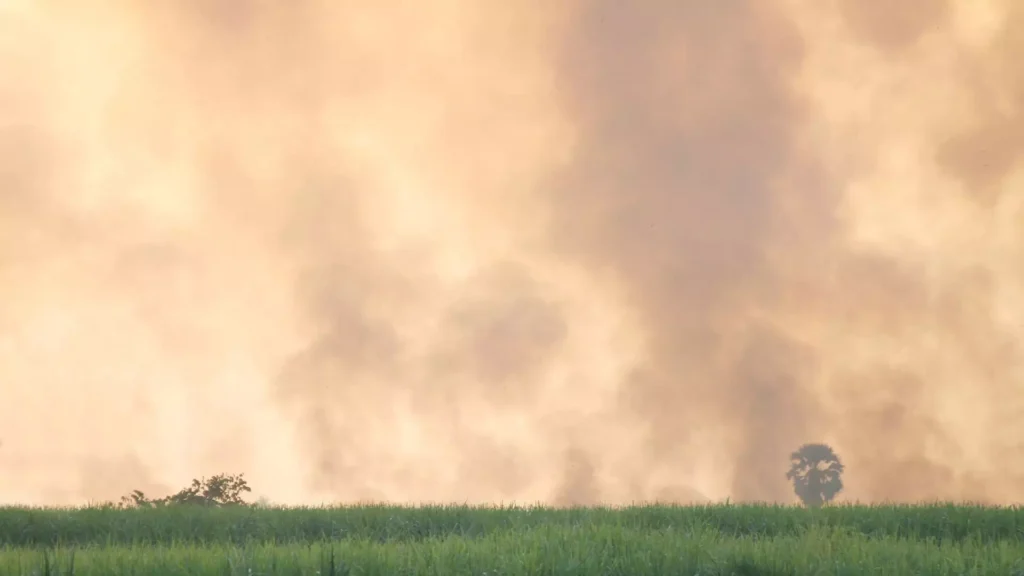
- Wildfire impacts: The 2023 wildfire season, especially in Canada, caused massive air quality issues across North America, with smoke even reaching Europe and Greenland.
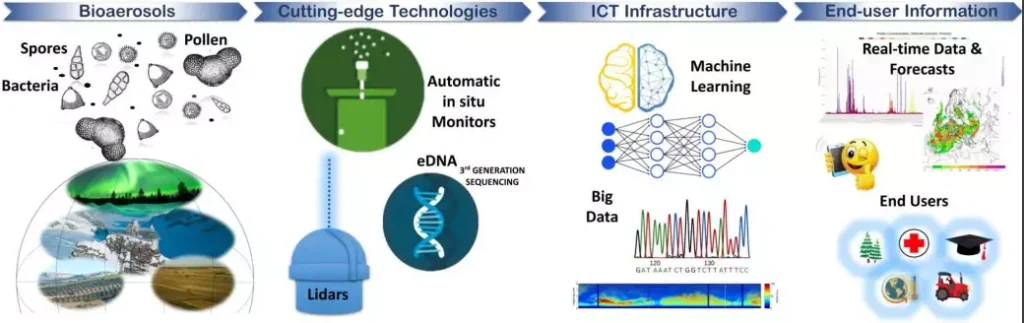
- Bioaerosol monitoring advancements: New technologies now allow for real-time tracking of bioaerosols like pollen and spores, offering critical insights for agriculture and climate studies.
- Decline in New Particle Formation (NPF): A global reduction in NPF could unintentionally alter the climate by affecting cloud formation and radiation balance.
What is Aerobiology?
- Aerobiology is the study of how biological particles, such as bacteria, viruses, fungal spores, and pollen, move through the atmosphere.
- It covers both droplet transmission (short-range, quick-settling particles) and airborne transmission (small particles that stay suspended longer).
- These particles affect human, animal, and plant health and are influenced by climate changes.
- Bioaerosols reflect biodiversity shifts, flowering patterns, and species distribution.
- Advanced tools like holography, fluorescence spectrometry, and DNA sequencing help study these particles and their effects on ecosystems.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
What is the significance of PM2.5 in air pollution?
PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter that poses serious health risks, particularly respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
How does air pollution affect climate change?
Air pollution contributes to climate change by affecting cloud formation, radiation balance, and temperature regulation.



