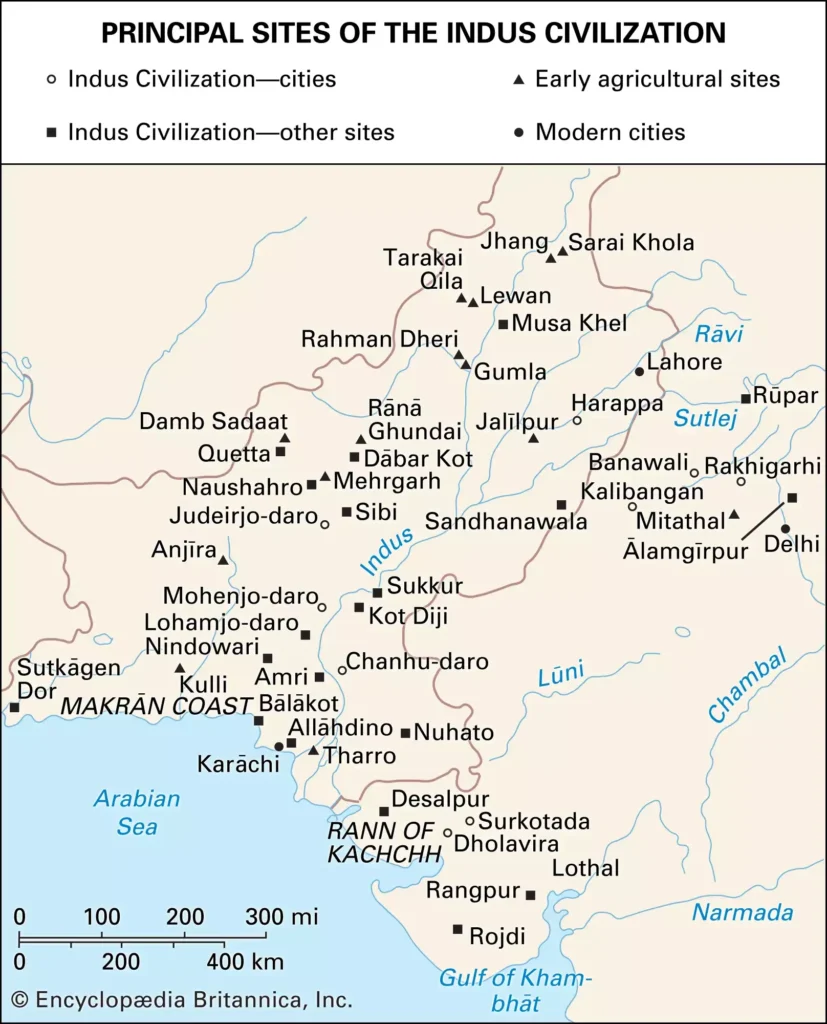
September 20, 2024, marks 100 years since the announcement of the discovery of the Indus Valley Civilisation, now called the Harappan Civilisation, which spans over 2,000 sites across 1.5 million sq. km in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan.
About Harappan Civilisation:
- Discovery: First announced in 1924 by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), revealing a Bronze Age civilisation on the banks of the Indus and Saraswati rivers.
- Geographical Extent:
- Spread: The civilisation spanned across 2,000 sites in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, mostly located between the Indus and Saraswati River basins.
- Key Sites: Mohenjo-daro, Harappa, Ganweriwala, Rakhigarhi, Dholavira.
- Outposts: Daimabad in Maharashtra (southernmost), Alamgirpur in UP (easternmost), Sutgakendor in Pakistan (westernmost), Manda in Jammu (northernmost).
- Timeline:
- Early Phase: 3200 BCE to 2600 BCE.
- Mature Period: 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE.
- Late Phase: 1900 BCE to 1500 BCE (decline of the civilisation).
Key Features of the Harappan Civilisation
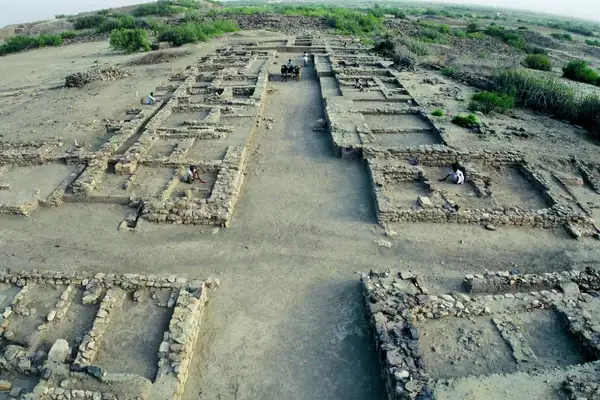
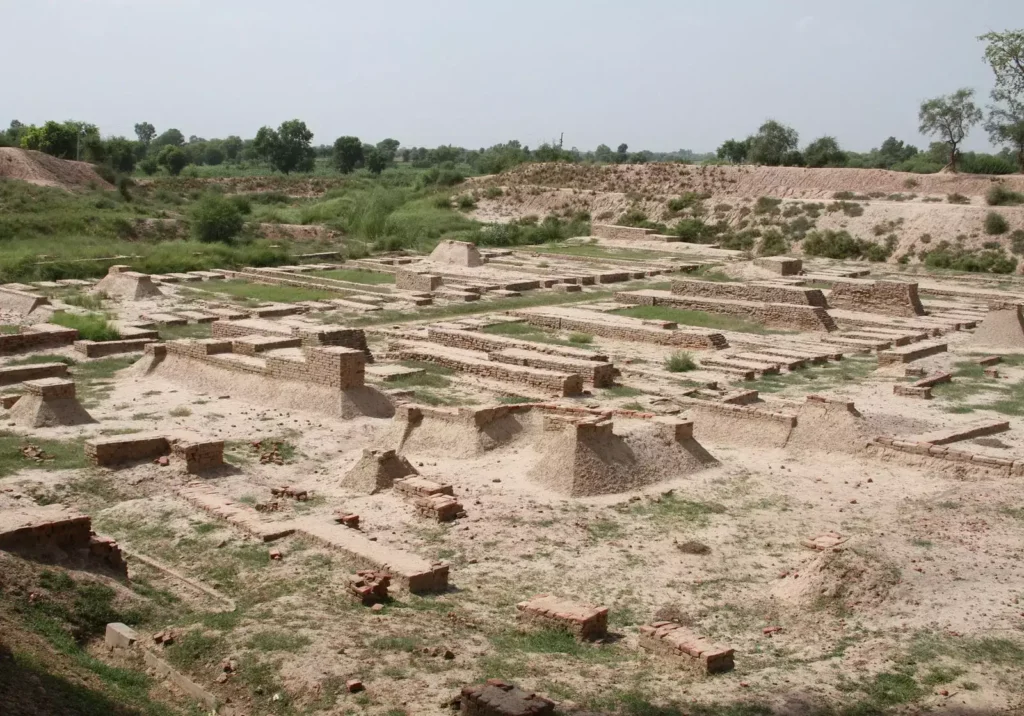
- Town Planning and Architecture:
- Citadels and Great Baths: Large-scale structures, including the Citadel and Great Bath in Mohenjo-daro.
- Drainage System: Well-planned drainage and sanitation systems.
- Burnt Bricks: Standardised bricks (1:2:4 ratio) used extensively.
- Street Planning: Streets at right angles, designed for movement of bullock-carts (e.g., Dholavira).
- Technology and Crafts:
- Craftsmanship:
- Highly developed micro-drilling technology.
- Bead-making (e.g., long beads from carnelian).
- Metalworking (bronze, copper) and pottery-making.
- Seal-Making: Steatite seals with inscriptions and animal motifs.
- Terracotta Toys: Evidence of advanced toy-making skills.
- Micro-Drilling: Highly developed micro-drilling technology for bead-making, especially with hard stones like carnelian.
- Standardised Weights: Cubic weights made of chert, carefully cut and polished, employed a combination of binary and decimal systems.
- Example: The Chanhudaro site is known for showcasing these crafts and technologies.
- Craftsmanship:
- Art of Writing: Indus Script: Fully developed but remains undeciphered.
- Trade and Commerce:
- Port City of Lothal: Major hub for maritime trade, showcasing Harappan trade links.
- Commercial Contacts: Strong trade connections with Afghanistan, Iran, and the Mesopotamian region (called “Meluha” by Mesopotamians).
Recent Discoveries and Studies
- New Excavation: Discovery of a 5,200-year-old Harappan settlement at Padta Bet in Kachchh, Gujarat.
- DNA Analysis: DNA studies from Rakhigarhi suggest a connection between Harappans and the current South Asian population, indicating genetic continuity.
- Genetic Mixture: Due to extensive trade and cultural interactions, Harappans carried genetic traces from various distant regions, indicating a mixture of genes in small quantities.
Significance of the Discovery
- Filling the Historical Gap: The discovery of the Harappan civilisation pushed back the history of settled life in South Asia by over 3,000 years, filling a gap previously thought to exist between the Stone Age and the Buddhist period.
- Global Importance:
- The Harappan civilisation is considered one of the ancient major civilisations, alongside Egyptian and Mesopotamian civilisations.
- It demonstrated maritime contacts with West Asia, with evidence of trade as early as 3000 BCE.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
When was the Harappan Civilisation discovered?
The Harappan Civilisation was first announced in 1924 by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
What were the key features of Harappan town planning?
Harappan cities had well-planned streets, citadels, advanced drainage systems, and buildings made from standardised burnt bricks.
Which site was the major hub for maritime trade in the Harappan Civilisation?
The port city of Lothal was a major hub for maritime trade in the Harappan Civilisation.
What does the recent DNA analysis from Rakhigarhi suggest about Harappans?
DNA studies suggest a genetic connection between Harappans and the current South Asian population, indicating genetic continuity.
What was the significance of micro-drilling technology in the Harappan Civilisation?
Harappans developed advanced micro-drilling technology, especially for crafting beads from hard stones like carnelian.