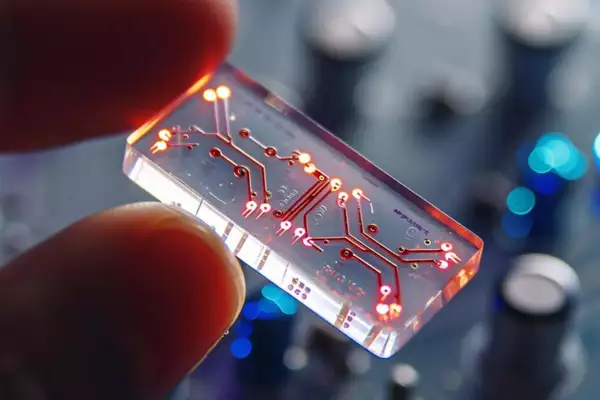
The Organs-on-chips (OOC) technology reached a record high valuation in 2023, and introduced 3D culture models, known as “new approach methods” (NAMs).
About Organs-on-chips (OOC) technology:
- New Approach Methodologies (NAMs) are innovative techniques that aim to reduce or replace animal testing in scientific research, particularly in toxicology and hazard assessment.
- These methods often involve using advanced technologies, such as in-vitro testing, In silico modeling, OOC technology, Omics technology.
- OOC is a revolutionary approach that mimics the physiological responses of human organs using microfluidic devices.
- It involves creating miniature replicas of human organs on microfluidic chips.
- These chips are engineered to contain tiny channels lined with cells that resemble the structure and function of specific organs, creating a microenvironment.

Key Components of OOC Technology:
- Microfluidic Channels: These tiny channels mimic the intricate structures and functions of human organs.
- Cells: Cells derived from human tissues or organoids are seeded into the channels to create functional organ models.
- Matrix: A biocompatible matrix provides a supportive environment for cell growth and differentiation.
- Mechanical Stimulation: OOCs can be subjected to mechanical forces, such as fluid flow or stretching, to replicate the physiological conditions experienced by organs in the body.
Benefits:
- It offers a more accurate and predictive model for studying disease mechanisms, drug testing, personalized medicine, and organ-organ interactions.
- It can significantly reduce the need for animal testing, making drug discovery more ethical and efficient.
- OOCs can be used to create personalized models of patients’ organs, enabling tailored drug testing and treatment strategies.
- Thiscan help identify potential drug candidates earlier in the development process, reducing the risk of failure in clinical trials.
Applications:
- Drug Discovery and Development: OOCs can be used to evaluate the efficacy and safety of new drugs before clinical trials.
- Customization: OOCs can be customized to model individual patients’ responses to drugs, leading to more targeted and effective treatments.
- Disease Modeling: OOCs can help researchers understand the underlying causes of diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Identifying Drug Targets: OOCs can be used to identify new drug targets for therapeutic intervention.
- Toxicity Testing: OOCs can be used to evaluate the toxicity of chemicals and environmental pollutants, reducing the need for animal testing.
- Tissue Engineering: OOCs can be used to create functional tissues for transplantation or regenerative medicine.
Ref: Source
| UPSC IAS Preparation Resources | |
| Current Affairs Analysis | Topperspedia |
| GS Shots | Simply Explained |
| Daily Flash Cards | Daily Quiz |
Frequently Asked Question:
What are Organs-on-Chips (OOC)?
OOCs are miniature replicas of human organs created on microfluidic chips. They are used to study disease mechanisms, test drugs, and understand organ-organ interactions.
How do OOCs work?
OOCs contain tiny channels lined with cells that resemble the structure and function of specific organs. These cells interact with each other and their environment within the chip, providing a more realistic model of human physiology.
What are the potential applications of OOC technology?
OOC technology has potential applications in various fields, including Drug discovery and development, disease modeling, toxicity testing, and tissue engineering.