Vedic literature of India dates back to the 1500 BC whose scientific logic is still helping many researches in India and around the globe. In this article, you will learn definition, history, different types of vedas, etc.
This article will provide key insights for GS Paper-I Art and Culture of UPSC IAS Exam.
Table of Content
- What is Vedic literature?
- History of Vedic literature
- Vedic literature chart
- About the Rig Vedas
- What is Sama Veda?
- What is Atharva Veda?
- What is Yajur Veda?
- What is Brahmanas?
- About Aranyak Vedic Literature
- What are Upanishads?
- What do you mean by Samhitas?
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Vedic literature?
- The Vedic literature are book that is compilation of the Srutis (“what is heard“) or hymns that were revealed to the sages or the rishis during the Vedic age.
- The hymns are full of symbols and myths.
- Vedic literature forms basic tenets of Hinduism.
- Vedic literature books: Rig Veda; Sama Veda; Yajur Veda and Atharva Veda
- These 4 Vedic literature books are also known as early vedic literature.
- All the Vedas prioritises yagna (sacrifice).
History of Vedic literature:
- Vedic literature was compiled or written around 1500 BC-1000 BC.
- Vedic literature was initially passed on by teacher to students orally.
- Thus, Vedic Literature is also known as Srutis.
- Origin and development of religion in vedic literature can be traced back to the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent during 1500–1100 BCE.
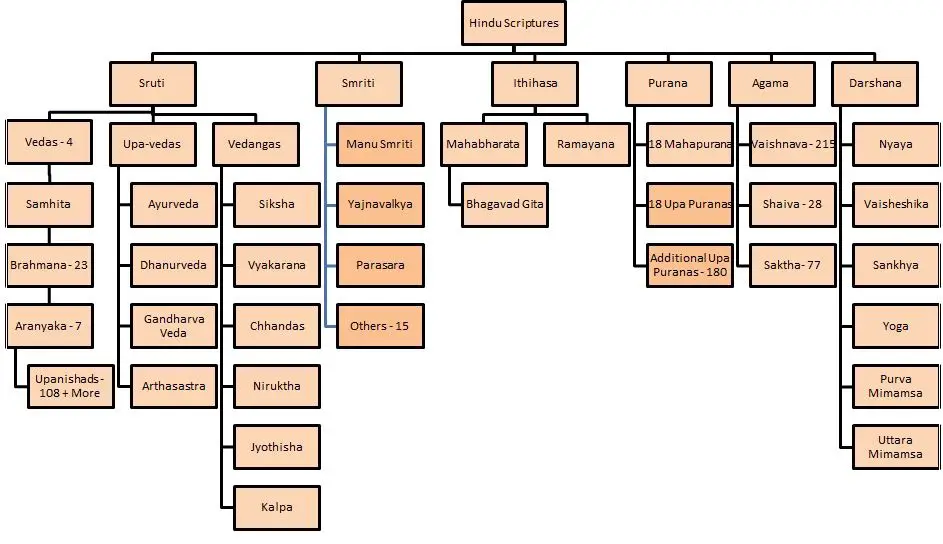
- Each Vedas has subdivision: Brahmanas; Aranyak; Upanishads and Samhitas.
- Vedangas are supplement to the original Veda consisting of siksha (education), nirukta (origin of words), Chhanda (metrics in grammar), jyotisha (astronomy) and vyakarana (grammar).
Chart of Vedic literature:
About Rig Veda:
- Rig Veda is the oldest Veda of all Vedas.
- Rig Veda consists of 1028 Sanskrit hymns on prosperity and natural beauty.
- These hymns are organised in 10 books– Mandalas.
- Each mandala comprises of several Suktas or hymns on sacrificial purposes.
- Rig Veda was compiled during 1200-900 BC.
- Common themes: life, death, creation, sacrifice and for seeking godly pleasure or soma.
- Deities: Indra (chief deity), Agni (God of fire), Varuna (God of water), Rudra (God of
- wind/storm), Aditya (a form of Sun God) etc.
- Goddesses: Usha (for dawn), Prithvi (for earth) and Vak (for speech).
What is Sama Veda?
- Sama Veda consists of 1875 hymns, detached verses, 16,000 raga (musical notes) and raginis on music.
- Many of hymns are derived from the Sakala branch of the Rig Veda.
- Sama Veda is often termed as ‘book of chants’, due to its lyrical nature.
What is Atharva Veda?
- Atharva Veda is hymns about the magic, medicine and treatment for almost 99 diseases.
- Atharva Veda consists of details of the human society and man’s daily life.
- Atharva Veda speculates the changes in the universe.
- Atharva Veda has been dedicated to the rishis– Atharvah and Angira.
- Atharva Veda is also known as Brahma Veda or Atharvangirasa.
- 2 branches of the text: Paippalada and Saunakiya.
What is Yajur Veda?
- Yajur Veda contains sacrificial hymns that were performed according to the Rig Veda.
- The term ‘Yajus’ means ‘sacrifice’.
- 2 branches of the text: Shukla (white or pure) and Krishna (black or dark).
- Yajur Veda is also known as Vajasaneyi Samhita or Taittiriya Samhita.
- Yajur Veda acts like a guide book for the rishis who conduct sacrificial rituals.
What is Brahmanas?
- Brahmanas is a collection of texts and commentaries on the particular Veda.
- Each Veda has a Brahmana attached to it.
- Rig Veda: Aitareya Brahmana and Kaushitaki Brahmana
- Sama Veda: Tandya Mahabrahmana and Sadvimsha Brahmana
- Yajur Veda: Taittiriya Brahmana and Shatpatha Brahmana
- Atharva Veda: Gopatha Brahmana, Jaimaniya Brahmana and Panchvish Brahmana.
- Brahmanas contains legends, facts, philosophy and explanations of Vedic rituals.
- Brahmanas contains instructions of how to properly conduct rituals and symbolic meaning of the words used in the rituals.
- Brahmanas was compiled between 900-700 BC.
About Aranyak Vedic Literature:
- Aranyak Vedic Literature describes “Karma-kanda” or rituals or sacrifices performed using the Vedas from different perspectives.
- Aranyak Vedic Literature provides information on the birth and death cycles and various dimensions of the soul.
- Aranyak Vedic Literature derives its name from “aranya” meaning forests as it was taught by Munis or the learned men who use to reside in the forests.
- Aranyak Vedic Literature forms the conclusions of Brahmanas, but contains some independent hymns too.
What are Upanishads?
- Upanishads provides detailing on monastic terms, origin of the universe, mystical terms and philosophical problems faced by humans.
- Upanishads was passed down orally by the teacher to students.
- The term literally means “to sit down near (the teacher)”, that describes the guru-shishya Parampara as a prevalent tradition during that time.
- Upanishads talks about humans’ life and death cycle and their material and spiritual quests in their lifetime.
- As it forms the last part of Vedas, it is also called Vedanta or ‘end (anta) of the Veda’.
- Upanishads contains ‘truth’ about human life including the path for salvation or moksha.
- There are more than 200 Upanishads out of which 108 are called the Muktika Canon.
- Upanishads focuses on “Jnana-kanda” or Knowledge or spirituality section of Vedas.
What do you mean by Samhitas?
- Samhitas is a Sruti structured combination of verses, texts, mantras, prayers and litanies of God.
- The term means “to arrange together in union”.
- Samhitas constitutes the oldest living part of Hindu tradition.
Conclusion
Vedas are one of the greatest literatures that survives till date from many generations. Government must take adequate steps like “Vedic Heritage portal” and introducing many of its scientific works in academic curricula in order to encourage and preserve the Indian tradition and culture
Ref: Source-1
| Other Articles in History & Culture | |
| Tripitaka | Ashoka’s Dhamma |
| Heterodox Schools of Philosophy | Indus Valley Civilization Sculpture |
| Orthodox Schools of Indian Philosophy | Basic Feature of Hindu Temple |
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is meant by Vedic literature?
The Vedic literature are book that is compilation of the Srutis (“what is heard”) or hymns that were revealed to the sages or the rishis during the Vedic age.
Which is the oldest Vedic literature?
Rig Veda is the oldest vedic literature.
Name the river most mentioned in early Vedic Literature.
The river most mentioned in early Vedic Literature is Sindhu River.
Name the eminent women figures in Vedic Literature Books.
The women eminent in Vedic Literature includes Ghosha, Lopamudra, Sulabha Maitreyi, and Gargi.


